Central banks are preparing for 2026 inflation risks, though they remain divided on solutions. Global Finance announces the 2025 Central Banker Report Cards in Western Europe.
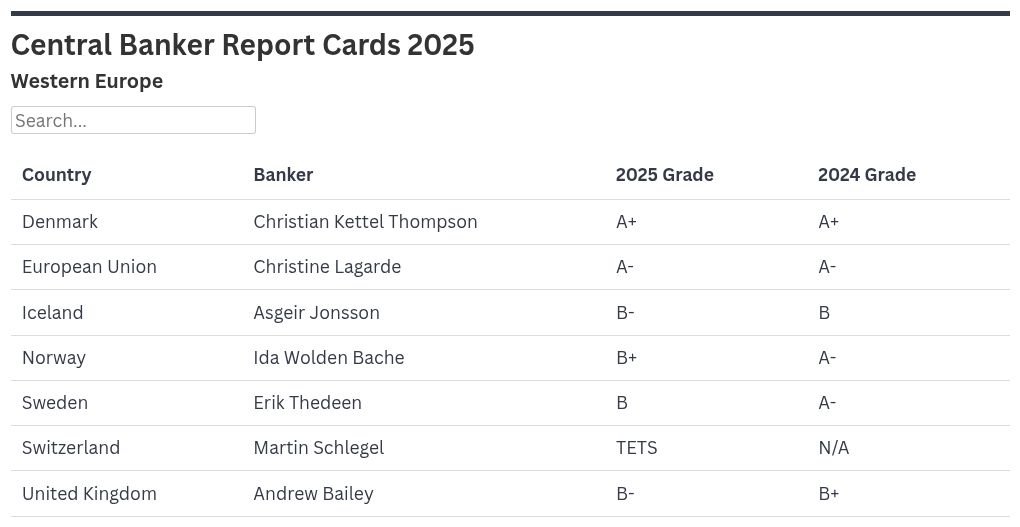
Denmark
Christian Kettel Thomsen: A+
The Danmarks Nationalbank continued to navigate the economic volatility of the past year with notable stability. Governor Christian Kettel Thomsen maintained a sharp focus on the central bank’s mandate of ensuring a stable euro-to-Danish krone exchange rate without disrupting prices.
Although the Nordic central bank does not set a fixed inflation target, the country’s CPI has averaged a modest 1.7% over the past year, allowing the bank to run negative real interest rates to further support broad economic growth.
Following a 15 bps cut in June, to 1.6%, among the lowest in Western Europe, he has held the rate steady through September. With a recent inflation reading at 2.3% year-on-year (YoY), this represents a negative real rate of 0.7%, offering strong support for businesses in the region.
The rationale behind these levels is to offset some of the pressures weighing on the country’s GDP growth, which showed mixed results in the first half of the year. These include slower-than-expected growth at pharmaceutical giant Novo Nordisk, which currently accounts for about 60% of the country’s yearly GDP, and newly imposed US tariffs, now set at 15% as part of the broader agreement between the US and the EU.
European Union
Christine Lagarde: A-
The massive more than 10% year-to-date strengthening of the euro against the dollar gave Governor Christine Lagarde additional room to widen the interest rate gap in the eurozone relative to the US Federal Reserve, thus bringing higher investor interest without spiking inflation.
Against this backdrop, the European Central Bank (ECB) brought deposit rates down to 2%, more than 225 bps lower than in the US. At the same time, inflation remained anchored to the bloc’s 2% target, showing greater stability than across the Atlantic.
This environment proved supportive of the economy, with several sectors receiving a significant boost during the first half of the year, particularly manufacturing and defense.
Yet, despite the positive outlook so far, the broader backdrop remains volatile for the bloc, in terms of the geopolitical situation—particularly as the war in Ukraine rages on—and on the macro side, with the US imposing a 15% base tariff on the continent’s exports.
Looking ahead, Governor Lagarde notes that the main risks stem from the economic growth side, with inflation risks remaining tilted to the downside. “Trade tensions could lead to increased volatility and risk aversion in financial markets, which would weigh on domestic demand and, consequently, also reduce inflation,” she added following the ECB’s most recent rate decision.
Iceland
Ásgeir Jónsson: B-
The Central Bank of Iceland continues to grapple with higher-than-average inflation, particularly when compared to its Western European neighbors and fellow Nordic economies.
This backdrop has prompted Governor Ásgeir Jónsson to hold rates significantly above the regional average, with a steep base rate of 7.50%, also one of the highest in the region.
The tight monetary policy has resulted in a mixed environment for the country’s economic growth so far this year. After a solid 2.7% expansion during the first quarter of the year, second-quarter numbers registered a sharp 1.9% contraction.
However, despite the short-term woes, the longer-term outlook for the Nordic country appears increasingly positive. Earlier this year, Moody’s and S&P Global upgraded Iceland’s sovereign rating, viewing an improvement in the country’s debt trajectory.
The credit rating agencies now expect the country to post a budget deficit of -3.0% in 2025, paving the way for a projected surplus by 2028.
The outlook follows a decade of structural reforms, both in the economic matrix and labor conditions. The trend is further buoyed by growing tourism revenues and resilient exports.
Norway
Ida Wolden Bache: B+
Faced with still above-target consumer inflation figures, Norges Bank continues to lag behind its rate cut cycle compared to the rest of the region.
As a result of the tight monetary policy environment, the country experienced subdued economic activity in the first two quarters of the year, growing 0.1% quarter-on-quarter in the first quarter and 0.8% in the second quarter. Adding to the challenging picture are mostly softer oil prices throughout the period and Trump’s 15% tariffs on the country’s imports into the US, which have kept a lid on export activity.
However, looking to the second half of 2025, signs are emerging that the Arctic country’s economy may be turning a corner.
On the one hand, resilient income growth and a rebounding housing market could keep domestic activity mostly trending upward in the second half of the year. On the other hand, a weaker Norwegian krone and ongoing global trade disruptions promise to keep new oil exploration activities and ocean transport demand high in the country.
This combination of factors has prompted local banking giant Nordea to revise its GDP growth projection for the mainland up to 1.7% for the full year, with a 2% unemployment rate.
But despite the improving second-half picture, the bank does not expect to see further rate cuts this year, citing that inflation should remain well above the 2% target, most likely “remain around or only slightly below 3% until the end of 2026,” said the bank in a recent research note.
Sweden
Erik Thedéen: B
The Sveriges Riksbank’s uphill battle for 2025 is primarily centered on economic growth, as the country continues to post mostly subdued GDP growth and worrisome unemployment levels.
Yet, despite recording a 1.1% YoY inflation rate in August, Governor Erik Thedéen has maintained interest rates at 1.75%, in line with the European Central Bank. This has pushed Swedish real rates to a positive 0.9%.
As a consequence, the Swedish krona has continued to appreciate, posting one of the strongest gains of the year—a whopping 18% against the US dollar and around 5% against the euro year-to-date.
While this backdrop has helped maintain inflation under control, it has also limited the country’s economic growth. Sweden is traditionally an export-dependent country, with around 55% of its GDP coming from exports in 2024, according to Riksbank data.
On the other hand, since most of those exports are to the EU, the country is likely to remain largely unaffected by Trump’s 15% base levy, given that exports to the US account for only 0.1% of the country’s GDP.
Nordea, the region’s leading bank, believes rates will remain at 2% into 2026, “as global trade conditions settle,” said the Nordic bank’s Chief Economist Annika Winsth. “The gradual recovery underway—including in Sweden—will thus continue and is expected to pick up pace in the coming years,” she adds.
Switzerland
Martin Schlegel: To Early To Say
The Swiss economy continued to sail unfazed by global inflationary pressures in 2025, averaging a near-zero rate through the past year—the lowest on the continent.
This has allowed Governor Martin Schlegel, who replaced Thomas Jordan in October 2024, not only to initiate the rate cut cycle earlier than other peer central banks but also to continue it while others waited.
Consequently, Switzerland is now the only developed economy in the world to operate at zero interest rates—after Japan ended its 17-year period of negative interest rates.
This has not yet spelled trouble for the Swiss franc. In fact, due to increasing currency risks for the dollar and the euro, investors fleeing for security have prompted a massive rally for the currency, which now stands near its highest level in roughly 15 years.
But while the headline numbers paint a perfect picture for the Swiss economy, perspectives for the near future do not seem as bright. The combination of a strong Franc with a very steep 39% US tariff on imports from the country, the highest in the region, is significantly threatening GDP growth.
Against this backdrop, analysts now expect Governor Schlegel to bring rates down to the negative territory before the end of the year, reigniting a policy that effectively ended in 2022.
United Kingdom
Andrew Bailey: B-
Following significant improvements in most economic indicators in 2024, the UK economy faced renewed headwinds in 2025.
Amid increasing macroeconomic pressures, such as global trade disruptions, slower-than-expected growth in exports, and strained public accounts, Governor Andrew Bailey has been unable to bring inflation close to the Bank of England’s 2% target.
After posting a year-high of 3.8% in August (YoY), the long-term CPI trajectory is now seen at 3.7% in 2025, before easing to 2.5% in 2026 and, finally, 2.1% in 2027. In addition to the macroeconomic issues, rising wages and national insurance hikes are also considered key drivers of price pressures.
Contributing to the picture is a significant bond crisis in the country, with British 30-year gilt yields dropping to the lowest levels since 1998. The dismal demand for British debt has brought long-term public borrowing costs to a high of 5.75%, threatening the country’s mid-term growth expectations.
Against this backdrop, Bailey made the decision to cut again in August, bringing rates down to 4% from 4.25%, and maintaining the rate in September.