GoFundMe has been accused of blocking “millions of dollars” of life-saving aid from reaching Gaza.
Charity leaders, activists and desperate Palestinians in Gaza have condemned the crowdfunding website for shutting down or blocking withdrawals for Palestine-related fundraising pages – and have accused bosses of having “blood on their hands”.
Despite questions from Al Jazeera, the company has not revealed the amount of money raised on its platform for Gaza that has been frozen in its system or has been refunded to donors.
But it has told Al Jazeera that more than $300m has been raised on the platform for both Palestinians and Israelis since Hamas’s October 7 attacks on Israel in 2023 and the beginning of Israel’s war on Gaza.
Hala Sabbah, the founder of mutual aid group The Sameer Project, said that in September, more than $250,000 of donations to her organisation was refunded.
The London-based NGO-sector worker described the closure of her GoFundMe page as a “disaster” for her group’s efforts to provide emergency aid in the enclave.
The Sameer Project runs a camp for displaced people in Deir el-Balah, providing healthcare and essentials to its residents – paid for by money that, until now, had been raised through GoFundMe, totalling more than $1m. It also funds food, water, shelter and clothing for people across Gaza.
Sabbah said she was “treated like scum” by GoFundMe, despite her group’s pages raising about $44,000 for it in transaction fees.
“Our GoFundMe page had daily updates with complete cost breakdowns of every single initiative we did – everything was well-documented, with receipts,” she said.
“This information – including all transfers – was forwarded to GoFundMe, yet they still chose to shut us down.”
GoFundMe notifies page organisers that there will be a “review” process after they launch fundraisers related to Palestine – or “the conflict in the Middle East”, as it is phrased by the company’s compliance team in emails seen by Al Jazeera. The company claims this is part of its “standard verification process”, but critics say it appears to inordinately restrict Gaza-related pages rather than those for other causes, such as Israel or Ukraine.
GoFundMe has refused to disclose figures that show how many Israel or Ukraine fundraisers have been closed compared with those for Gaza.
Intrusive reviews
Social media has been flooded with Palestinian advocates speaking out about their pages being shut down. Fundraisers for Israel and Ukraine appear to face little of the same scrutiny. And when they do, media campaigns can quickly force GoFundMe to act. One Ukraine fundraiser that was shut down in March 2022 was reinstated the next month after media coverage of the case.
The company’s long and intrusive review process often results in Gaza fundraisers being shut down and money refunded to donors or pages being “paused”, preventing funds from being accessed by account holders until the review is concluded.
One United States-based fundraiser for the Sulala animal shelter in Gaza says it had about $50,000 dollars refunded to donors when its first page was closed. The team behind the fundraiser then created another page without specifically mentioning Gaza or Palestine, which was not flagged by GoFundMe, placed under review or paused, and ran for months uninterrupted.
In the case of The Sameer Project, GoFundMe’s compliance team said it was concerned about how funds were being distributed, and said that the documentation Sabbah had provided was not “accurate, complete or clear”. An email to Sabbah added that there were “material discrepancies” between the information shared and how funds were distributed to beneficiaries.
Before shutting the page down, the compliance team asked for personal information about who was receiving funds, evidence of bank transfer statements and details about partner organisations, which Sabbah says The Sameer Project provided.
“We spent weeks fighting back, and they completely ignored us – even denying us access to our donor lists,” Sabbah told Al Jazeera.
“People can raise funds to help the Israeli military… and their pages don’t get closed. But we try to raise money for diapers and lifesaving medication, and we get scrutinised and shut down.”
“We have children in our camp on the verge of death. The company has blood on its hands.”
The mutual aid group – named after Sabbah’s Gaza-based uncle who died in January – says it has provided more than 800,000 litres (211,330 gallons) of water, $100,000 in cash aid, 850 tents and medical treatment for 749 children across the enclave.
It transfers money to intermediaries via makeshift exchange sites and by sending money directly to doctors or pharmacies.
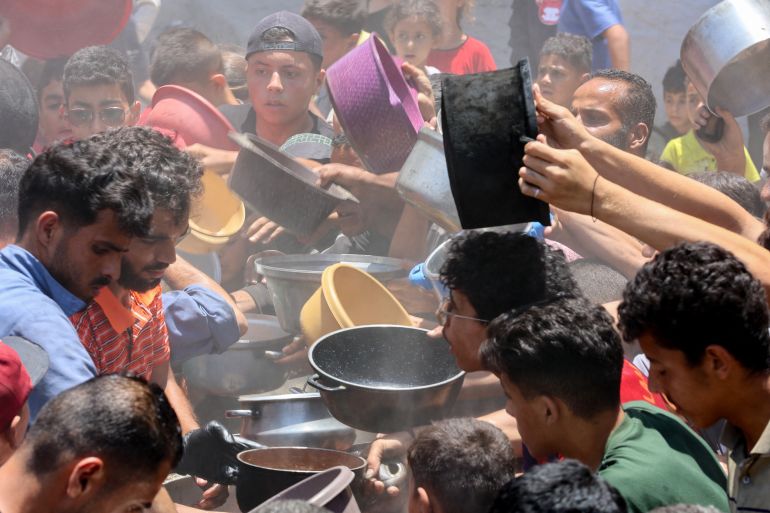
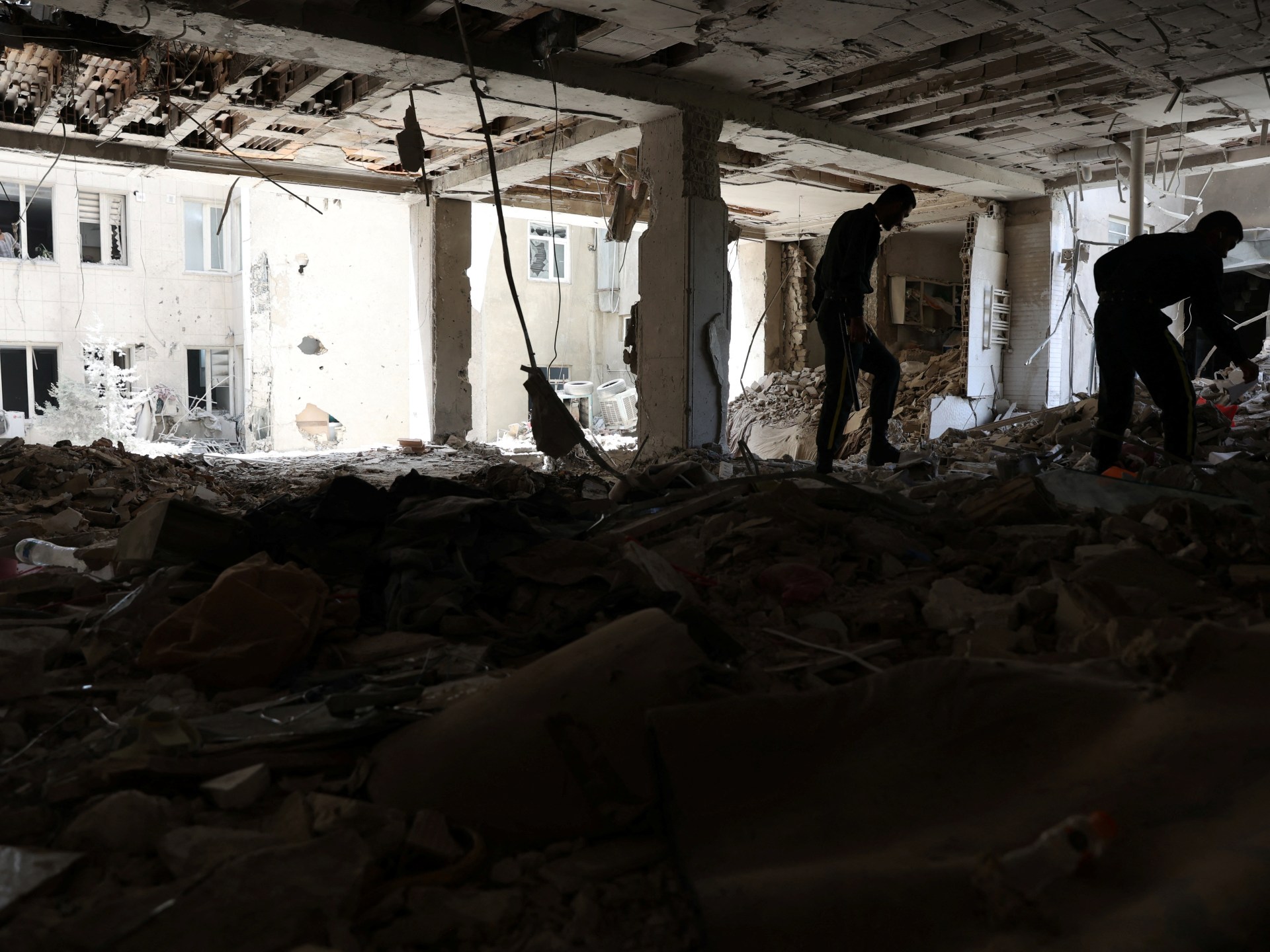
Crowdfunding websites have for months been one of the only feasible ways to help those trapped in Gaza.
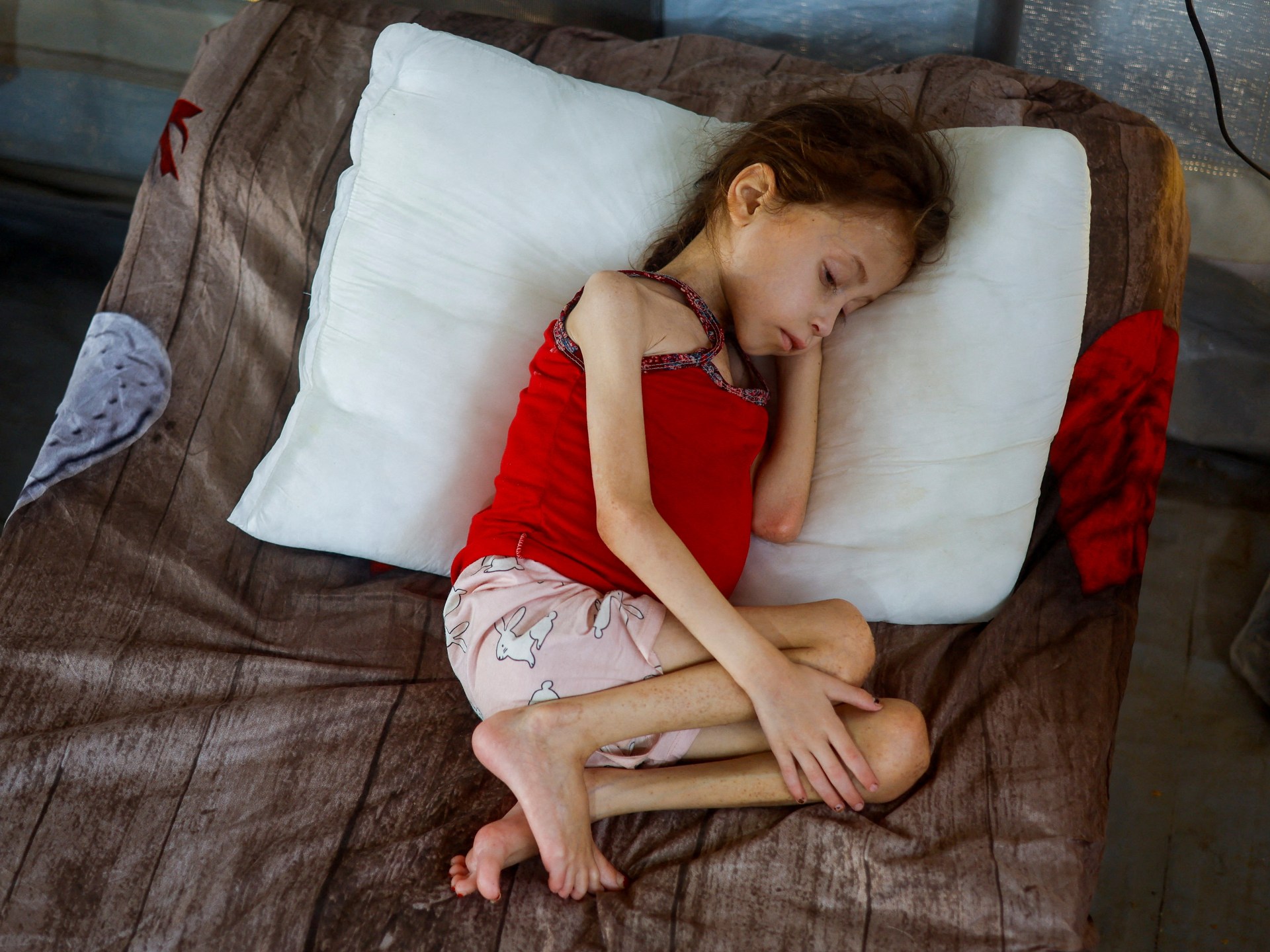
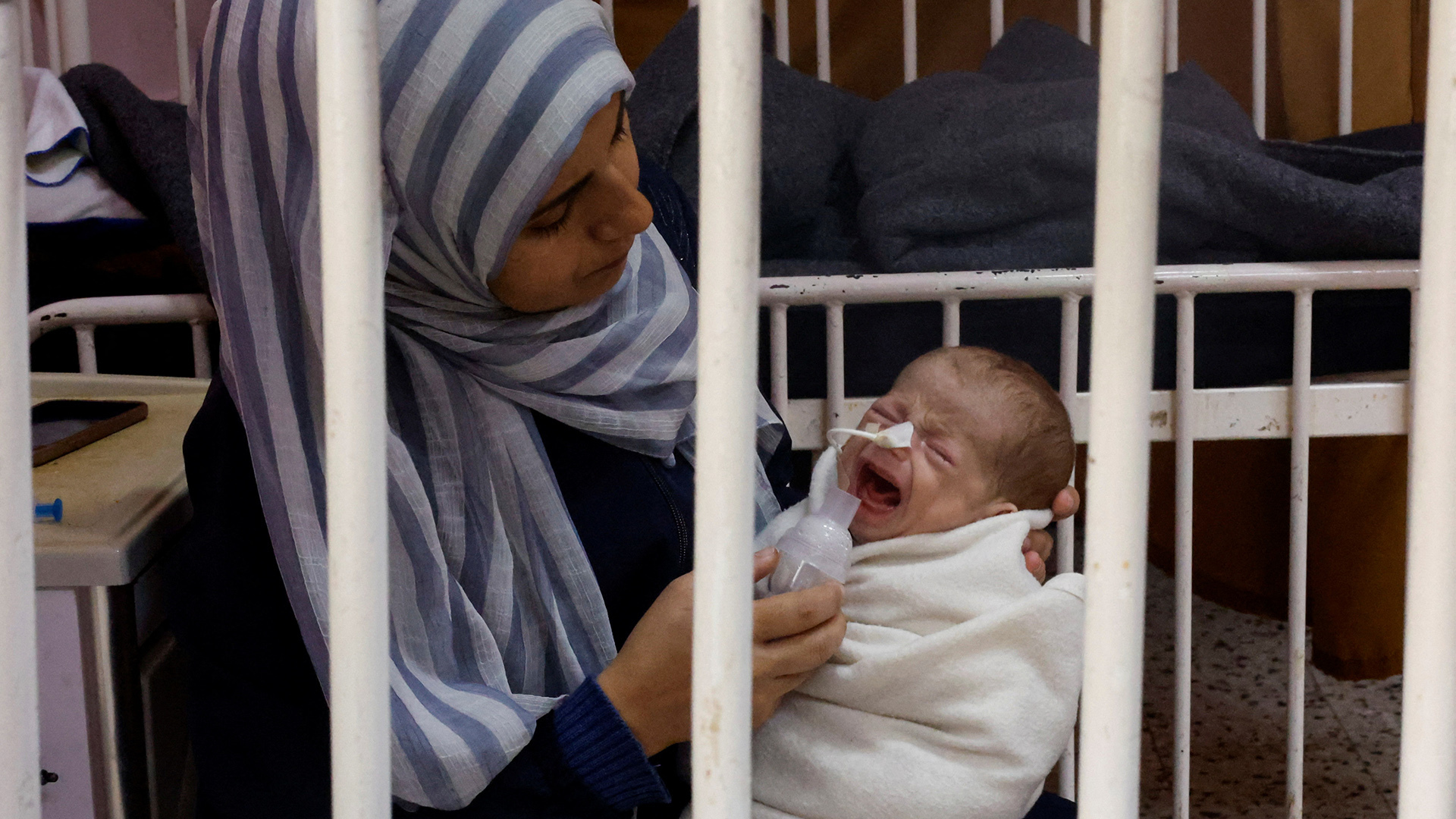
Famine is creeping further into the enclave, humanitarian aid is being blocked for long periods, civilian infrastructure lies in ruin and banks and ATMs have either been destroyed or have halted operations.
Sabbah slammed GoFundMe for not justifying shutting her page down despite the huge amount of money the company made from the group’s pages in”payment processing fees”. It charges 30 cents per donation and a 2.9 percent cut of the total raised.
There are no banking services left in Gaza, but there are exchange offices – often people using POS (point of service) cash machines charging exorbitant interest rates – and the option to swap cryptocurrency for physical currency, amid critical shortages of the latter.
Without regular aid flowing into the enclave, most charities rely on sending money via these limited routes to intermediaries who will distribute essentials and medical supplies.
Some tinned food, tents and health products are on sale in Gaza markets. But cash is scarce, stocks are extremely limited, and most people cannot afford to pay. Since breaking the ceasefire agreement with Hamas brokered in January, Israel resumed bombing and re-established a blockade on humanitarian aid lasting months.
Now, aid is only reaching the enclave through the heavily criticised US-backed Gaza Humanitarian Foundation (GHF). Hundreds of desperate Palestinians have been shot and killed by Israeli forces at GHF aid collection sites.
‘Treated like animals’
Both still trapped in Gaza, Mostafa Abuthaher and his brother Yahya Fraij, aged 30, have twice created GoFundMe pages, and on both occasions, the company closed them down.
Yahya lost his home and three of his cousins to Israel’s onslaught, and now his family survives with only a makeshift tent near the beach in al-Mawasi in southern Gaza.
His wife gave birth to their six-month-old daughter during the war. Yahya told Al Jazeera that she has experienced nothing but suffering during her short life – and he has had to protect her from extreme cold and the trauma of Israeli bombardment.
“My daughter and I face death almost every day,” he said. “And now we have nothing – not even a tent. The war has taken everything from us.
“We’ve been treated like animals and insulted by the world for the last 20 months.”
The brothers had raised more than $12,000 to support their families until their first page was suddenly shut down. The company blocked them from withdrawing nearly $5,000.
In an email exchange with GoFundMe, a compliance officer said Mostafa’s page breached the company’s terms of service for “prohibited conduct”, which covers fundraisers that are “fraudulent, misleading, inaccurate, dishonest or impossible”.
He was asked to send a photo ID, provide his location and explain why his page description had changed so often and how the funds would be used. Then his page was closed, after which he expressed astonishment and accused the platform of bias.
The brothers say that many people in Gaza have set up GoFundMe pages because of the platform’s size and reputation, and then found themselves “trapped” once their pages began the often ill-fated verification process. Critics of GoFundMe say campaigns fundraising for Israel appear to be able to avoid similar interventions from its compliance team.
Other fundraisers on the website state they aim to raise funding for “equipment” that supports the Israeli military, or “training” and travel for new recruits.
A page raising money for gun sights and other equipment to “safeguard” the Kishorit kibbutz in the north of Israel appeared to breach the website’s terms of service, but was active for nearly a year before no longer becoming accessible.
The terms of service prohibit fundraising for “weapons meant for use in conflict or by an armed group”.
Sabbah added that there is no guarantee that money from similar pages to fundraise for “equipment” or “security” won’t be used to buy weapons, at a time when the Israeli government is actively arming its citizens.
Double standards?
Al Jazeera sent several questions to GoFundMe, asking how many Gaza-related fundraisers there are, how much they had raised, the number listed as “transfers paused and the total removed or taken down. We also asked the company to provide like-for-like figures for Israel and Ukraine.
At the time of writing, GoFundMe refused to provide the specific information and data we requested. A spokesperson said: “GoFundMe has helped raise and deliver over $300m from donors in more than 215 countries and jurisdictions to support individuals and organisations helping those in both Gaza and Israel.
“Any suggestion of double standards is wholly without merit, baseless, and contrary to the values that guide our platform.
“Any decision to remove a fundraiser from the platform is never taken lightly and is informed explicitly by our Terms of Service. Taking action like this is difficult, but it protects our ability to support people who are fundraising to help others.”
Amr Shabaik, the legal director at the Council for American Islamic Relations (CAIR), told Al Jazeera that the fundamental issue with platforms like GoFundMe was the “imbalanced application of rules” – behaviour consistent with other forms of digital censorship since October 7.
“Algorithmic discrimination and targeting, looking for certain descriptors and categories – like Gaza or Palestine specifically in the last 18 months – means some pages are subjected to an unfair and high level of scrutiny that other fundraisers are not,” he said.
“All platforms have their rules and regulations, but they’re applying them disproportionately and unfairly towards Palestinians.”
“There is a clear indication of a double standard. If you are actively preventing lifesaving aid – intentionally or unintentionally -– from reaching Gaza, it’s tough to say you’re not supporting a genocide.”
Shabaik points to studies undertaken by Human Rights Watch (HRW), The Arab Centre for the Advancement of Social Media and Palestine Legal that detail platforms’ inordinate targeting of pro-Palestine pages or accounts.
HRW says that between October and November 2023, 1,049 pro-Palestinian posts on Facebook and Instagram were taken down by the platform’s owner, Meta. Palestine Legal says that between October 7 and December 31, 2023, the organisation received 1,037 requests for legal support from people “targeted for their Palestine advocacy”. The Arab Centre for the Advancement of Social Media documented more than 1,639 “censorship violations” in its 2023 annual report, including content removal and suspensions.
Last December, the Industrial Workers of the World (IWW) Freelance Journalists’ Union said that GoFundMe prevented $6,000 of funding from reaching the Palestinian Journalists’ Syndicate after its fundraiser was shut down. This is despite the organisation being based in Ramallah in the occupied West Bank, not in Gaza.
One union delegate, using the name “Arv” as he wanted to remain anonymous, told Al Jazeera the money would have provided protective helmets, press vests and other safety apparatus for journalists reporting in the territory. He added that GoFundMe said the fundraiser was shut down due to a lack of compliance with unspecified “laws and regulations”.
In December, a union spokesperson said on its Twitter page: “Over the course of the fundraiser, we received a dozen requests for further information from GoFundMe, all of which were answered as thoroughly and in as timely a manner as possible, given the ongoing war.”
Arv added that the union had been pushed to explore the use of other fundraising platforms because of the difficulty of working with GoFundMe.
“Current GoFundMe users should do the same before they too are caught in such Kafkaesque circumstances,” he said.
The GoFundMe compliance team asked for business information, such as bank accounts, and even after informing the union the information had been accepted, the page was still closed down.
GoFundMe boasts that it is the world’s number one crowdfunding platform, but it only allows fundraisers to be created in 20 nations (not including Israel, Ukraine or Palestine) – meaning people in Gaza are reliant on intermediaries thousands of miles away if they want to receive donations.
All those interviewed for this story and other campaigners have endorsed a boycott of the platform. Sabbah says she has since begun using the Australian crowdfunding website Chuffed, which reviewed her documentation and swiftly permitted her to withdraw, allowing her to continue her group’s work in Gaza.
The platform says it advocates on behalf of campaigners to sort out verification issues with its payment providers to prevent pages from being frozen or refunded.
Chuffed general manager Jennie Smith said: “We’ve been helping campaigners migrate from GoFundMe to Chuffed by the thousands over the last year and have seen firsthand the devastation the shutting down of their GoFundMe campaigns causes.”
Yahya described life for his family in his makeshift tent. He walks miles every day to get water and wraps up his baby daughter for the cold winter nights, fearing they may not wake up in the morning.
He says his family may have escaped the enclave if GoFundMe had allowed him to withdraw the money he raised.
“I try not to think about losing our money,” Yahya said. “If I kept thinking about how terrible everything is, I wouldn’t be alive now!
“But it makes you feel like everyone is conspiring against us. They are leaving us to die slowly.”