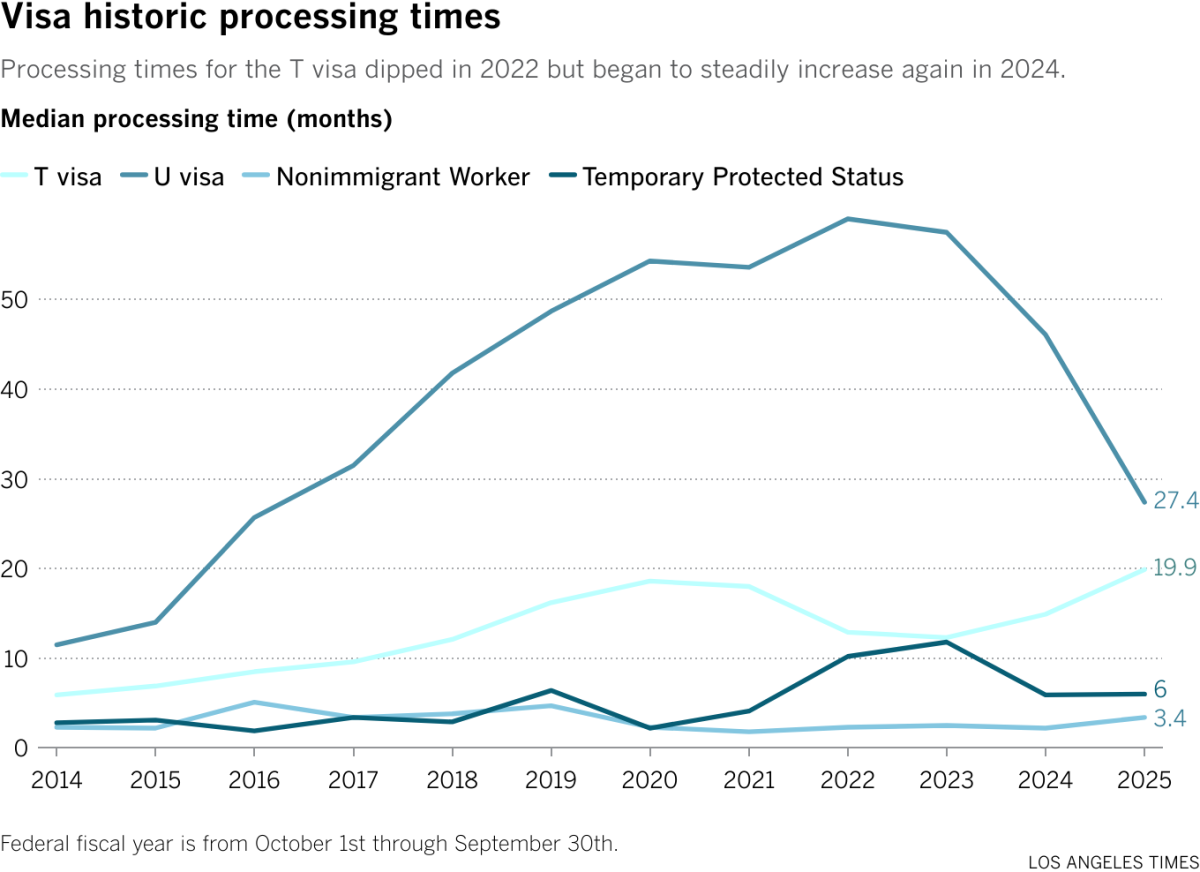
The T visa, an underutilized lifeline for immigrant survivors of human trafficking, is experiencing a sharp rise in applications, despite increasing processing times and deportation risks.
Also known as T nonimmigrant status, the visa allows people who have experienced severe forms of human trafficking to remain in the country for up to four years if they are helpful to law enforcement in the investigation and prosecution of their trafficker. Approved applicants can work in the U.S., are eligible for certain state and federal benefits, and can apply for a green card after three years on the visa (or earlier if the criminal case is closed).
Julie Dahlstrom, founder and director of the Human Trafficking Clinic at Boston University, said increased awareness of the visa and the courts’ expanding definitions of trafficking may have contributed to the increase, along with mounting barriers to other pathways for immigrant relief.
Congress created the T visa in 2000 as part of the Victims of Trafficking and Violence Protection Act, intending to bolster law enforcement agencies’ capabilities to prosecute human trafficking crimes while offering protections to survivors. The same law also established the U visa, which provides legal status for victims who have suffered substantial abuse as a result of serious crimes including trafficking, domestic violence and sexual assault. U visa applicants must also be willing to assist law enforcement in their investigation of these crimes.
“Many [applicants] are eligible for the U visa as well, but they’re taking now over 20 years for an individual to get access … so I think that has influenced lawyers and survivors, if they are eligible for the T visa … to go ahead and also file T visa applications,” Dahlstrom said. “Especially under the Trump administration, we’ve seen more barriers to asylum access, special immigrant juvenile status access, so I expect we’ll continue to see that move.”
USCIS updated the T visa rules in August 2024 with a process called called bona fide determination that gave survivors earlier access to benefits while their application is pending approval. It also granted them deferred action, which places individuals on a lower priority for removal proceedings.
Erika Gonzalez, training and technical assistance managing attorney from the Coalition to Abolish Slavery & Trafficking, explained that although early access to benefits had existed in the federal statute, it was never implemented because applications were processing fast enough to not need it.
“They have updated the [bona fide determination] process to now have a formal process to engage with, and it does parallel with the sharp increases in filing,” Gonzalez said.
As T visa applications rose, so too did approvals. Last year, the number of approvals broke 3,000 for the first time though it still fell short of the 5,000 cap.
Processing times for T visas have also increased, jumping from a median of 5.9 months in 2014 to 19.9 months this fiscal year.
Denial rates for T visas, meanwhile, have fluctuated.
“We were seeing increased denial rates under the prior Trump administration and then improved rates under Biden,” Dahlstrom said.
Denials can leave T visa applicants vulnerable to deportation. In 2018, USCIS began allowing removal proceedings if an application was rejected with a notice to appear (NTA).
According to a 2022 report co-written by Dahlstrom, which obtained USCIS data through Freedom of Information Act litigation, USCIS issued a total of 236 NTAs to denied T visa applicants from 2019 to 2021. President Biden rescinded this policy with a January 2021 executive order, but last February, USCIS published new guidance once more expanding the circumstances where the agency could issue NTAs.
These policies, alongside escalated coordination between law enforcement and other agencies, have heightened fear among survivors applying for the T visa, Dahlstrom explained.
“We are seeing in real time the results of including requirements around law enforcement engagement, especially when there’s greater cooperation with ICE and greater concerns about deportation,” Dahlstrom said. “These programs are being politicized and, in some ways, weaponized if you’re denied and you’re placed in proceedings.”
Since February’s policy update, at least one person has self-deported after Immigration and Customs Enforcement denied her stay despite her pending T visa application.
So far in the fiscal year 2025, USCIS has approved 1,035 T-visas and rejected 693, which surpasses the number rejected in each of the last four years.
“It’s too early to tell what we’re going to see, but if we continue to see these numbers, it’s both going to mean a rise in denials and very few cases adjudicated amidst more and more applications being filed, which is really troubling,” Dahlstrom said. “These are statutorily protected programs, but what they can do is really slow them down, make them ineffective just in the way that they’re processing applications.”