DRC’s conflict demands a new peace model rooted in inclusion and reform | Conflict
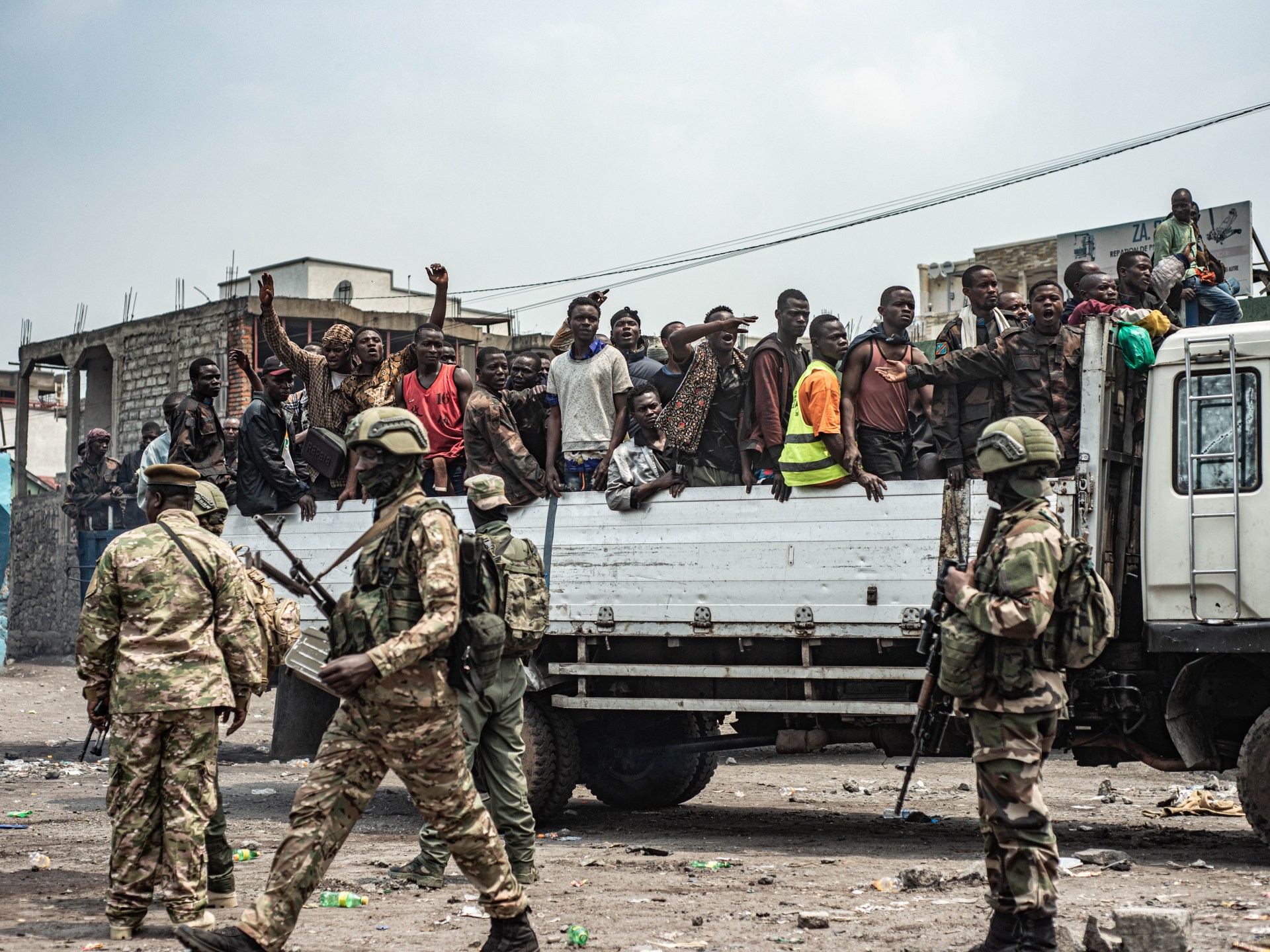
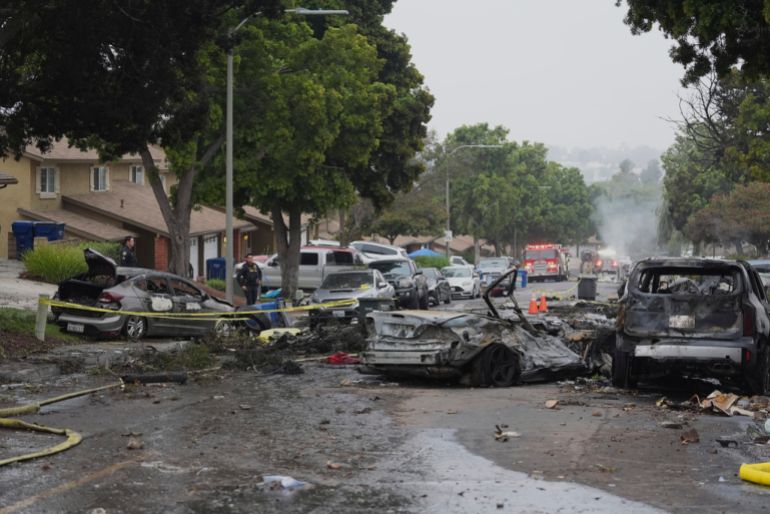
The resurgence of conflict in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo has drawn renewed international attention following M23’s swift capture of Goma and Bukavu in late January 2025. In response, global actors have called for an immediate ceasefire and direct negotiations. Notably, Qatar and the United States have stepped forward as emerging mediators. This new momentum offers a rare opportunity to revisit the shortcomings of past mediation efforts – particularly failures in disarmament, demobilisation and reintegration (DDR), wealth-sharing, and regional consensus. Any new diplomatic initiative must prioritise these elements to forge a durable settlement and lasting regional stability.
To achieve a sustainable and enduring peace in eastern DRC, it is essential to address the root causes of the conflict. The region’s vast deposits of natural resources – especially rare earth minerals – have attracted international, regional and local actors competing for control, fuelling instability. Compounding this is the Congolese central government’s limited capacity to govern the eastern provinces, enabling the proliferation of armed groups with diverse allegiances. Ethnic tensions further exacerbate the crisis, particularly since the 1994 Rwandan genocide, after which the arrival of Hutu refugees and the formation of hostile militias heightened insecurity and cross-border conflict.
While regional dynamics, including Rwandan involvement, are undeniably significant, attributing the conflict solely to Rwanda risks oversimplification. Such narratives obscure the DRC’s longstanding structural inequalities, particularly the marginalisation of Congolese Tutsi communities. A durable peace must engage with these internal dynamics by ensuring the meaningful inclusion of Congolese Tutsi in the national political framework and addressing their grievances through equitable and just mechanisms.
Despite repeated international engagement, past mediation efforts in eastern DRC – from the Pretoria Agreement to the 2009 peace accords – have consistently failed to deliver lasting peace. These initiatives were undermined by structural weaknesses that eroded both their credibility and effectiveness.
A central flaw has been the absence of credible enforcement mechanisms. Most agreements relied on voluntary compliance and lacked robust, impartial monitoring frameworks capable of verifying implementation or deterring violations. Where monitoring mechanisms existed, they were often under-resourced, poorly coordinated, or perceived as biased. The international community’s inconsistent attention and limited political will to exert sustained pressure further undermined these efforts. In the absence of meaningful accountability, armed groups and political elites repeatedly violated agreements without consequence, fuelling a cycle of impunity and renewed violence.
Equally problematic has been the exclusionary nature of the peace processes. Negotiations were often dominated by political and military elites, sidelining civil society, grassroots communities, and particularly women – actors essential for building sustainable peace. Without broad-based participation, the accords failed to reflect the realities on the ground or earn the trust of local populations.
Moreover, these efforts largely ignored the root causes of the conflict, such as land disputes, ethnic marginalisation, governance failures and competition over natural resources. By prioritising short-term ceasefires and elite power-sharing arrangements, mediators overlooked the deeper structural issues that drive instability.
DDR programs – vital to breaking the conflict cycle – have also been inadequately designed and poorly executed. Many former combatants were left without viable livelihoods, creating fertile ground for re-recruitment into armed groups and further violence.
Crucially, these flaws were compounded by a lack of political will within the Congolese government. Successive administrations have, at times, instrumentalised peace talks to consolidate power rather than to advance genuine reform, undermining implementation and eroding public confidence.
More recent efforts, such as the Luanda and Nairobi processes, aimed to revive political dialogue and de-escalate tensions. However, they too have struggled to gain legitimacy. Critics argue that both initiatives were top-down, narrowly political and failed to include the voices of those most affected by the conflict. Civil society actors and marginalised communities perceived these dialogues as superficial and disconnected from local realities.
These processes also fell short in addressing the underlying drivers of violence – displacement, land ownership disputes, poor governance and the reintegration of ex-combatants. Without credible mechanisms for local participation or structural reform, the Luanda and Nairobi processes came to be seen more as diplomatic performances than genuine pathways to peace.
Taken together, these recurring shortcomings explain why international mediation efforts in DRC have largely failed. For any new initiative – including those led by Qatar and the United States – to succeed, it must move beyond these limitations and embrace a more inclusive, accountable and locally rooted approach.
The latest round of international facilitation – led by the United States and Qatar, alongside African-led efforts by the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern African Development Community (SADC) under Togolese President Faure Gnassingbe – offers renewed potential for meaningful progress. However, success will depend on whether these efforts can overcome the systemic failures that have plagued previous mediation attempts.
To chart a more effective and durable path to peace, Qatari and American engagement should be guided by three core principles drawn from past experience:
First, prioritise inclusive participation. Previous peace processes were largely elite-driven, involving governments and armed groups while excluding civil society, women and affected communities. This lack of inclusivity weakened legitimacy and failed to address the grievances of those most impacted by violence. A credible mediation process must include these actors to build a broad-based coalition for peace and ensure that negotiated outcomes reflect the lived realities of eastern DRC communities.
Second, address the root causes of the conflict – not just its symptoms. Earlier efforts focused narrowly on ceasefires and power-sharing, without tackling the structural drivers of instability. Effective mediation must engage with unresolved land disputes, ethnic marginalization, governance failures and the socioeconomic reintegration of former combatants. Without addressing these underlying issues, any agreement will be fragile and short-lived.
Third, establish credible enforcement and accountability mechanisms. One of the most persistent weaknesses of past agreements has been the absence of strong implementation tools. Agreements often lacked independent monitoring bodies, clear benchmarks and consequences for violations. The international community, including Qatar and the United States, must commit to sustained diplomatic pressure and support mechanisms that can ensure compliance and respond decisively to breaches. Without this, the risk of relapse into violence remains high.
By adopting these principles, current mediation efforts stand a greater chance of breaking the cycle of failed peace initiatives and laying the groundwork for a more just and lasting resolution in eastern DRC.
The crisis has once again reached a critical juncture. The involvement of new actors such as Qatar and the United States, working alongside African regional mechanisms, presents a rare opportunity to reset the approach to peacebuilding. By learning from past failures and committing to an inclusive, root cause oriented, and enforceable mediation framework, these efforts can move beyond temporary fixes and lay the foundation for a durable peace – one that finally addresses the aspirations and grievances of the Congolese people.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera’s editorial stance.