July 8 (UPI) — The Department of Defense’s announcement that it would end a weather-data sharing program surprised some climate watchdogs but forecasters assure it does not heighten risks.
The department announced the termination of the Defense Meteorological Satellite Program late last month, citing cybersecurity concerns. The program is slated to end on July 31.
The Department of Defense has been monitoring meteorological data using satellites for more than 60 years, though during the first decade of the DMSP it was kept classified. It is currently operated by the U.S. Space Force.
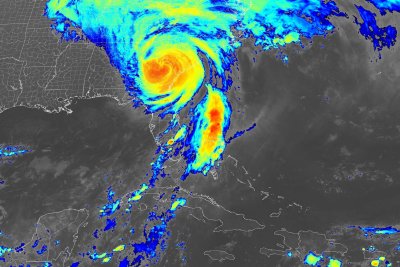
Three DMSP satellites remain in operation, with the newest satellite having launched in 2014. These microwave satellites capture data through the clouds that is used for weather prediction, including tactical weather prediction used by the U.S. military.
“We and other countries have microwave satellites up there. There’s many of them up there,” Clifford Mass, professor of atmospheric and climate science at the University of Washington, told UPI. “It’s one of the most important sources of data for all weather prediction. It’s like a cat scan of the atmosphere.”
A network of satellite systems, including those that are part of the DMSP, take readings of large portions of Earth from low-earth orbit. DMSP satellites are in low-earth polar orbit and can scan an area of about 1,600 nautical miles, covering the entirety of the planet about every 14 hours, according to the U.S. Space Force.
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration is among the agencies that uses data from the DMSP. Kim Doster, communications director for NOAA, told UPI in a statement that the DMSP is a “single dataset in a robust suite of hurricane forecasting and modeling tools in the [National Weather Service] portfolio.”
Other sources of data used by NOAA and the National Weather Service include geostationary Earth-observing satellites, polar orbiting satellites, ground-based weather radar and other microwave satellite systems such as the Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder.
“In particular, the Advanced Technology Microwave Sounder, currently flying on NOAA’s [Joint Polar Satellite System], provides the richest, most accurate satellite weather observations available,” Doster said. “NOAA’s data sources are fully capable of providing a complete suite of cutting-edge data and models that ensure the gold-standard weather forecasting the American people deserve.”
Erin Sikorsky, director of The Center for Climate and Security, told UPI she remains concerned about ending the DMSP. It is not about ending the program alone but about ending the program in combination with staffing reductions at NOAA and peeling back climate change mitigation policies.
“For me, it’s looking at the broader pattern of risky actions we’ve seen from the administration when it comes to weather and climate data since they took office in January,” Sikorsky said. “If this was an isolated incident — I’d be less concerned. But the fact that this also comes at a time when we’ve seen the shutdown of climate.gov and the U.S. Global Change Research Program and other cuts to NOAA staffing. It all kind of adds up to a picture of blinding ourselves to critical information about climate hazards in a way that puts Americans at risk.”
Sikorsky’s concerns also stem from a lack of clarity about the decision to end the program. The Department of Defense’s reasoning being a cybersecurity threat is vague, lacking more detailed information.
U.S. Space Force did not respond to requests for comment.
“It caught everybody off guard in the weather community,” Sikorsky said.
Mass explained that there are a number of redundancies in the U.S. government’s weather data systems, with multiple agencies carrying out overlapping functions.
“They’re basically running three redundant numerical weather prediction enterprises, run by the U.S. government,” Mass said. “It’s an interesting question about whether we need so many different groups doing the same thing. NASA runs numerical weather predictions as well. The EPA does.”
Redundancy can be, and often is good for ensuring there is a reliable and consistent flow of data. It is also a source of inefficiency, according to Mass. However, the Trump administration’s goal of reducing government inefficiency does not appear to play into the decision to end the DMSP.
“It has nothing to do with the Trump administration’s attempts to reduce government waste,” Mass said. “The DOD decided they had a security issue. This is a DOD problem. They decided to shut it down very abruptly and they didn’t talk to anybody about that.”
The cybersecurity threat may be the result of an outdated operating system, Mass adds. Meanwhile satellite launches are becoming more frequent, less costly and advancements continue to be made in satellite technology.
“There’s all of these new generations of satellites that are going up. It turns out that Elon Musk’s Starlink satellites might be very useful for further weather observation,” he said. “Having a lot of satellites in low-earth orbit, seeing how those signals are bent by the earth’s atmosphere, it might be possible to get vastly more observations. Having all of the satellites up there is very useful for weather predictions.