What we know about Israeli strike on Iran’s Arak nuclear facility
Israel has struck Iran’s Khondab nuclear facility – formerly known as Arak.
Source link
Israel has struck Iran’s Khondab nuclear facility – formerly known as Arak.
Source link
United States President Donald Trump will decide on whether his country will join the Israel-Iran conflict in the next two weeks, the White House has said, amid growing speculation of US involvement and fears of wider escalation.
On Thursday, White House press secretary Karoline Leavitt told reporters that Trump had shared a message: “Based on the fact that there’s a substantial chance of negotiations that may or may not take place with Iran in the near future, I will make my decision whether or not to go within the next two weeks. That’s a quote directly from President Trump,” she said.
“The president is always interested in a diplomatic solution … he is a peacemaker in chief. He is the peace through strength president. And so if there’s a chance for diplomacy, the president’s always going to grab it. But he’s not afraid to use strength as well,” the press secretary added.
The US described its ally Israel’s initial June 13 strike on Iran as a “unilateral action”. But Trump himself has signalled that he knew of the attack in advance and supported Israel’s military campaign.
At the same time, according to the Reuters news agency, which cited three unnamed diplomats, Trump’s special envoy Steve Witkoff has spoken to Iranian Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi several times on the phone since Israel began its attacks.
Amid the talk of diplomacy, Tel Aviv and Tehran have continued to trade attacks.
On Thursday, Israel targeted Iran’s Arak heavy water nuclear reactor. Iran, in turn, hit the Soroka Medical Centre, which it claimed was near an Israeli military and intelligence centre.
At the same time, Israeli Defence Minister Israel Katz threatened to eliminate Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. “Such a person is forbidden to exist,” he said in a statement cited by the Yedioth Ahronoth newspaper.
Over the past few days, Trump has hinted at joining Israel’s strikes on Iran’s nuclear sites, but at the same time has proposed a swift diplomatic solution in a confusing message from Washington.
Following a report by the Wall Street Journal on Wednesday night that Trump had already signed off on striking Iran but had not decided on when they would do it, the president took to his Truth Social social media account to deny the report.
“The Wall Street Journal has No Idea what my thoughts are concerning Iran!” Trump wrote.
But Al Jazeera’s senior political analyst Marwan Bishara said that Leavitt’s comments could well be a ploy, and if so, Trump would be able to use it as a “pretext in order to camouflage whatever his intentions are and attack tomorrow”.
As Araghchi is expected to meet his British, French and German counterparts in Geneva on Friday, along with the European Union’s top diplomat, Kaja Kallas, to discuss Tehran’s nuclear programme, Bishara said Trump could be waiting to hear the outcome of those talks before making his decision to attack.
“If one has to over-interpret, I would say the following: He’s giving the Europeans some time so that everyone could save face,” Bishara said.
Al Jazeera’s Doha Jabbari, reporting from Doha, said the lack of trust between Tehran and Washington will make it difficult for the Iranians to fully believe Trump is open to diplomacy.
“Assuming that the Israelis have the green light from the Americans to carry out these attacks inside Iran, there is going to be very little trust there,” Jabbari said.
“But really, this is the diplomatic game they have to play,” she added, referring to the upcoming talks in Geneva. “If they [Iran] don’t go, they’re going to be accused of basically saying we’re not going to talk, we just want war. They’re going to have to travel, and the Europeans are acting as a mediator between Iran and the US.”
At the same time, Russia and China have repeatedly warned against the US’s involvement in the conflict and called for a ceasefire.
A White House spokesperson has delivered a message from President Trump, saying he will decide whether to attack Iran “within the next two weeks”. Karoline Leavitt says US and Iranian officials are still in contact and US action rests on the outcome of talks.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
Israel has accused Iran of "war crimes” after it attacked one of its hospitals.
Source link
Israel’s attacks on Gaza have not let up since it also began attacking Iran. Hundreds of Palestinians have been killed in recent days, including dozens seeking aid and families who were bombed in displacement tents.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
Global fears rise over nuclear risk from confrontation in the Middle East.
Israel says that ending Iran’s nuclear programme is a key aim of its attacks on the country.
Israel is widely believed to have nuclear arms, but has never admitted that.
So, what are the nuclear capabilities of both sides, and what are the risks from this conflict?
Presenter: Laura Kyle
Guests:
Dan Smith – Director at the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute
Sahil Shah – Nuclear weapons policy analyst in London
Rebecca Johnson – Director at the Acronym Institute for Disarmament Diplomacy and former senior adviser to Dr Hans Blix, who was formerly the top UN weapons inspector in Iraq and an IAEA chief
Iran has no clear off-ramps to end its war with Israel, which could soon drag in the United States and lead to a new quagmire in the Middle East, analysts told Al Jazeera.
Since June 13, Israel has killed at least 240 Iranians, many of them civilians. Top Iranian military leaders and nuclear scientists have been among the dead.
Israel has struck Iran’s state television station, hit a hospital, targeted apartment blocks, and damaged the country’s air defences.
In response, Iran has fired barrages of ballistic missiles at Israel, targeting military and security installations, and hitting the Haifa oil refinery, residential buildings, and a hospital. At least 24 people have been killed in Israel as a result of the attacks.
Israel aims to destroy Iran’s nuclear programme and potentially go as far as bringing about regime change, analysts say.
These goals make it difficult for Iran to navigate a quick end to the conflict. Iran’s official position is that it will not negotiate while under attack, fearing it will be forced to fully surrender to US and Israeli terms.
Iran may instead have to hope that US President Donald Trump can be persuaded to rein in Israel, which may be in his interest to avoid getting entangled in a far-away war, even if the US leader has recently appeared to favour striking Iran, and has reiterated that Iran cannot be allowed to have a nuclear weapon.
“If the United States recognises the urgency of de-escalation and manages to persuade Israel to halt its military campaign, then – given the mounting costs of war for Iran and the fact that Iran’s primary goal is to stop, not expand, the conflict – it is highly likely that Iran would agree to a ceasefire or political resolution,” said Hamidreza Aziz, an expert on Iran for the Middle East Council for Global Affairs think tank.
In theory, Iran could return to the negotiating table and sign a deal while under fire.
However, Iran would be forced to entirely give up its nuclear programme, enabling its enemies to then aggressively pursue regime change without fear of consequence, analysts previously told Al Jazeera.
This is an unlikely scenario, according to Reza H Akbari, an analyst on Iran and the Middle East, North Africa and South Asia Program Manager at the Institute for War and Peace Reporting.
“[Iran’s nuclear] program continues to remain a leverage for Iran, which enables them to even engage with the US. Giving it up would be a shocking development which I don’t foresee for the time being,” he told Al Jazeera.
The US and Iran had already engaged in five rounds of negotiations before Israel instigated the conflict.
The two sides had reached an impasse when Trump demanded that Iran give up its entire nuclear programme, which every country has an “inalienable right” to use for peaceful purposes, according to the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons, which Iran is a signatory to.
Trump has since warned Iran to quickly surrender to a deal or face even more dire repercussions, hinting at regime change.
Iran has few good options, said Negar Mortazavi, an expert on Iran with the Center for International Policy (CIP).
She believes Iran has little to lose by retaliating against Israel, but also notes that the strategy would not necessarily give Tehran a way out of the conflict.
“If Iran does not retaliate after each attack, [Iranian officials] think [the Israeli attacks] will get harder and I think they’re correct,” Mortazavi told Al Jazeera. “But every time [Iran] retaliates, they give Israel the excuse to attack them again.”
Over the last year, Iran’s regional influence has suffered major setbacks, leaving it geopolitically vulnerable.
Iran had long relied on its ally, the Lebanese armed group Hezbollah, to provide deterrence from direct Israeli attacks, but Hezbollah was significantly weakened after fighting an all-out war against Israel last year.
In addition, Iran lost another ally when Syria’s former President Bashar al-Assad was toppled in December 2024.
Iran could still direct attacks against US bases and personnel through a web of Iranian-backed armed groups in the region, particularly in Iraq, said Barbara Slavin, an expert on Iran and a distinguished fellow at the Stimson Centre think tank.
She believes Iranian-backed groups in Iraq could fire “warning shots” to try and exploit US public opinion.
Trump’s nationalist “America First” base remains staunchly opposed to any US involvement in wars abroad, which they view as unrelated to their domestic concerns.
And anti-interventionist sentiments are likely to increase if US troops are put in harm’s way as a result of any attacks related to the conflict with Iran.
“The thought of Americans dying in this would make it even more controversial for [the US] than it already is,” Slavin told Al Jazeera.
Iran could also make Americans feel the impact of the war economically. It has threatened to attack commercial ships in the Strait of Hormuz, which would affect global trade and increase oil prices. But Slavin said this move would badly hurt Iran’s economy, too.
Slavin added that Iran also relies on commercial shipping in the Strait of Hormuz, which lies between Iran and Oman and is one of the most important shipping routes in the world, to export oil. Instead, Slavin said that Iran’s best option was to contain the war with Israel and wait out the conflict, arguing that any manoeuvre to escalate against US personnel, even as a warning, is a risky gambit.
Trump’s administration, which includes many war hawks, has explicitly warned Iran against targeting its assets or soldiers.
Iran is also wary of giving the US any easy pretext to directly enter the war on behalf of Israel, Akbari said.
“Iran’s leadership knows that drawing the US further into the war could be catastrophic for both the regime and in terms of industrial damage. [It would risk destroying] everything Iran has built over the last 40-plus years,” Akbari said.
Iran’s formal position is to inflict significant political, military and material cost on Israel for instigating the war.
This position was echoed by Hassan Ahmadian, an assistant professor at Tehran University, who suggested Israel’s Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu may stop the war if Israelis feel the impact of a crisis he instigated.
“Iranians are quite confident that they can inflict enough retaliatory pain to make Israel stop [its attacks],” Ahmadian told Al Jazeera.
It is unclear how much damage Iran is doing to Israel’s military infrastructure since the latter bars the media from reporting such information.
Furthermore, it’s hard to assess how long Iran can sustain a war against Israel.
But Israel itself may struggle to attack for a protracted period without the US, said Slavin.
She referenced media reports that Israel is running low on defensive interceptors, which could make it more vulnerable to long-range strikes by Iran.
The challenges facing both foes could prompt them to end the fighting sooner rather than later – at least that appears to be what Iran is betting on.
“Right now, Iran is trying to hunker down and somehow get through this,” Slavin said.
“No outside power will save Iran. It’s up to them [to save themselves],” she told Al Jazeera.
Speaking with reporters on the White House lawn, President Donald Trump played coy when asked if he would bring the United States into Israel’s war on Iran.
“I may do it. I may not,” he said on Wednesday.
US officials and the president’s allies have stressed that the decision to get involved in the war – or not – lies with Trump, stressing that they trust his instincts.
“He is the singular guiding hand about what will be occurring from this point forward,” Department of State spokeswoman Tammy Bruce told reporters on Tuesday.
But antiwar advocates have been arguing that it should not all be up to Trump and Congress must be the ultimate decider over war and peace, according to the US Constitution.
As Trump increasingly appears to hint at the possibility of US engagement in the conflict, some lawmakers are seeking to reassert that congressional role under the War Powers Act.
But what are the laws guiding a declaration of war, and could Trump get the US involved in the war without the consent of Congress?
Here’s what you need to know about the laws that govern decisions about war in the US.
Section 1 of the US Constitution, which established the legislative branch of the government and outlines its duties, says Congress has the power to “declare war”.
Some advocates take that provision to mean that lawmakers, not the president, have the authority over US military interventions.
In 1942, during World War II. Since then, the US has gone to war in Korea, Vietnam, the Gulf, Afghanistan and Iraq while carrying out strikes and interventions in numerous countries – Serbia, Libya, Somalia and Yemen to name a few.
According to Article II of the constitution, the president is designated “commander in chief” of the armed forces.
Presidents have the power to order the military to respond to attacks and imminent threats. Beyond that, their war-making powers are constrained by Congress. Article II empowers them to direct military operations once Congress has authorised a war. They are responsible for mobilising the military under the guidelines of lawmakers.
That said, successive presidents have used the ability to direct the military on an emergency basis to carry out attacks that they frame as defensive or in response to threats.
Short of a declaration of war, Congress may grant the president powers to use the military for specific goals through legislation known as the Authorization for Use of Military Force (AUMF).
For example, in the wake of the 9/11 attacks in 2001, Congress passed an AUMF that gave then-President George W Bush broad powers to conduct what would become the global “war on terror”.
And one year later, it passed another AUMF allowing the use of the military against the government of Saddam Hussein in Iraq, which became the basis of the 2003 invasion.
The two authorisations remain in place, and presidents continue to rely on them to carry out strikes without first seeking congressional approval. For example, the assassination of top Iranian General Qassem Soleimani in 2020 in Baghdad was authorised by Trump under the 2003 AUMF.
During Trump’s first term, there were concerns that he could use the 2001 AUMF to strike Iran under the unfounded claim that Tehran supports al-Qaeda.
Despite the articles outlined in the constitution, presidents have found ways to sidestep Congress in war matters. So in 1973, after decades of US intervention in Vietnam and elsewhere in Asia, lawmakers passed the War Powers Resolution to reassert their authority over military action.
The law restricts the president’s war-making powers – or that was its intention at least.
It was passed after President Richard Nixon’s secret bombing of Cambodia, which killed tens or even hundreds of thousands of civilians and led to widespread protests in the US.

The federal law was designed to limit the US president’s power to commit the US to armed conflict.
Enacted over Nixon’s veto, the resolution requires “in the absence of a declaration of war” that the president notify Congress within 48 hours of military action and limits deployments to 60 or 90 days unless authorisations to extend them are passed.
Before US troops are committed abroad, Congress must be consulted “in every possible instance”, it says.
Why is the War Powers Act relevant now?
With the possibility of a US intervention in Iran mounting, lawmakers have been eyeing the five-decade law and pushing for their own version.
On Monday, Democratic Senator Tim Kaine introduced a bill requiring that Trump, a Republican, seek authorisation from Congress before ordering military strikes against Iran. That was followed by a similar bill put forward in the House of Representatives on Tuesday by US Representatives Thomas Massie of Kentucky, a Republican, and Democrat Ro Khanna of California.
A No War Against Iran Act, introduced by Democratic Senator Bernie Sanders of Vermont, seeks to “prohibit the use of funds for military force against Iran, and for other purposes”.
But even as some polls find Trump supporters are against war with Iran, passage of such bills in the Republican-controlled legislature remains unlikely.
Why is new legislation needed if it’s in the constitution?
Despite the constitutional separation of war powers, the executive and legislative branches have jockeyed over those roles throughout US history.
The most prominent of these incidents – and the last time such a case made it to the Supreme Court in fact – took place in 1861 at the start of the US Civil War when President Abraham Lincoln blockaded southern ports months before Congress legally declared war on the Confederacy. The highest court eventually ruled the president’s acts were constitutional because the executive “may repel sudden attacks”.
Throughout history, formal congressional declarations of war have remained scarce. There have been just 11.
Instead, Congress has traditionally authorised a wide range of military resolutions.
Almost since its passage, the 1973 law has been viewed by some critics as deeply ineffective – more of a political tool for lawmakers to voice dissent than as a real check on power. (In the 1980s, then-Senator Joe Biden led a subcommittee that concluded the law fell short of its intent.)
Congressional resolutions seeking to end military involvements unauthorised by Congress are subject to a presidential veto, which can be overridden only by two-thirds majority votes in the House and the Senate.
Others have argued the law served an important role in asserting Congress’s rights and creating a framework for speedy, presidential reporting to Congress. The more than 100 reports that have been sent to Congress since 1973 offer a semblance of transparency.
While Nixon was the most vociferous in his opposition to the War Powers Act, he’s hardly the only president to appear critical. Modern presidents have routinely sidestepped the act, using creative legal arguments to work around its requirements.
The executive branch has since steadily expanded its war-making powers, particularly after the September 11, 2001, attacks.
The 2001 AUMF and the 2002 Iraq AUMF have been used to justify attacks on “terrorist groups” in at least 19 countries, according to the Friends Committee on National Legislation.
“The executive branch has stretched this authorization to cover groups that had no connection to the 9/11 attacks, including those such as ISIS [ISIL], which did not even exist at the time,” Heather Brandon-Smith, the nonprofit’s legislative director of foreign policy, wrote in a briefing.
And while organisations like the International Crisis Group have urged a rehaul or repeal of the AUMF, successive administrations have shown little interest in doing so. In recent years, congressional efforts to repeal the 2001 and 2002 AUMFs have only begun chipping away at the acts.
The Senate in 2023 voted to repeal the 2001 AUMF although the move was largely viewed as symbolic. The House similarly voted to repeal the 2002 AUMF in 2021. But both laws still remain in effect.
That remains to be seen, but it does not seem likely.
During Trump’s first term in office, Congress sought to limit presidential war authority for the first time since the Vietnam War.
In 2019, Congress approved a bill to end US support for the Saudi-United Arab Emirates war in Yemen, which Trump quickly vetoed.
A year later, a similar situation played out after Trump ordered the drone strike that killed Soleimani.
In response, both houses of Congress passed legislation seeking to limit a president’s ability to wage war against Iran.
That legislation was vetoed by Trump, and once again, there were not enough Republicans to meet the two-thirds majority necessary in both houses to override the veto.
With the balance of power in Congress since then fully shifting to the Republicans in Trump’s second term, the newest war powers resolutions face an even stiffer battle.
‘We’re observing a systematic war against the entire country.’
Al Jazeera’s Tohid Asadi reports from Tehran under attack from Israel, which has been striking Iran’s nuclear facilities as well as civilian areas.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
“This man absolutely should not continue to exist.” Israel’s defence minister threatened to assassinate Iran’s supreme leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, after Iranian missile strikes across Israel. The missiles injured dozens, damaging a hospital, a high-rise, and several residential buildings.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
Israeli social media users have gone viral for videos mocking an Iranian TV anchor whose live broadcast was interrupted by an Israeli bombing, mimicking her clothes and her reaction to the attack. Some comments criticised the videos as a ‘despicable’ celebration of war crimes.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
An Iranian missile slammed into the main hospital in southern Israel, wounding people and causing “extensive damage,” according to the medical facility.
However, IRNA, the Islamic Republic News Agency, has said on Telegram that the “main target” of the missile attack early on Thursday “was the large [Israeli army] Command and Intelligence (IDF C4I) headquarters and the military intelligence camp in the Gav-Yam Technology Park”.
It said that this facility is located next to Soroka hospital in Be’er Sheva.
IRNA claimed that the hospital only suffered minor damage from the shockwave resulting from the missile attack.
“The military infrastructure was a precise and direct target,” it said.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu condemned the attack and promised a response, saying: “We will exact the full price from the tyrants in Tehran.”
Another missile hit a high-rise building and several other residential buildings in at least two sites near Tel Aviv. At least 47 people were wounded in the attacks, according to Israel’s Magen David Adom rescue service.
Israel, meanwhile, carried out strikes on Iran’s Arak heavy water reactor in its latest attack on the country’s sprawling nuclear programme, on the seventh day of a conflict that began with a surprise wave of Israeli air strikes targeting military sites, senior officers and nuclear scientists.
Israel’s military said its fighter jets targeted the Arak facility and its reactor core seal to stop it from being used to produce plutonium.
Israel separately claimed to have struck another site around Natanz that it described as being related to Iran’s nuclear programme.
Iranian state TV said there was “no radiation danger whatsoever” from the attack on the Arak site.
Israel is the only nuclear-armed state in the Middle East – but does not acknowledge having such weapons.
A new wave of Iranian missiles has struck multiple sites across Israel, damaging a hospital, and Israel has attacked Iran’s Arak heavy water nuclear reactor as the two countries trade fire for a seventh consecutive day.
Rescue operations were under way on Thursday after an Iranian missile hit the Soroka Medical Center in the city of Beersheba in southern Israel. Iran said it was targeting a military site in the attack.
Reports said the Iranian projectiles made impact in at least six other locations, including in Tel Aviv and two of its districts – Holon and Ramat Gan. Emergency crews said at least 50 people were injured, including four who were in critical condition.
The Israeli army said its fighter jets struck dozens of sites in Iran, including the Arak heavy water nuclear reactor.
The partially built reactor was originally called Arak and is now named Khondab.
The military said it specifically targeted “the structure of the reactor’s core seal, which is a key component in plutonium production”.
Iranian media reported air defences were activated in the area of the Khondab nuclear facility and two projectiles hit an area close to it.
Officials told Iranian state TV that evacuations were made before the strikes and no risk of radiation or casualties was detected. There was no mention of any damage.
The attacks were carried out as the two countries traded fire for a seventh day after Israel launched a major attack on Friday on Iranian military facilities and nuclear sites, killing senior military officials and top nuclear scientists.
Iran responded to that attack with air strikes on Israel, and the conflict has since widened to include civilian targets, including residential areas and oil and gas facilities.
Iran has fired hundreds of missiles and drones at Israel although most have been shot down by Israel’s multitiered air defences.
The Soroka Medical Center, which has more than 1,000 beds and provides services to about 1 million residents of southern Israel, said in a statement there was “extensive damage” in several areas of the hospital and the emergency room was treating several minor injuries. The hospital was closed to all new patients except for life-threatening cases.
Many hospitals in Israel have activated emergency plans in the past week, converting underground parking to hospital floors and moving patients underground, especially those who are on ventilators or are difficult to move quickly.
“This is a war crime committed by the Iranian regime,” Israeli Health Minister Uriel Buso was quoted as saying by Israeli Army Radio in reference to the attack on Soroka. Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu warned the Iranian leaders they would pay “a heavy price” for the attack.

The Iranian news agency IRNA said the “main target” of the Beersheba attack “was the large [Israeli army] Command and Intelligence (IDF C4I) headquarters and the military intelligence camp in the Gav-Yam Technology Park”. The facility is next to the Soroka Medical Center, it said, claiming the health facility suffered only minor damage from the shockwave resulting from the missile strike.
Tight military censorship in Israel means information about sites such as military and intelligence facilities are not released to the public. According to Israeli media reports, a building next to the hospital described as “sensitive” sustained heavy damage.
Ori Goldberg, an Israeli political commentator, told Al Jazeera that Israeli authorities were focusing on the hospital attack and trying to send a “message that the Iranians target hospitals”.
“Of course, Israelis target hospitals as well. It’s important to mention that there really are very sensitive installations and headquarters very near to the hospital because Israel places its military headquarters in the midst of civilian neighbourhoods and towns,” he added, speaking from Tel Aviv.
Iranian state TV, meanwhile, reported the attack on the Arak site, saying there was “no radiation danger whatsoever”. An Iranian state television reporter, speaking live in the nearby town of Khondab, said the facility had been evacuated and there was no damage to civilian areas around the reactor.
Israel had warned earlier on Thursday morning that it would attack the facility and urged the public to leave. The Israeli military said its latest round of air strikes also targeted Tehran and other areas of Iran, without elaborating.
The strikes came a day after Iranian Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei rejected United States calls for a surrender and warned that any US military involvement in the conflict would cause “irreparable damage to them”.
A Washington, DC-based Iranian human rights group said at least 639 people, including 263 civilians, have been killed in Iran in the past week of air strikes and more than 1,300 have been wounded. Iran has fired about 400 missiles and hundreds of drones at Israel, killing at least 24 people and wounding hundreds.
Iran launched a missile attack against Israel, causing severe damage and striking Israel's main hospital in the south.
Source link
Video shows distressing scenes as a badly wounded Palestinian girl in Gaza embraces the body of her father, who was killed in an Israeli attack on Khan Younis. Luna Rasras was sheltering in a tent with her family when the attack happened. Her siblings were also killed.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
The Russian president says Iran’s nuclear programme continues and society remains united behind political leadership.
Russian President Vladimir Putin declined to comment on speculation that Israel or the United States may try to assassinate Iranian Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, and continued to push for a political solution to the Iran-Israel conflict during a meeting with international journalists.
“If I may, I hope that this will be the most correct answer to your question. I do not even want to discuss this possibility. I do not want to,” he said in response to questions about Khamenei on Thursday from the sidelines of the Saint Petersburg International Economic Forum.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said earlier this week that the conflict could lead to regime change in Iran, where Israeli attacks have targeted senior military leaders and top nuclear scientists.
Israeli strikes have killed at least 585 people, among them 239 civilians, since last Friday, according to a US-based Iranian human rights group.
US President Donald Trump earlier said that Washington knew the location of Khamenei. He said the US would not act for now, although he has not ruled out the possibility that the US may join Israel’s attack on Iran.
Despite the threats from Netanyahu, Putin said that Iranian society remains united behind its government.
“We see that today in Iran, with all the complexity of the internal political processes taking place there … that there is a consolidation of society around the country’s political leadership,” he said.
The Russian leader has presented himself in recent days as a possible mediator between the two sides, although his overtures have been rebuffed by world leaders like Trump due to Moscow’s close ties with Tehran.
Despite the roadblocks, Putin has continued to push for a peaceful resolution that would need to ensure Iran’s “peaceful nuclear activities” and the “interests of Israel from the point of view of the unconditional security of the Jewish state”.
“This is a delicate issue, and of course, we need to be very careful here, but in my opinion, a solution can be found,” he said.
Russia has yet to supply Iran with weapons, despite signing a strategic partnership in January, he said, although it continues to help with Iran’s nuclear programme. Tehran says this programme is designed for civilian use and has consistently denied seeking a bomb, but Israel claims Iran intends to build a nuclear weapon.
Putin said Tehran’s nuclear programme continues underground despite the recent Israeli air strikes.
“These underground factories, they exist, nothing has happened to them,” Putin said.
Putin also said that more than 200 Russians continue to work at the Russian-built Bushehr nuclear power plant in southern Iran. The group is safe, he said, after Moscow “agreed with the leadership of Israel that their security would be ensured”.
US President Donald Trump says he is still weighing his options regarding United States military intervention amid escalating hostilities between Israel and Iran.
Standing on the South Lawn of the White House on Wednesday, Trump said, “The next week is going to be big,” adding that Iranian officials are eager to negotiate. However, he warned them that “it’s very late to be talking,” after they reached out to him.
Officials and experts have suggested that the US’s 30,000-pound (13,000kg) bunker buster bomb is the only weapon capable of destroying the Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant, a facility believed to be central to Tehran’s nuclear programme and carved deep into a mountain.
The United States is the only country to possess these bombs, which it delivers using B-2 bombers. If deployed against Iran, it would represent a major shift from primarily intercepting missiles on Israel’s behalf to conducting active offensive strikes against Iran.
“Bunker buster” is a general term for bombs designed to destroy targets located deep underground that conventional bombs cannot reach.
The US military’s most powerful bunker buster is the GBU-57 Massive Ordnance Penetrator. Weighing about 30,000 pounds (13,600 kg), including a 2,700kg (6,000-pound) warhead, this precision-guided bomb is made of high-strength steel and built to penetrate up to 200 feet (61 metres) underground before exploding.
The B-2 Spirit, a US stealth bomber, is currently the only aircraft designed to deploy the GBU-57 and can carry two bunker buster bombs at a time. The US Air Force says multiple bombs can be dropped sequentially, either by the same aircraft or by several, allowing each strike to burrow deeper, amplifying the overall impact.
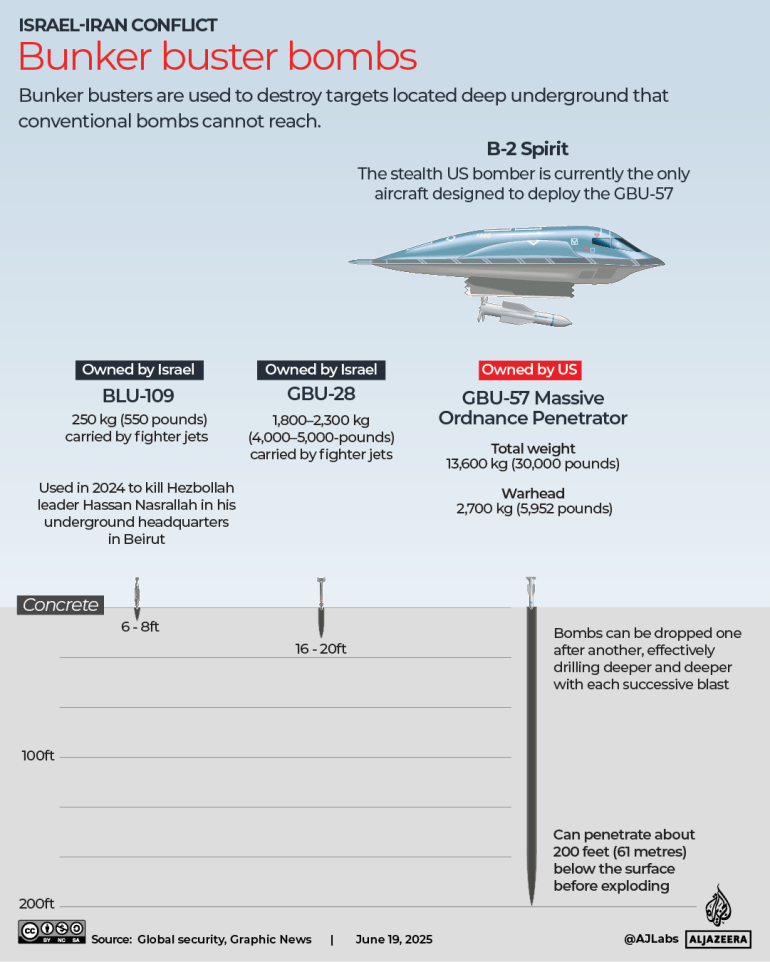
Israel also operates US-made bunker busters, including the GBU-28 and BLU-109, which are typically dropped from fighter jets such as the F-15. These weapons, however, have a much shallower penetration range and are not capable of reaching extreme depths of fortified sites like Iran’s Fordow nuclear facility. In 2024, Israel reportedly used successive BLU-109 bombs to kill Hezbollah leader Hassan Nasrallah in his underground headquarters in Beirut.
Iran’s Fordow Fuel Enrichment Plant, located about 95km (60 miles) southwest of Tehran, is built into the side of a mountain, reportedly up to 80-90 metres (260-300 feet) underground, to survive air strikes and bunker buster attacks.
Construction of the Fordow facility is believed to have begun in about 2006, and it became operational in 2009, the same year Iran officially acknowledged it.
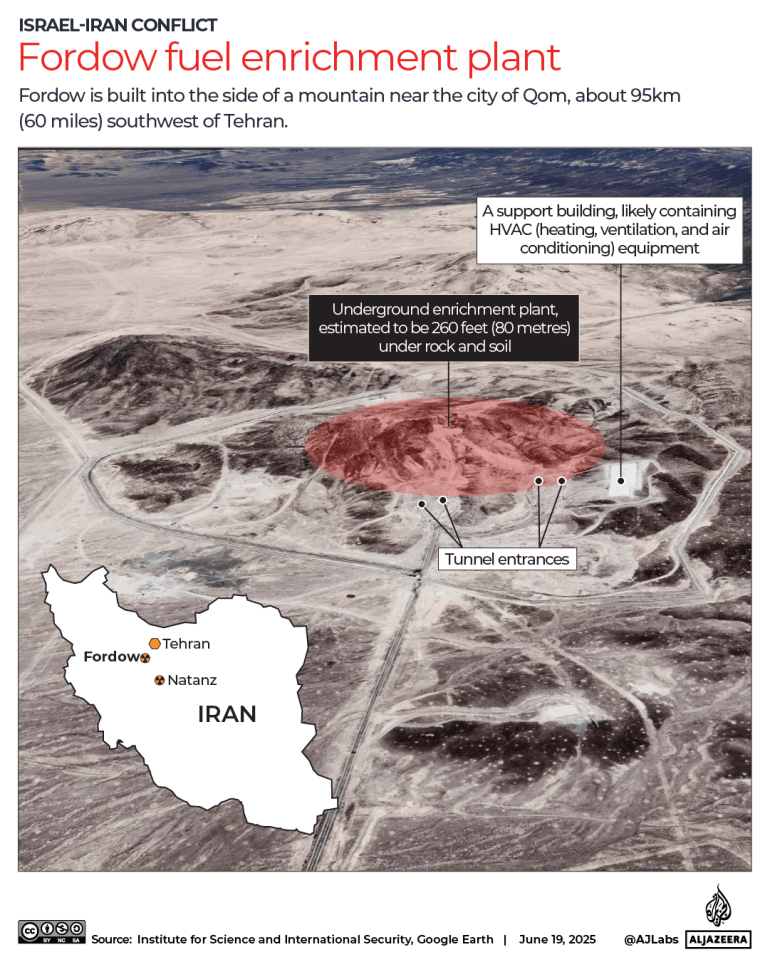
Under the 2015 Iran nuclear deal, known as the JCPOA, Iran agreed to halt enrichment at Fordow and convert the site into a research centre. However, after the US withdrew from the agreement in 2018, Iran resumed uranium enrichment at the facility. Iran has insisted its nuclear programme is for civilian purposes.
Fordow is reportedly defended by Iranian and Russian surface-to-air missile systems, though those defences may have already been targeted in Israel’s ongoing strikes.
Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu has framed the campaign as a mission to dismantle Iran’s missile and nuclear capabilities, describing them as an existential threat. Officials have confirmed that Fordow is a key target.
“This entire operation … really has to be completed with the elimination of Fordow,” said Yechiel Leiter, Israel’s ambassador to the United States, in an interview with Fox News.
Israel is believed to have destroyed the above-ground section of Iran’s uranium enrichment facility at Natanz, the country’s largest nuclear site.
According to the United Nations’ International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the resulting power loss may have also caused damage to the underground enrichment halls at the facility.
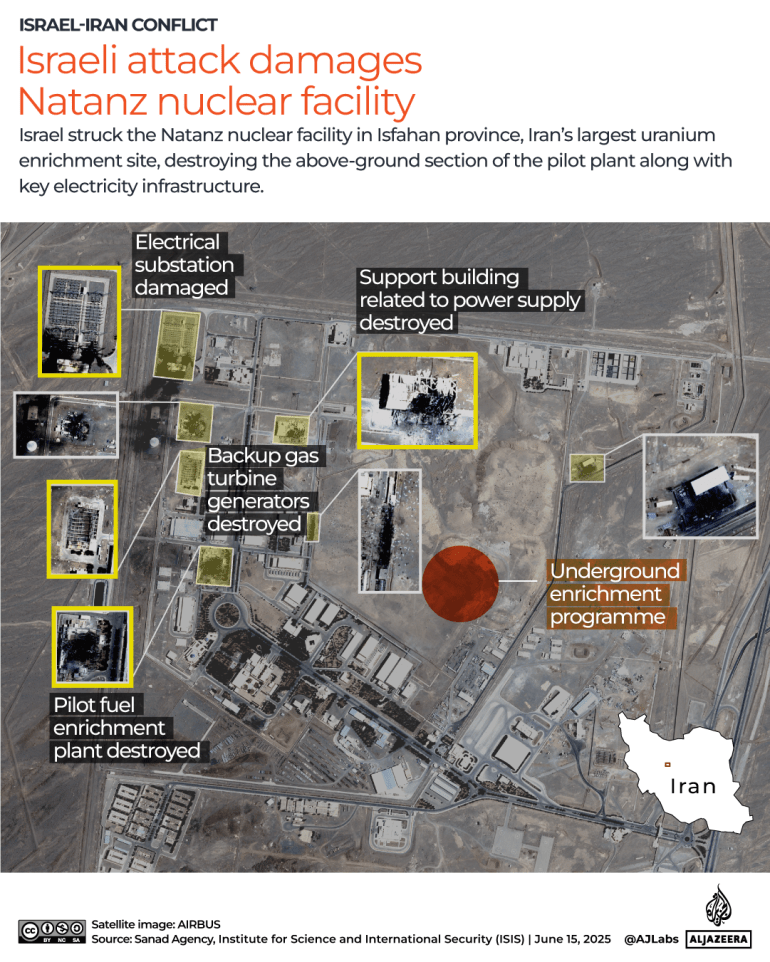
Before and after satellite imagery reveals the extent of the damage at Natanz.
Israeli attacks have also damaged the Isfahan enrichment facility in central Iran.
On Monday, Rafael Grossi, the head of the UN nuclear watchdog, said there was a possibility of both radiological and chemical contamination from the damaged Natanz site.
Speaking at an emergency IAEA session in Vienna, Grossi said radiation levels remain normal outside Iran’s Natanz and Isfahan nuclear sites, both of which were hit in Israeli strikes. However, he warned that ongoing military escalation increases the risk of a radiological release.
Fordow is located about 32 kilometres (20 miles) south of the city of Qom, Iran’s seventh-largest city with a population of some 1.4 million and a major religious and political centre.
The streets of Tehran are telling a story of chaos: suitcases dragged across pavements, a single mother holding her young son with one hand while balancing a blanket and pillow in the other, heading into a subway station to spend yet another night underground. With no shelters, alerts, or public evacuation plans, young Iranians are turning to the only safe space left as Israel attacks Iran: the internet, and chat apps like Discord and WhatsApp.
“We don’t know where to go,” says Momo, a 24-year-old IT engineering student in Tehran.
“We never know if the building next door houses the IRGC [Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps] or the Ministry of Intelligence. I don’t know if my upstairs neighbour is a regular person or a regime official. The facility near me might be part of a secret military programme,” he said, alluding to Israel’s attacks on residential buildings, ostensibly to target individuals associated with Iran’s military or with its nuclear programme.
Despite it all, Momo has chosen to stay in Tehran – not just for his two-year-old rescue cat, but out of principle. “Where would I even go? My home is here. My life is here. We won’t give in to a repressive regime or Israeli aggression. Many of us are staying. We don’t know how long this will last, but I’d rather my home become my grave than live in displacement.”
With conventional safe havens out of reach and communication networks under heavy surveillance or blocked entirely, Iran’s Generation Z – those born between the mid-1990s and mid-2010s – are carving out new refuges in the digital world. Forums have become lifelines, serving as makeshift shelters, therapy rooms, and organising hubs.
Momo has been a Discord user for seven years. “It’s the only place where I can breathe,” Momo says. “I used Discord just for voice chats while gaming with friends. Now, it feels like home. We’re often in touch with people there more than our families. In the middle of the bombings, we watched movies and TV series together. Sometimes, we even fall asleep online.”
This generation of Iranians came of age in the shadow of sanctions, political unrest, and censorship. Many were also key players in the 2022 anti-government protests sparked by the death of Mahsa Amini in police custody after she was arrested for wearing “improper hijab” – a movement known globally by the slogan “Woman, Life, Freedom”. Online platforms played a pivotal role then, and they continue to serve as vital tools today.
According to Iranian daily Shargh, nearly 14 million Iranians – around 15 percent of the population – are Gen Z gamers and frequent Discord users. Despite official restrictions, they remain digitally connected, using VPNs and encrypted apps to stay in touch.
“When the attacks began, we were in the middle of a game,” Samin, a 23-year-old from northern Iran, says. “It was surreal – not knowing if the explosions were coming from inside the game or real life. These games are full of gunfire and bombs, creating this bitter irony: I couldn’t tell if I was playing Call of Duty or living it. Sadly, the sounds weren’t from the game – they were real bombings.”
Discord was blocked in Iran in April 2024, with some suspecting that the government shut it down in recognition of its use as a platform to organise protests, although Iran’s judiciary officially cited concerns over indecent content. But the ban hasn’t stopped Gen Z from finding their way back to the app.
“Sometimes we go to great lengths just to find a working VPN, just to log into Discord and join our channels. If someone doesn’t come online, we call them. If their voice cuts out mid-call, our hearts race – we worry they might have been killed in a bombing,” Samin says. “We’re online more than ever, constantly checking in on each other. We’ve shared so much – birthdays, the sound of missiles overhead, the loss of loved ones. We share our fears and daily struggles in that space. It’s a painful atmosphere, but there’s hope, solidarity, and care, too.”
Meanwhile, a WhatsApp group created initially for prenatal yoga in Tehran has become an unexpected hub of resilience. Its members – pregnant women who were unable to flee the capital – now share breathing techniques, emergency tips, and voice messages during blackout periods.
Ameneh and her friend Zohreh, PhD holders and United States green card recipients, had been waiting for their parents’ visas to be approved by the US for months. While both were expecting babies, they made different decisions: Zohreh returned to Iran to have her family’s support for childbirth, while Ameneh stayed in San Francisco to give birth alone – but safely – in the US.
Now, four days into Israel’s bombardment of Iran, both women are devastated – but still connected via a group chat on the encrypted messaging app called “Yoga for Pregnancy”.
“We give each other advice on self-care and breathing to manage panic attacks and do yoga together online. We light candles and send voice notes when things go quiet again,” says Zohreh, who is eight months pregnant in Tehran.
“The sound of an explosion woke me. A friend guided me to focus on breathing and heartbeat to calm my contractions. Another time, when my baby didn’t move for hours, they told me to play music, do a massage, and try yoga again.”
US President Donald Trump’s threat that Tehran be “evacuated” sent waves of panic through Tehran. Zohreh and many other pregnant women found themselves unable to leave the city due to their physical condition and limited access to medical care. “We had planned to leave Tehran,” she says, “but after seeing the traffic and the possibility of going into labour early, I decided to stay so I’d have access to a hospital.”
As the bombs fall and uncertainty deepens, Iranians’ defiance lives in digital spaces – quiet, steadfast, and deeply human. Even when the sky offers no warning and the regime offers no refuge, they are still finding each other and refusing to face the dark alone.
Editor’s note: Due to the sensitive nature of this story, names have been changed to protect the people involved.
This story was published in collaboration with Egab.
Footage shows Pakistani citizens evacuated from Iran fleeing the country as the Israel-Iran conflict deepens. Pakistan shut all crossings with Iran indefinitely on Monday, raising concerns the conflict could destabilise the nuclear-armed nation.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025
Russian President Vladimir Putin says Israel has given assurances about the safety of its personnel at Iran’s Russian-built nuclear power plant in Bushehr. Russia and Iran have been working on the joint project for three decades. He made the comments at a meeting with foreign press.
Published On 19 Jun 202519 Jun 2025