Five key takeaways from US President Donald Trump’s Middle East trip | Donald Trump News
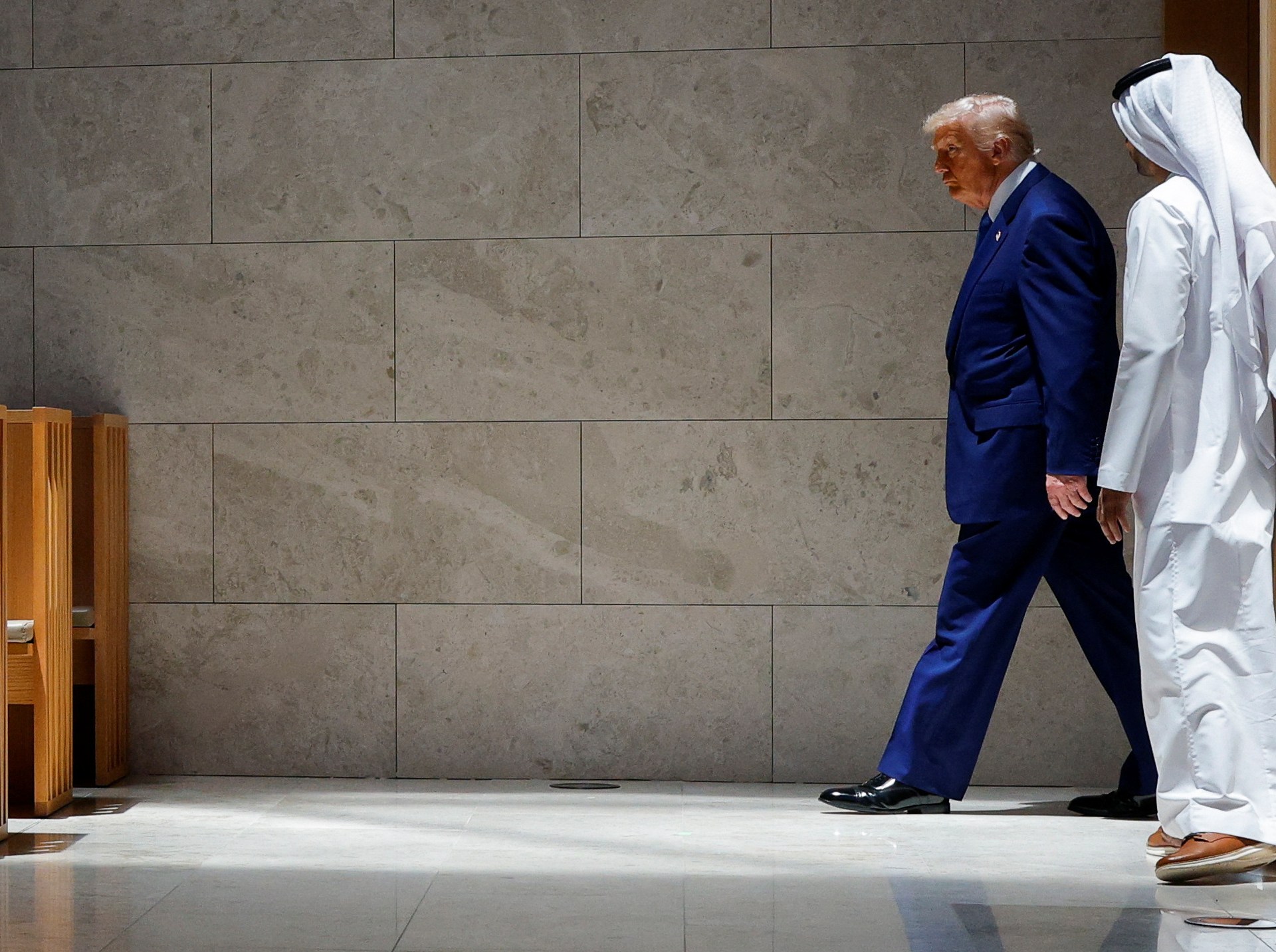
Washington, DC – Three days, three countries, hundreds of billions of dollars in investments and a geopolitical shift in the United States’s approach to the region: Donald Trump’s trip to the Middle East has been eventful.
This week, the United States president visited Saudi Arabia, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates in the first planned trip of his second presidency, after attending Pope Francis’s funeral last month.
Trump was visibly gleeful throughout the trip as he secured investments, criticised domestic political rivals and heaped praise on Gulf leaders. The word “historic” was used more than a few times by US officials to describe the visits.
With Trump returning to the White House, here are five key takeaways from his trip:
A rebuke of interventionism
Addressing an investment summit in Riyadh, Trump promoted a realist approach to the Middle East — one in which the US does not intervene in the affairs of other countries.
He took a swipe at neoconservatives who oversaw the US wars in Iraq and Afghanistan, as he lauded Gulf leaders for developing the region.
“This great transformation has not come from Western intervention or flying people in beautiful planes, giving you lectures on how to live and how to govern your own affairs,” he said.
“The gleaming marbles of Riyadh and Abu Dhabi were not created by the so-called nation-builders, neo-cons or liberal nonprofits like those who spent trillions and trillions of dollars failing to develop Kabul, Baghdad, so many other cities.”
Trump built his political brand with his “America First” slogan, calling for the US to focus on its own issues instead of helping — or bombing — foreign countries.
But his words at the investment summit marked a stern rebuke of the neo-cons who dominated Trump’s Republican Party a decade ago.
“In the end, the so-called nation-builders wrecked far more nations than they built, and the interventionists were intervening in complex societies that they did not even understand themselves,” Trump said.
Israel sidelined, but no Gaza solution
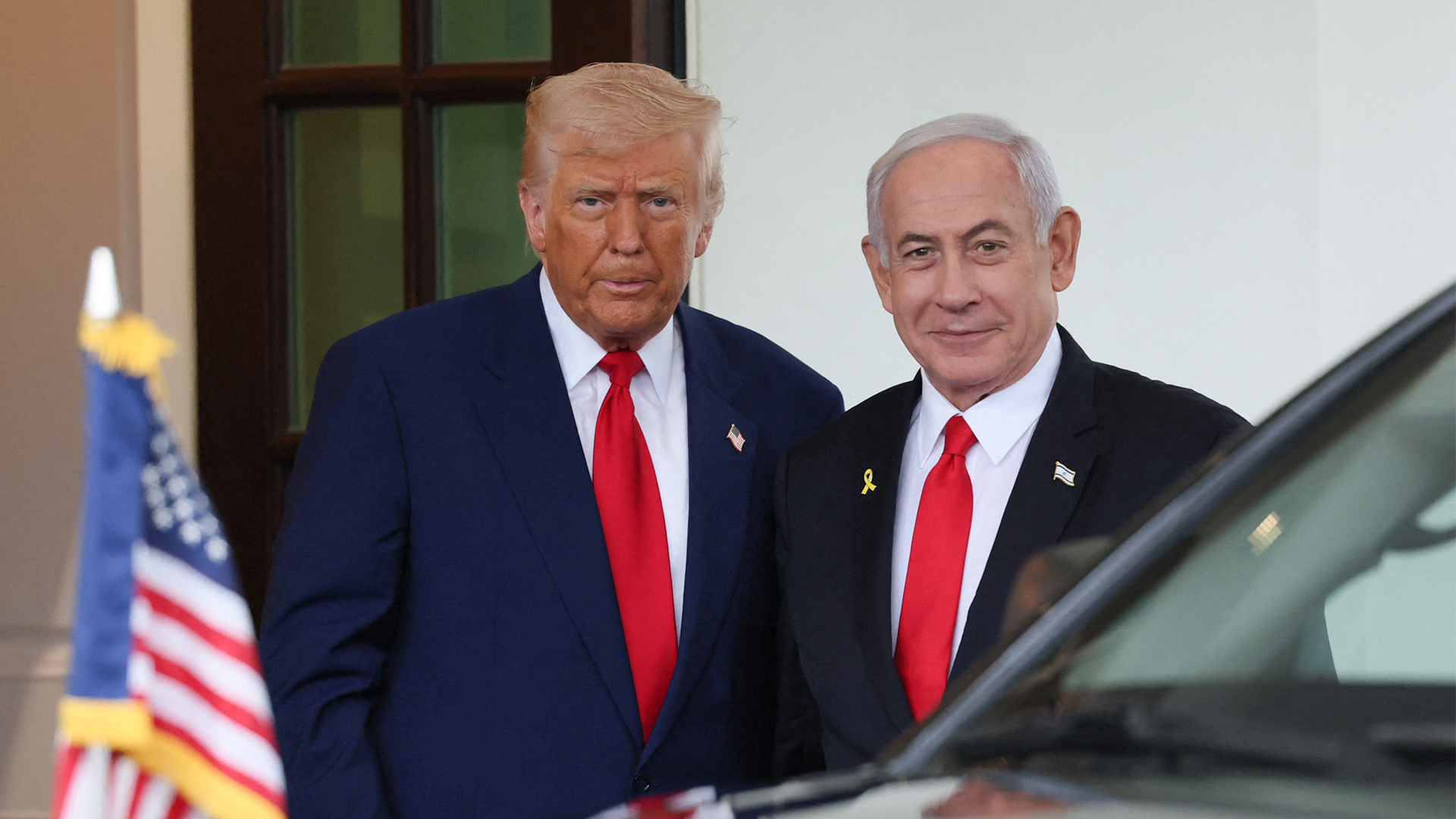
It is rare for US presidents to travel to the Middle East and not visit Israel, but Trump omitted the US ally from his itinerary as he toured the region.
Skipping Israel was seen as a reflection of the deteriorating ties between the US administration and the government of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu.
This week’s trip also came in the context of several moves perceived as evidence of the US marginalising Israel. The US has continued to hold talks with Israel’s rival Iran, announced a ceasefire with the Houthis in Yemen, and conducted unilateral negotiations to release Israeli soldier Edan Alexander, a US citizen, from Hamas captivity.
Moreover, while touring the Gulf, Trump did not use his remarks to prioritise the establishment of formal diplomatic ties between Saudi Arabia and Israel, which had been a top goal during his first term.
It remains unclear how Trump’s decisions will affect the “special relationship” between the two allies, but experts say it is becoming increasingly apparent that the US no longer views the Middle East solely through the lens of Israel.
“Is it a tactical problem for Netanyahu and the entire pro-Israel lobby? I think it is,” Khaled Elgindy, a visiting scholar at Georgetown University, said of Trump’s shift.
“It does throw a wrench in the machinery because it is a president who is showing openly daylight with Israeli decision-making, and not just in rhetoric, but acting on it — leaving Israel out of the process.”
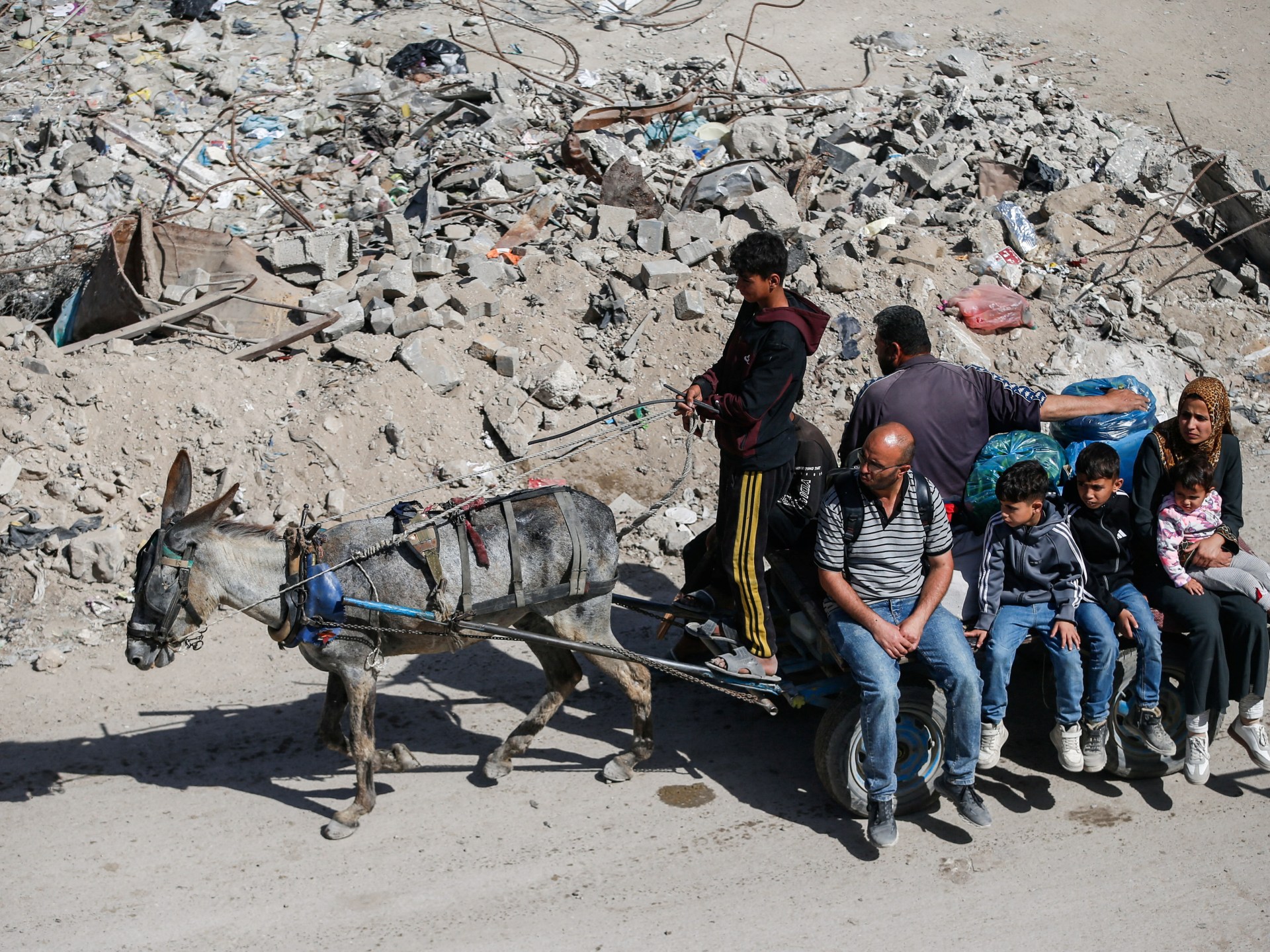
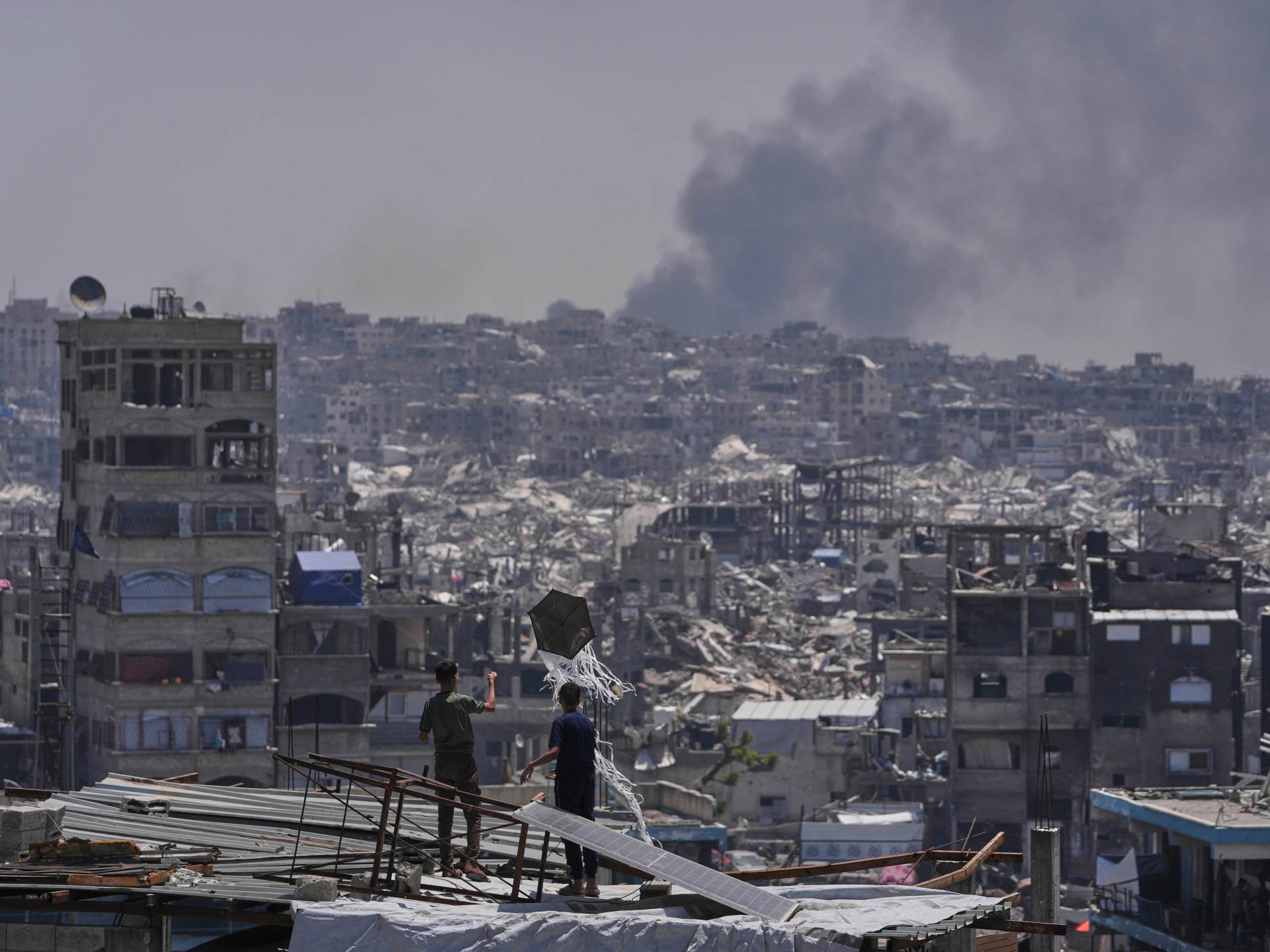
With that chasm emerging, some Palestinian rights advocates had hoped that the US president’s trip to the region would see Washington pursue a deal to end Israel’s war on Gaza.
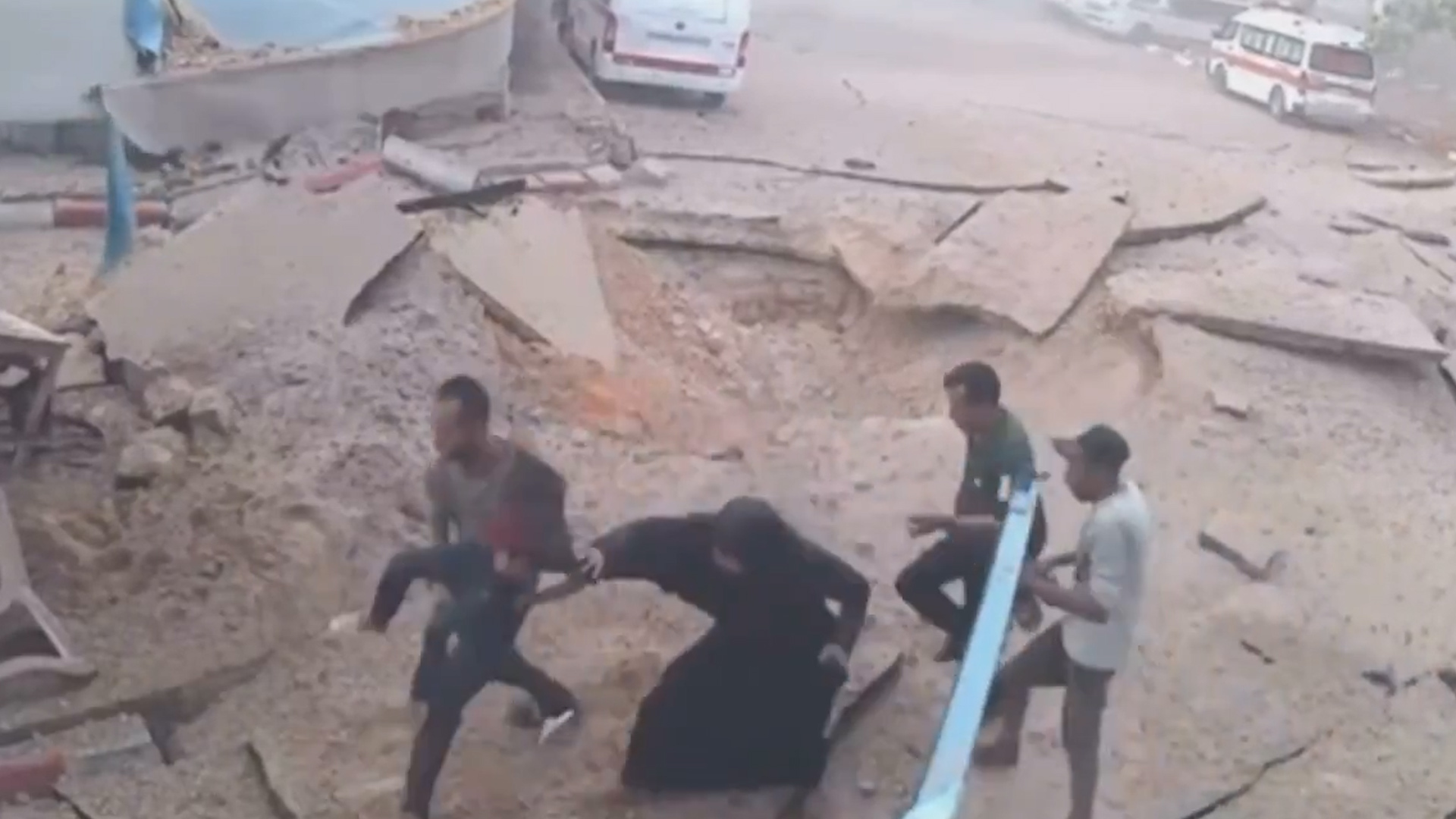
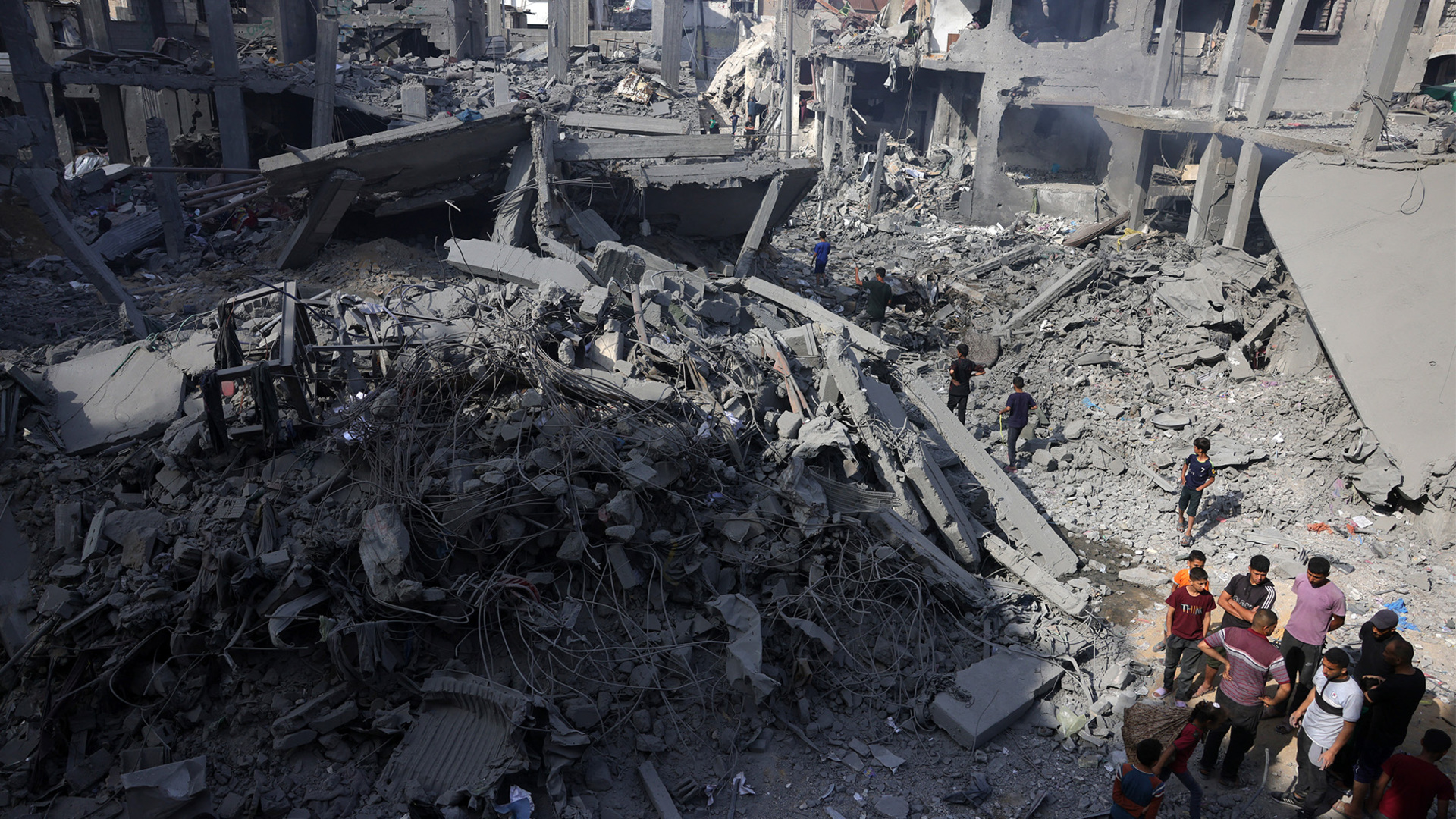
But as Trump marvelled at the luxurious buildings in the Gulf, Israel intensified its bombardment to destroy what’s left of the Palestinian territory.
No ceasefire was announced, despite reports of continuing talks in Doha. And Israel appears to be pushing forward with its plan to expand its assault on Gaza as it continues to block aid for the nearly two million people in the enclave, leading to fears of famine.
United Nations experts and rights groups have described the situation as a genocide.
But despite preaching “peace and prosperity” for both Israelis and Palestinians, Trump made no strong push to end the war during this week’s trip.
On Thursday, Trump suggested that he has not given up on the idea of depopulating Gaza and turning it over to the US — a proposal that legal experts say amounts to ethnic cleansing.
“I have concepts for Gaza that I think are very good. Make it a freedom zone,” he said. “Let the United States get involved, and make it just a freedom zone.”
Lifting Syria sanctions
In a move that surprised many observers, Trump announced from Riyadh that he will offer sanction relief to Syria, as the country emerges from a decade-plus civil war.
Trump also met with interim Syrian President Ahmad al-Sharaa and described him as a “young, attractive guy”.
A wholesale lifting of sanctions was not expected, in part because of Israel’s hostility to the new authorities in Syria. Israeli officials often describe al-Sharaa, who led al-Qaeda’s branch in Syria before severing ties with the group, as a “terrorist”.
But Trump said he made the decision to lift the economic penalties against Syria at the request of Saudi Arabia’s Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman and Turkiye’s President Recep Tayyip Erdogan.
“I will be ordering the cessation of sanctions against Syria in order to give them a chance at greatness,” the US president said.
The White House said on Wednesday that Trump had a list of requests for al-Sharaa, including establishing diplomatic relations with Israel and deporting “Palestinian terrorists”.
Removing US sanctions, which had been imposed on the government of former President Bashar al-Assad, is likely to be a boost for the new Syrian authorities, who are grappling with an ailing economy after years of conflict.
“Lifting sanctions on Syria represents a fundamental turning point,” Ibrahim Nafi Qushji, an economist, told Al Jazeera.
“The Syrian economy will transition from interacting with developing economies to integrating with more developed ones, potentially significantly reshaping trade and investment relations.”
A carrot and a stick for Iran
In Saudi Arabia, Trump declared that he wants a deal with Iran — and he wants it done quickly.
“We really want them to be a successful country,” the US president said of Iran.
“We want them to be a wonderful, safe, great country, but they cannot have a nuclear weapon. This is an offer that will not last forever. The time is right now for them to choose.”
Trump warned Iran that, if it rejects his “olive branch”, he would impose a “massive maximum pressure” against Tehran and choke off its oil exports.
Notably, Trump did not threaten explicit military action against Iran, a departure from his previous rhetoric. In late March, for instance, he told NBC News, “If they don’t make a deal, there will be bombing.”
Iran says it is not seeking nuclear weapons and would welcome a stringent monitoring programme of its nuclear facilities.
But Israel and some hawks want the Iranian nuclear programme completely dismantled, not just scaled back.
US and Iranian officials have held multiple rounds of talks this year, but Tehran says it has not received an official offer from Washington. And Trump officials have not explicitly indicated what the endgame of the talks is.
US envoy Steve Witkoff said last month that Iran “must stop and eliminate” uranium enrichment, but days earlier, he had suggested that enrichment should be brought down to civilian energy levels.
Several Gulf countries, including the three that Trump visited this week, have welcomed the nuclear negotiations, as relations between Iran and its Arab neighbours have grown more stable in recent years.
Investments, investments and more investments
Before entering politics, Trump was a real estate mogul who played up his celebrity persona as a mega-rich dealmaker. He appears to have brought that business mindset to the White House.
While in the wealthy Gulf region, Trump was in his element. He announced deals that would see Saudi Arabia, Qatar and the UAE buy US arms and invest in American firms. According to the White House, Trump secured a total of $2 trillion in investments from the Middle East during the trip.
And his administration is framing the deals as a major political and economic victory for Trump.
“While it took President Biden nearly four years to secure $1 trillion in investments, President Trump achieved this in his first month, with additional investment commitments continuing to roll in,” the White House said.
“President Trump is accelerating investment in America and securing fair trade deals around the world, paving the way for a new Golden Age of lasting prosperity for generations to come.”