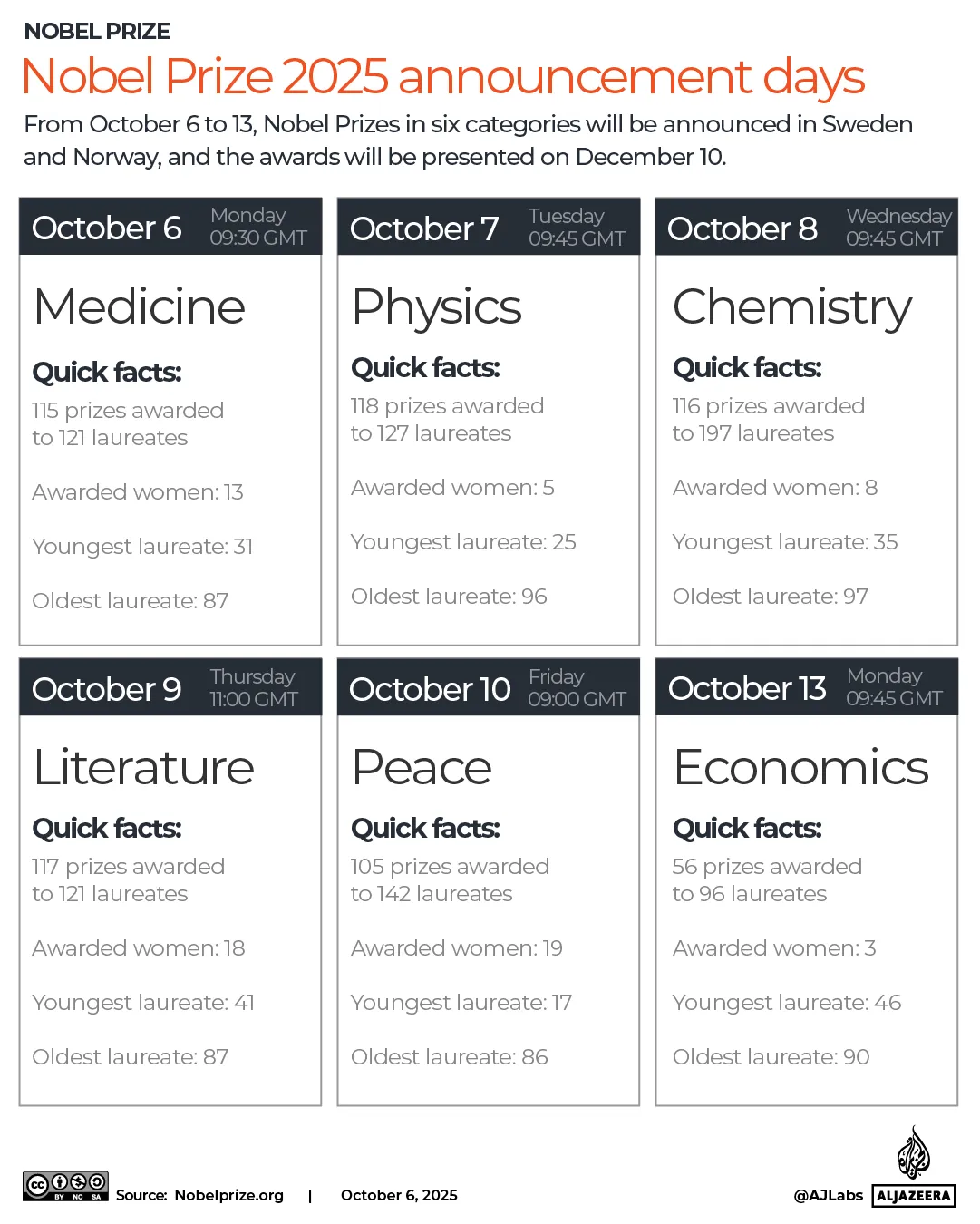
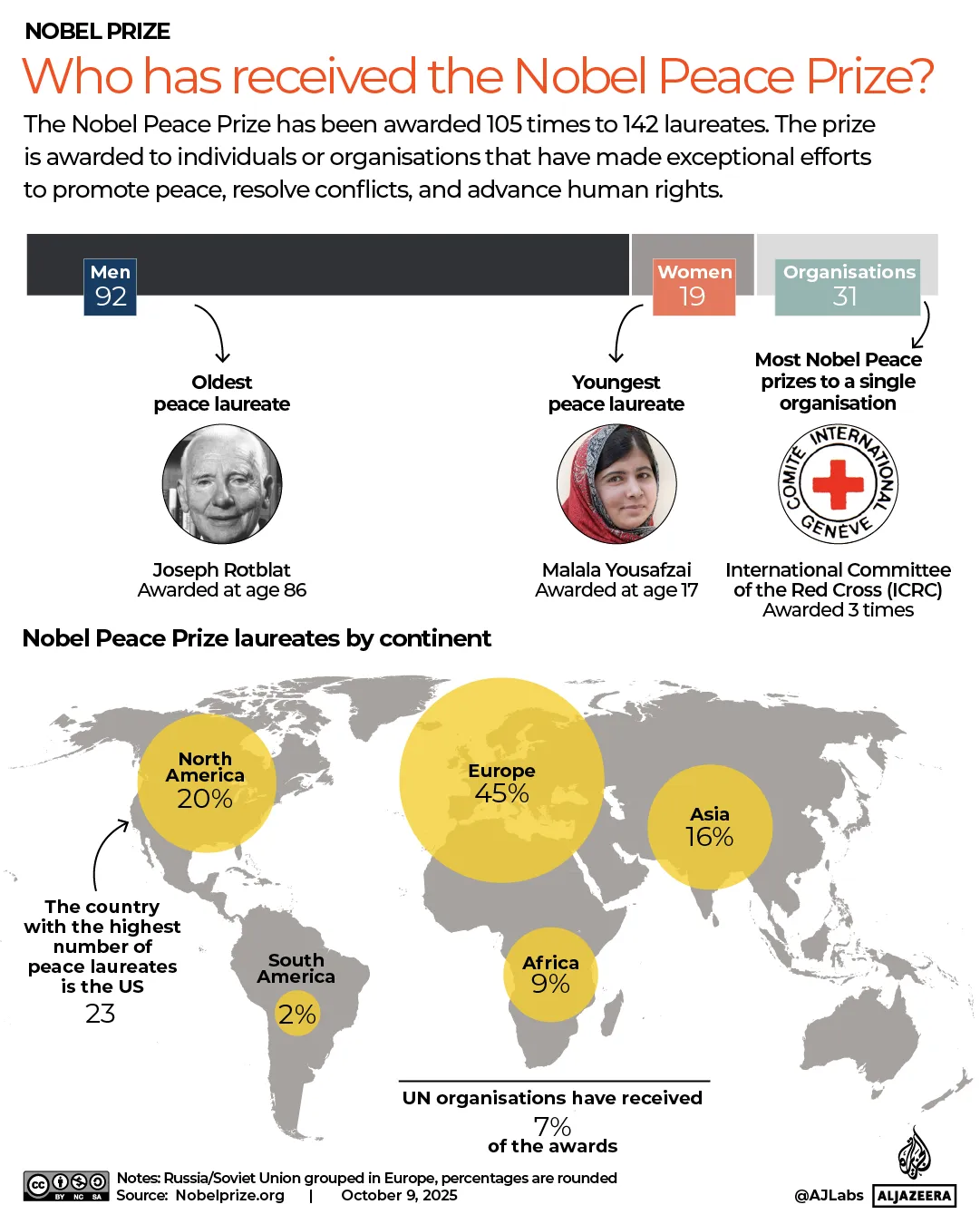
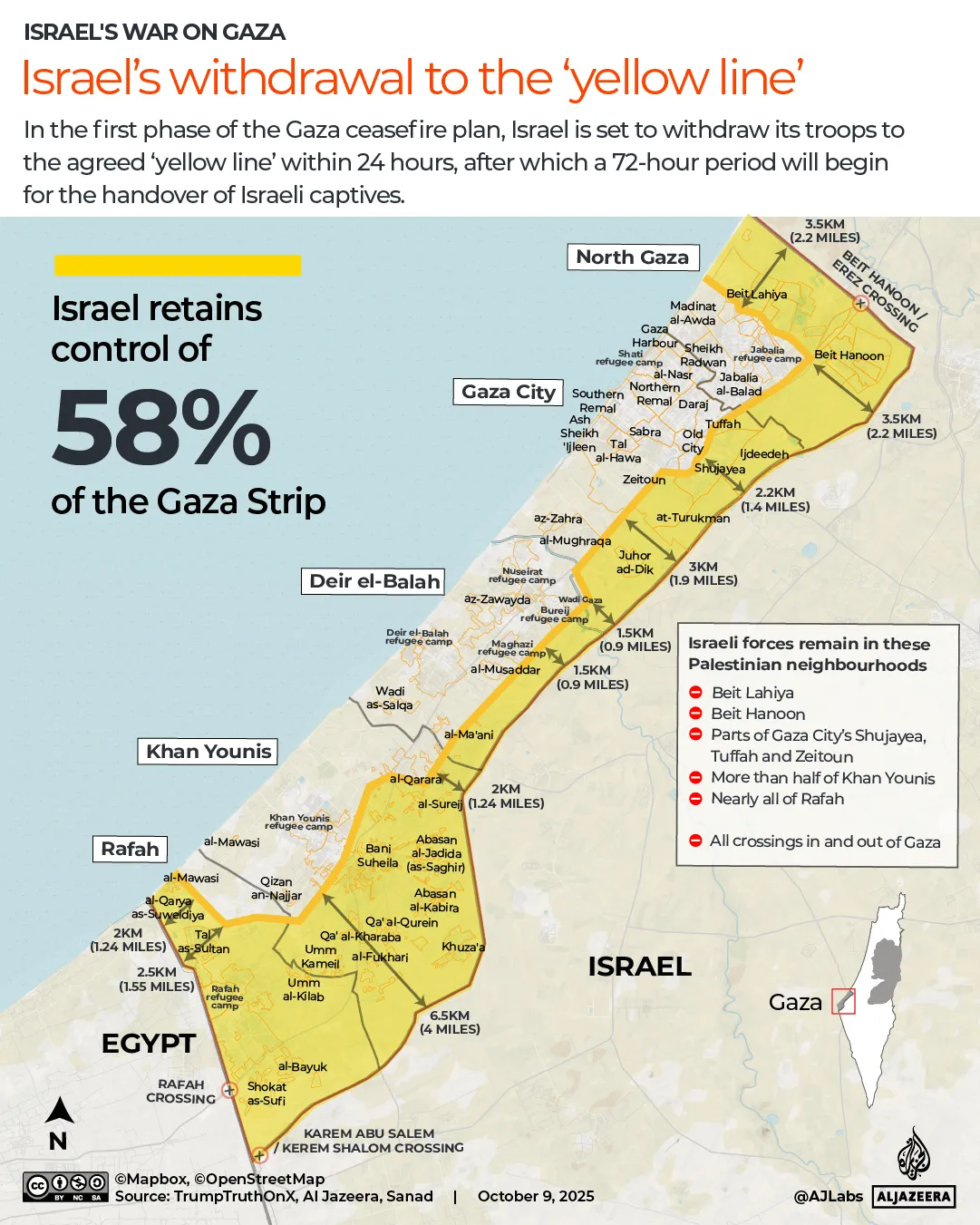
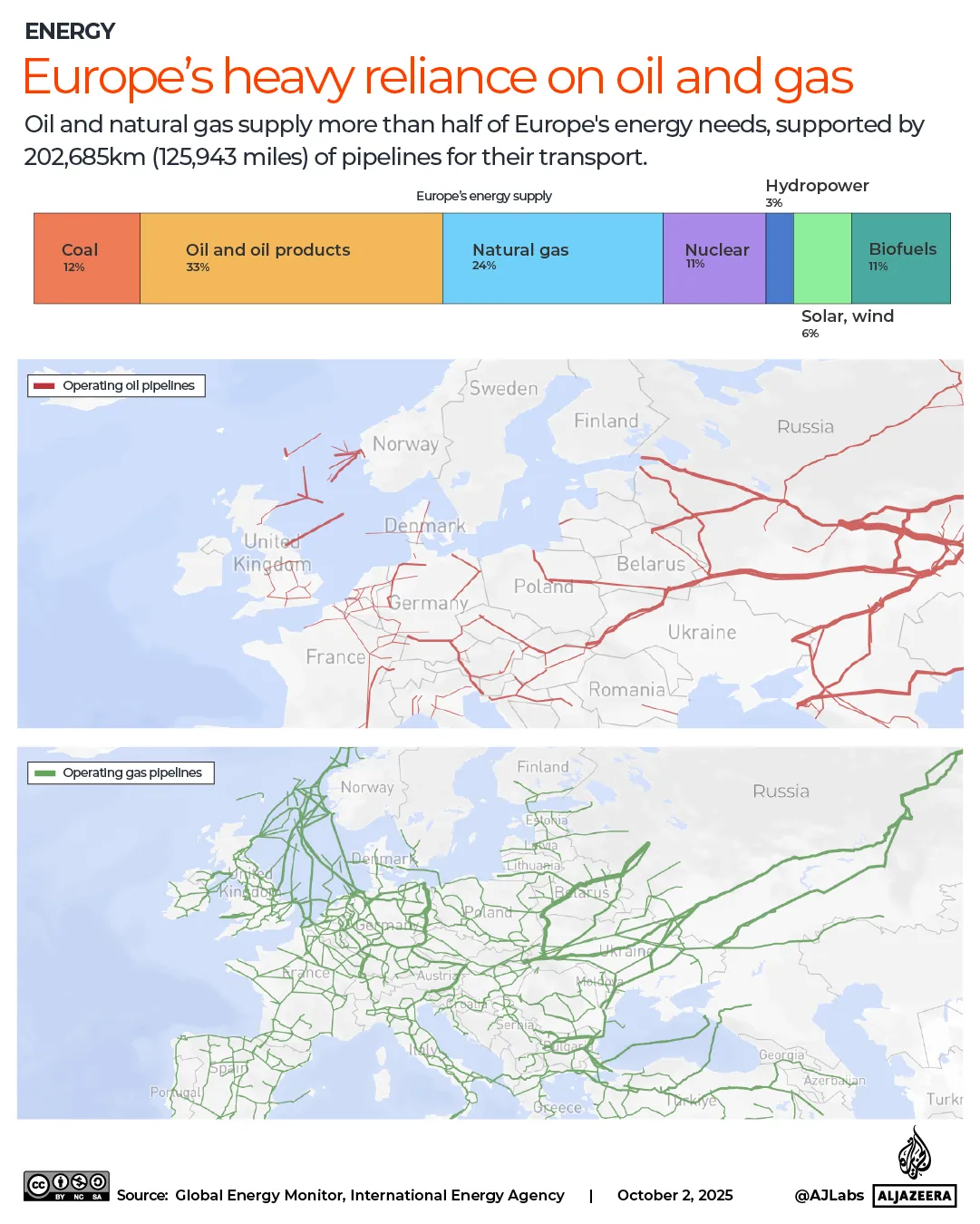
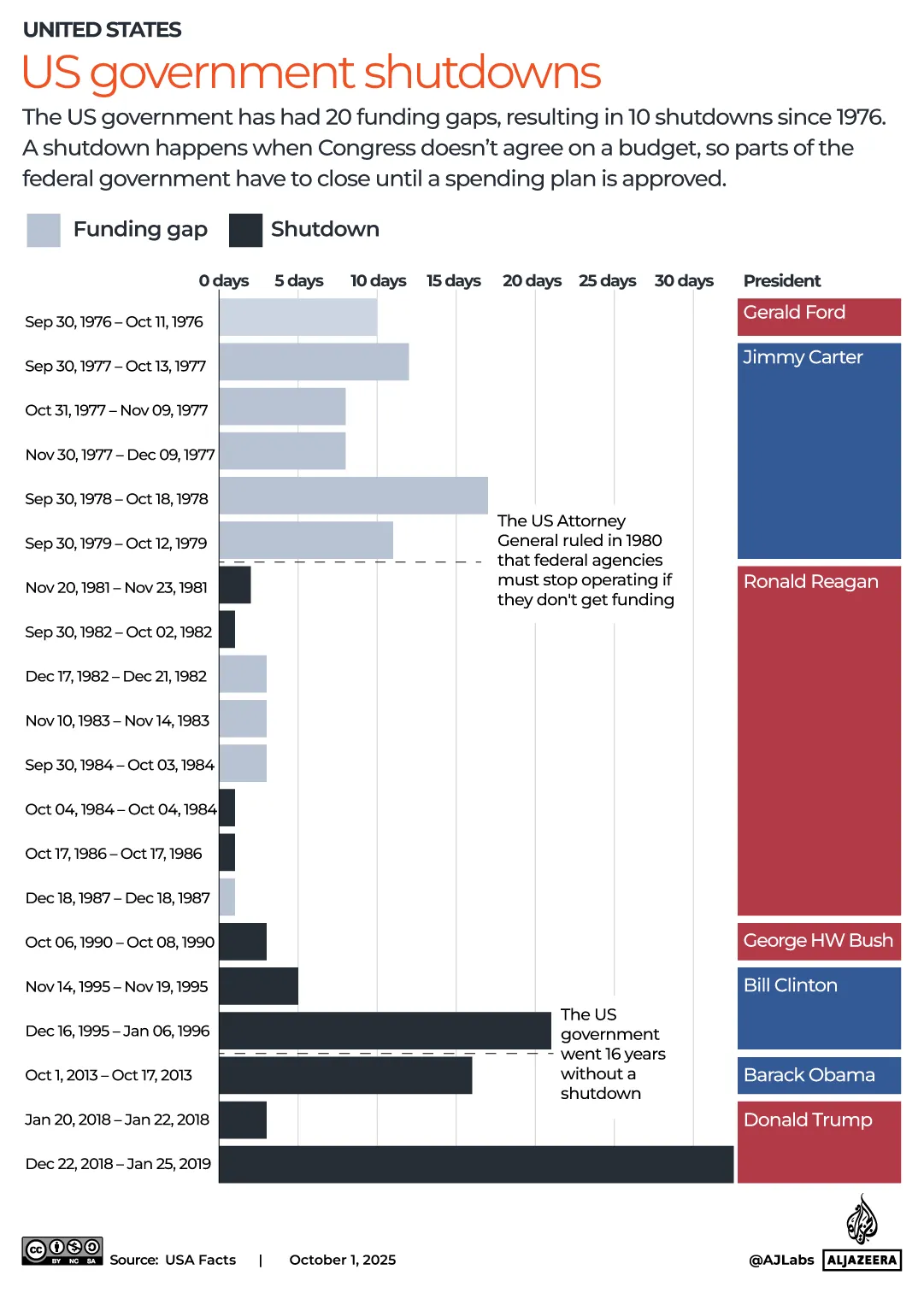
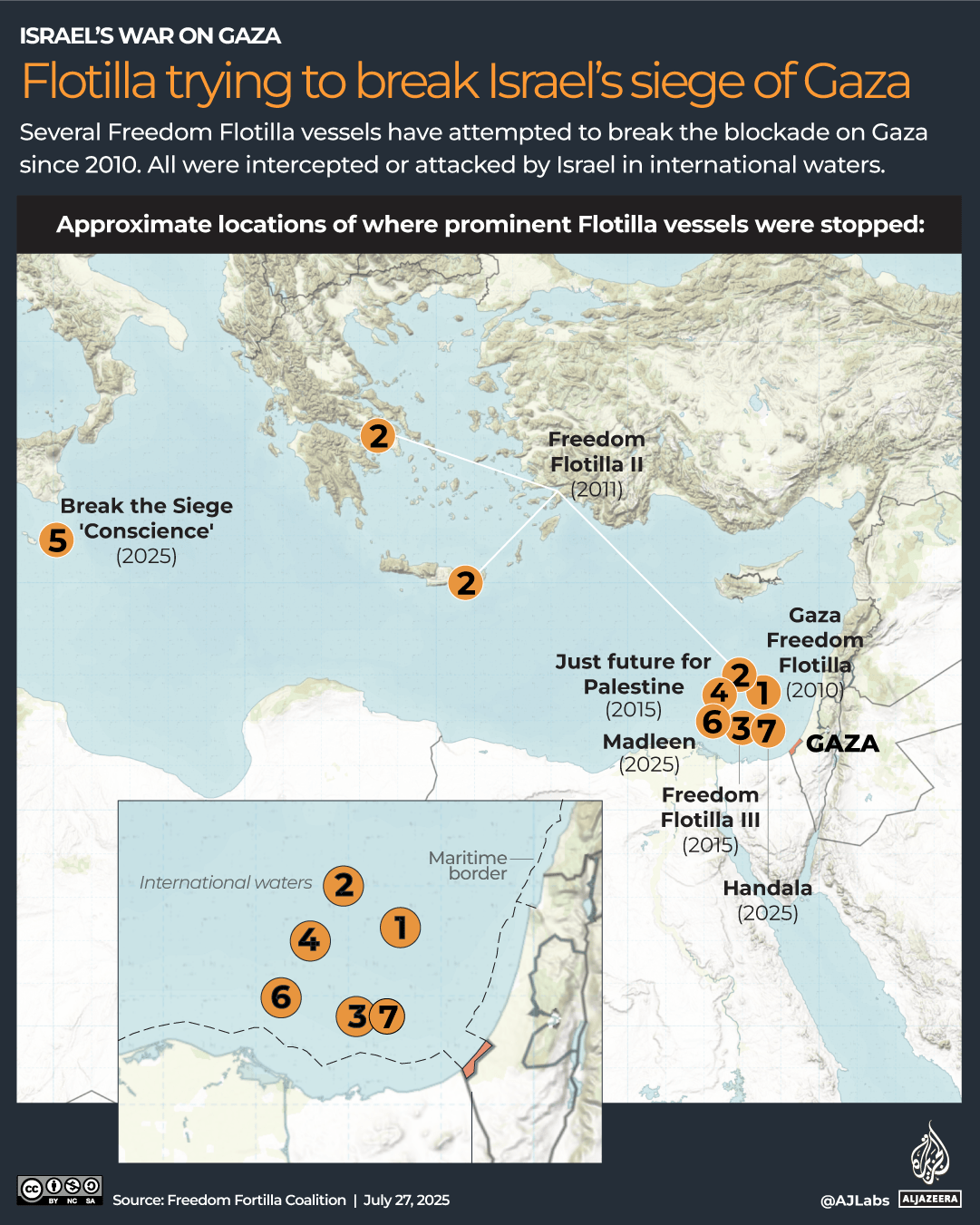
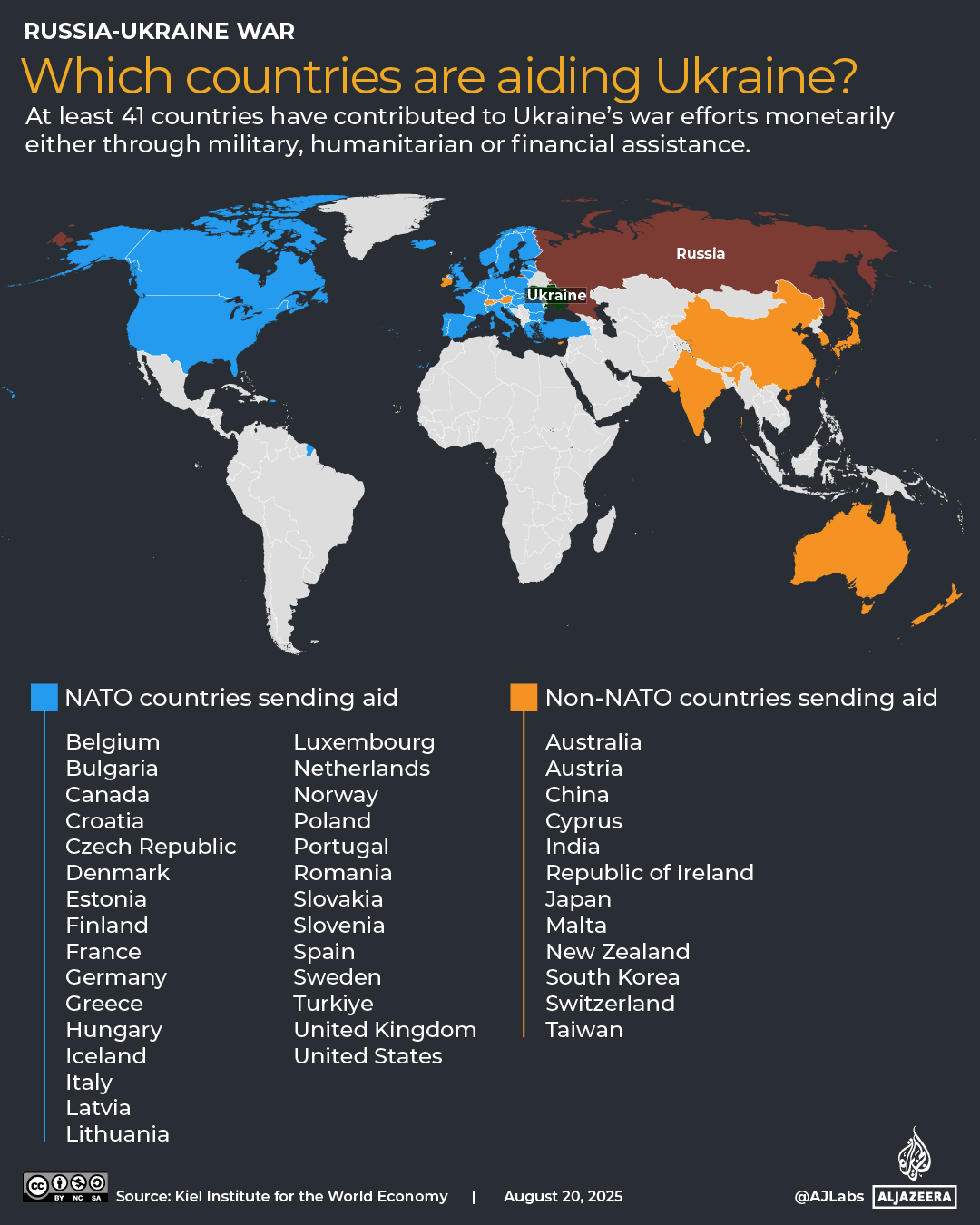
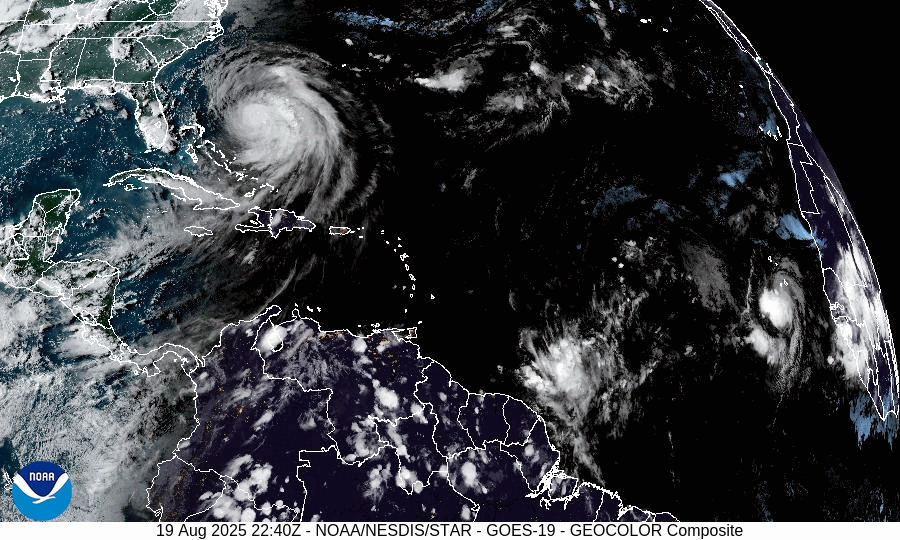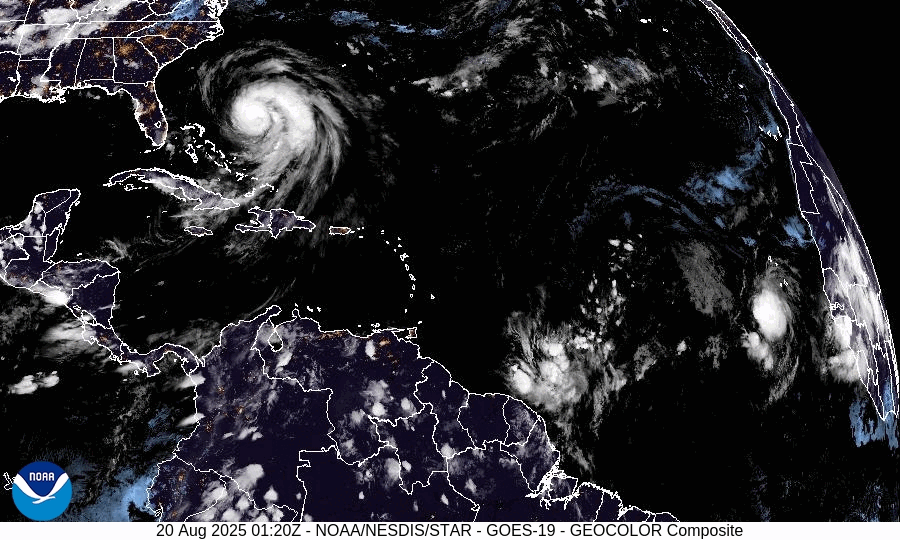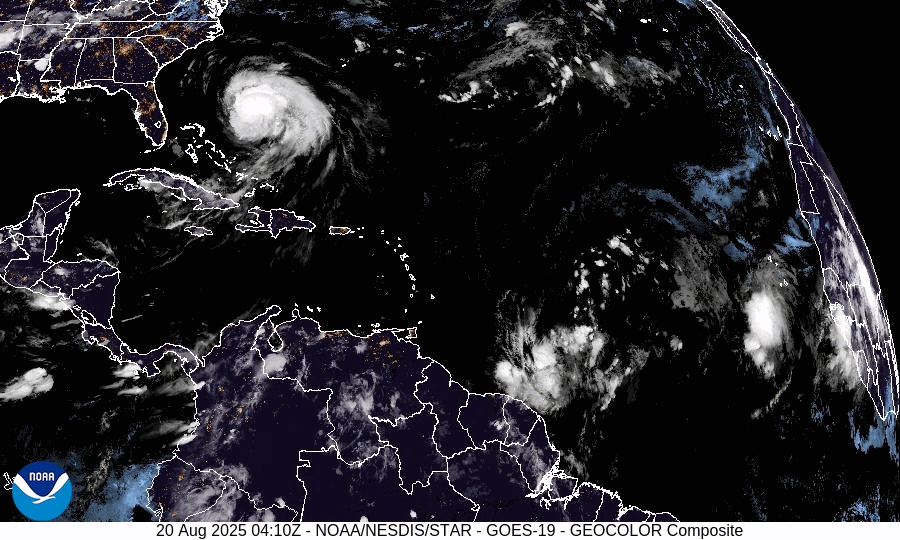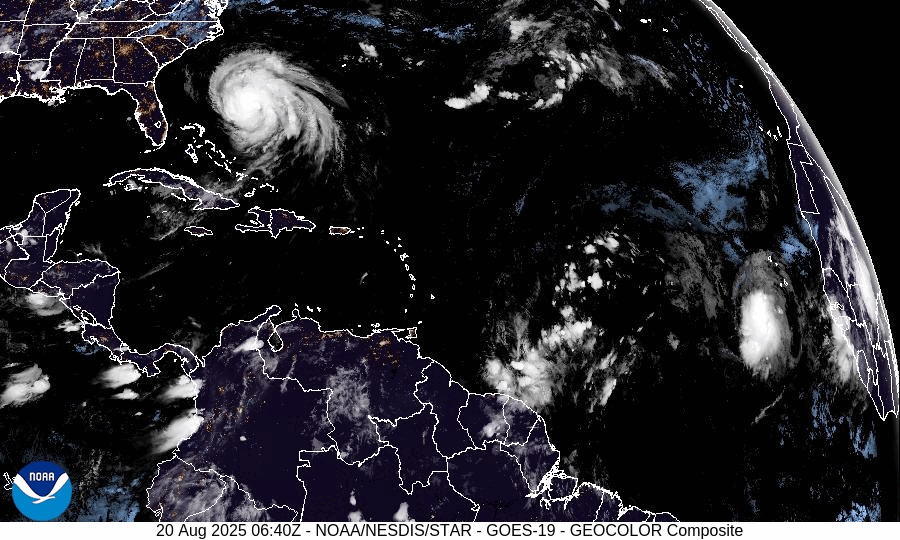
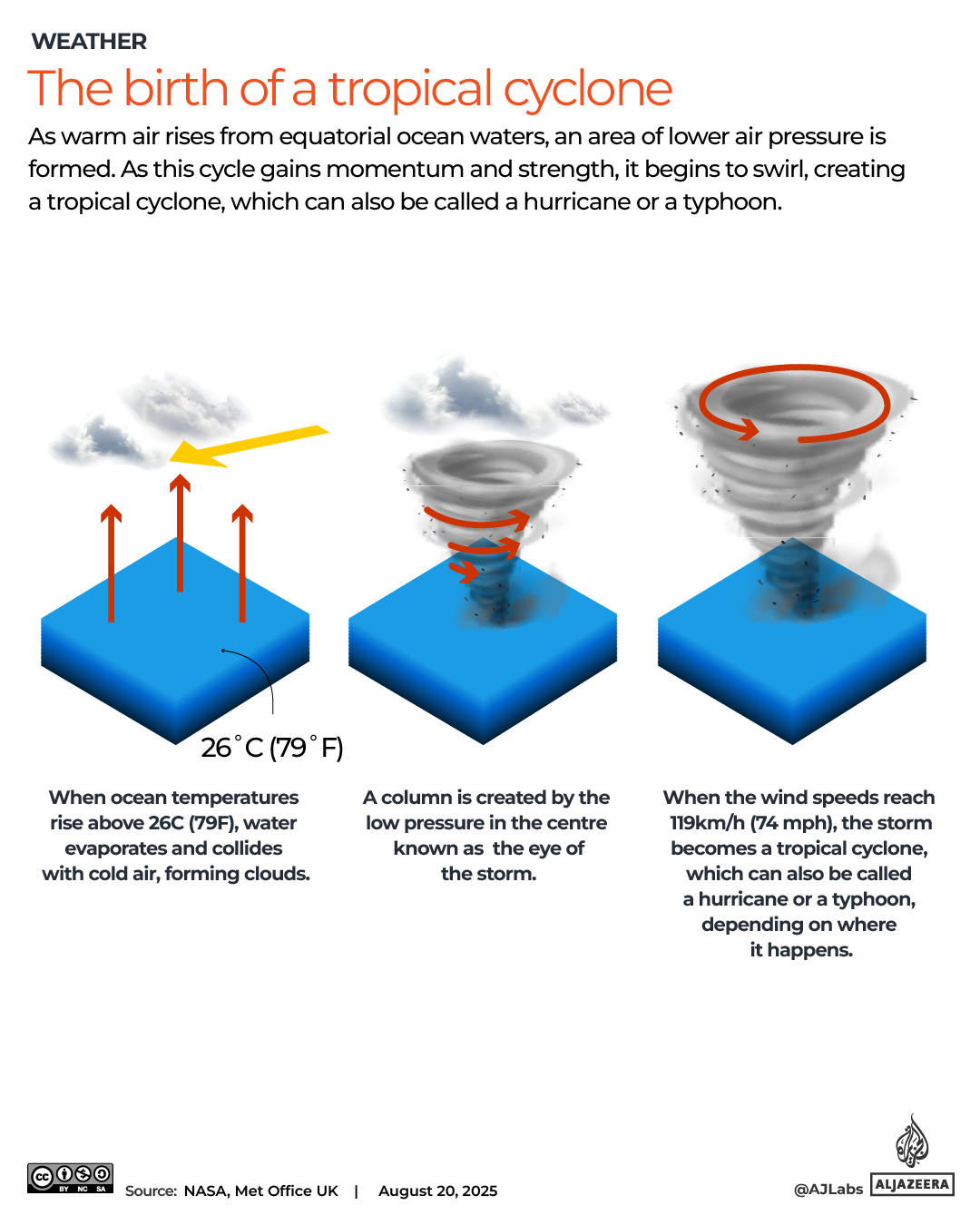
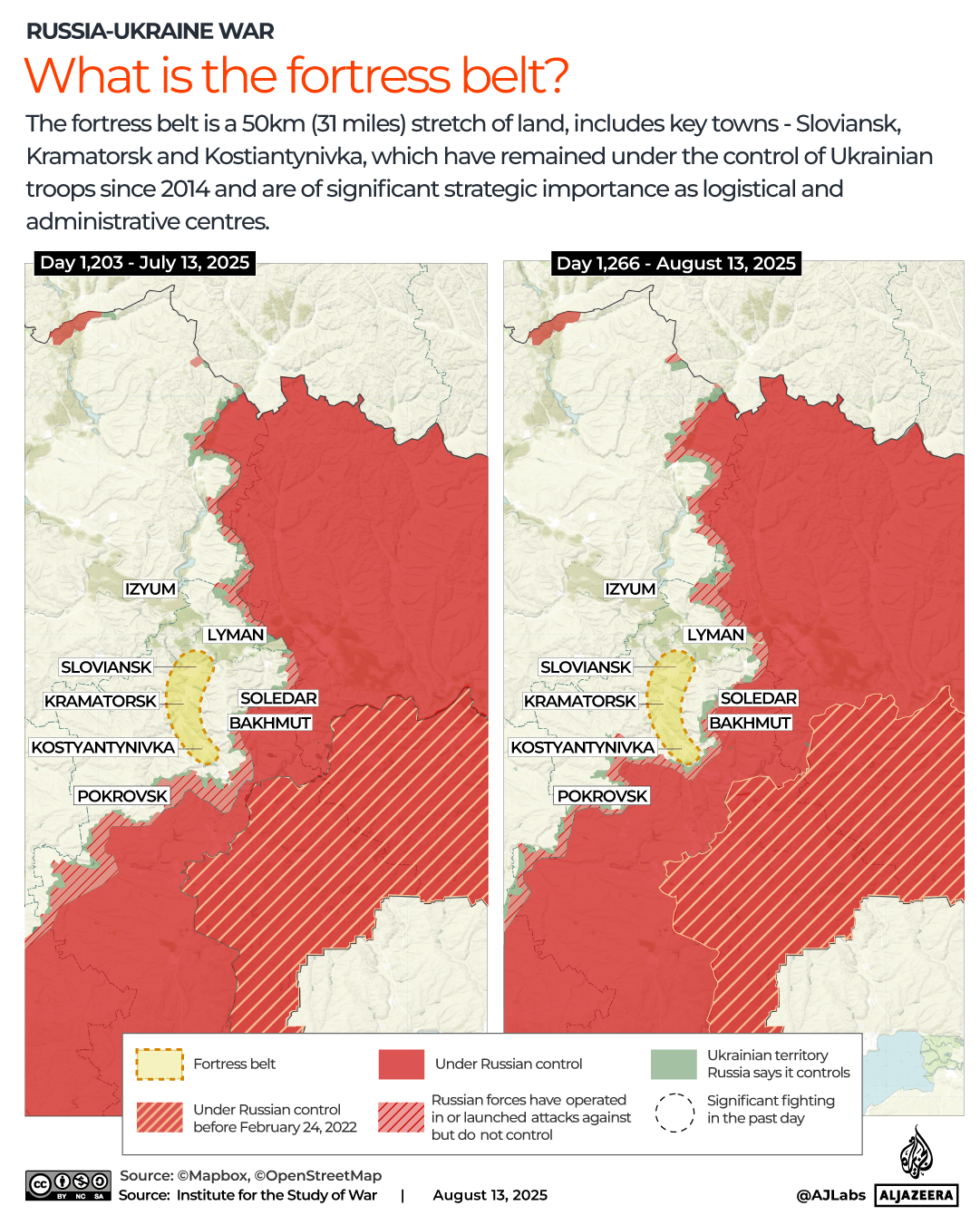
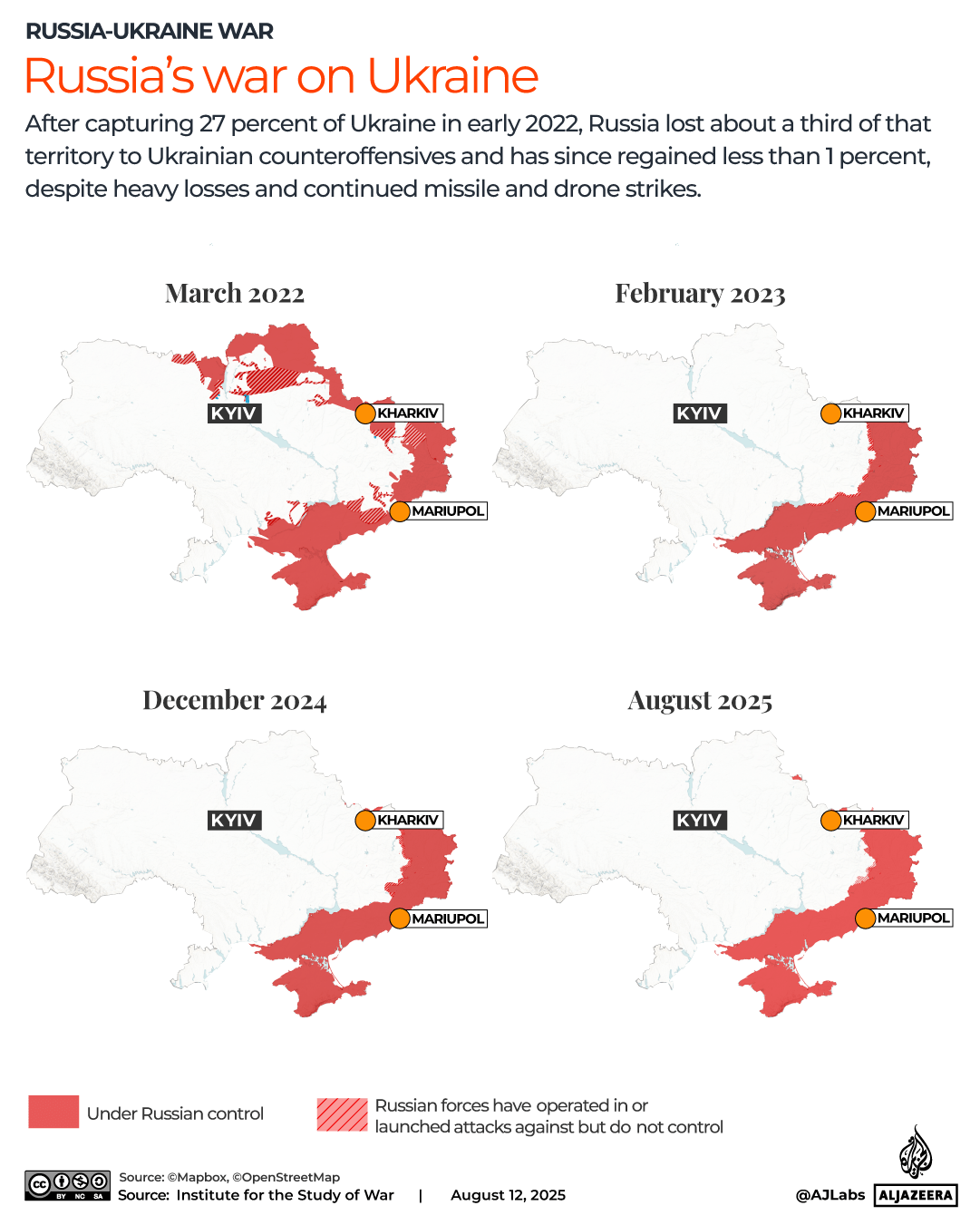
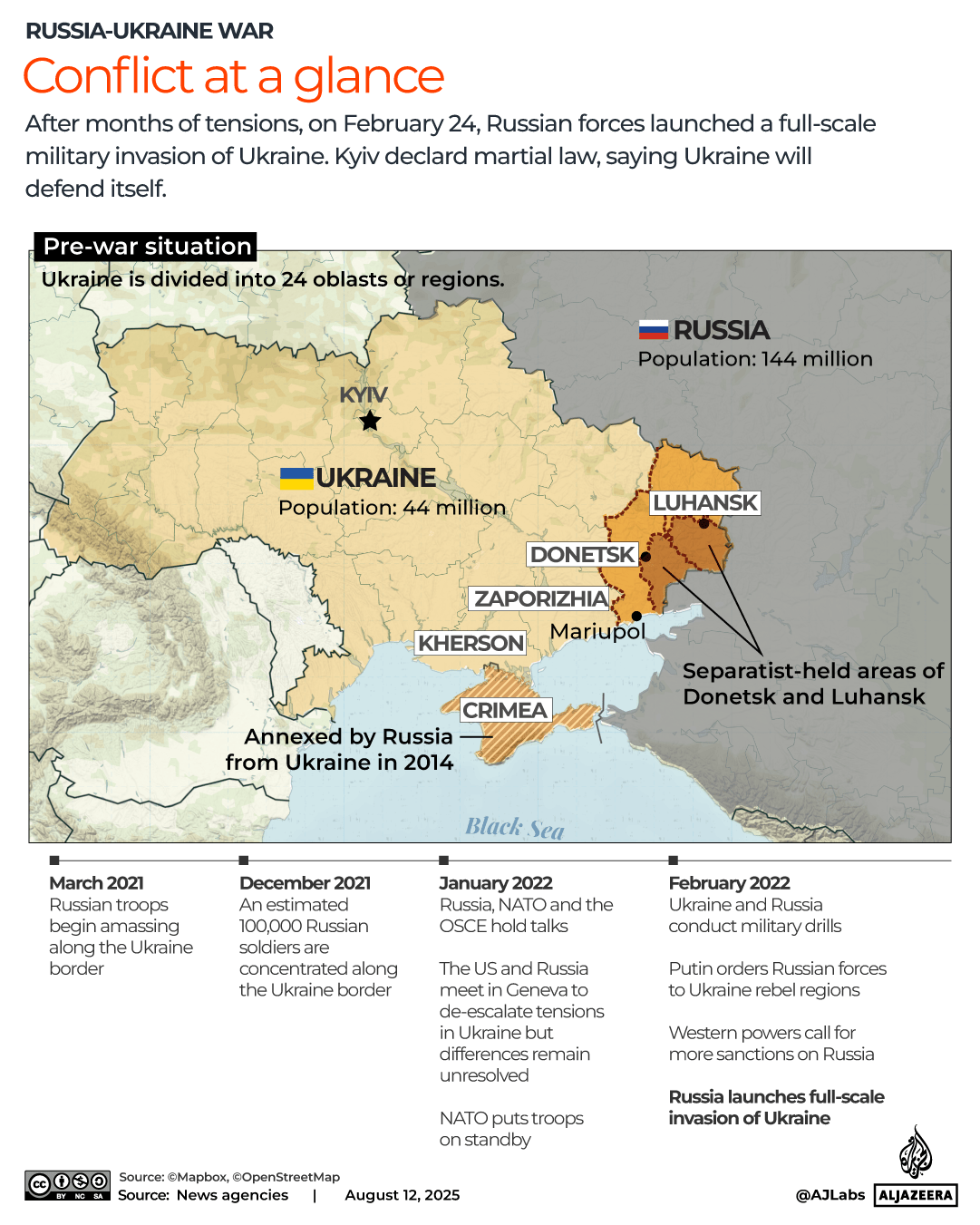
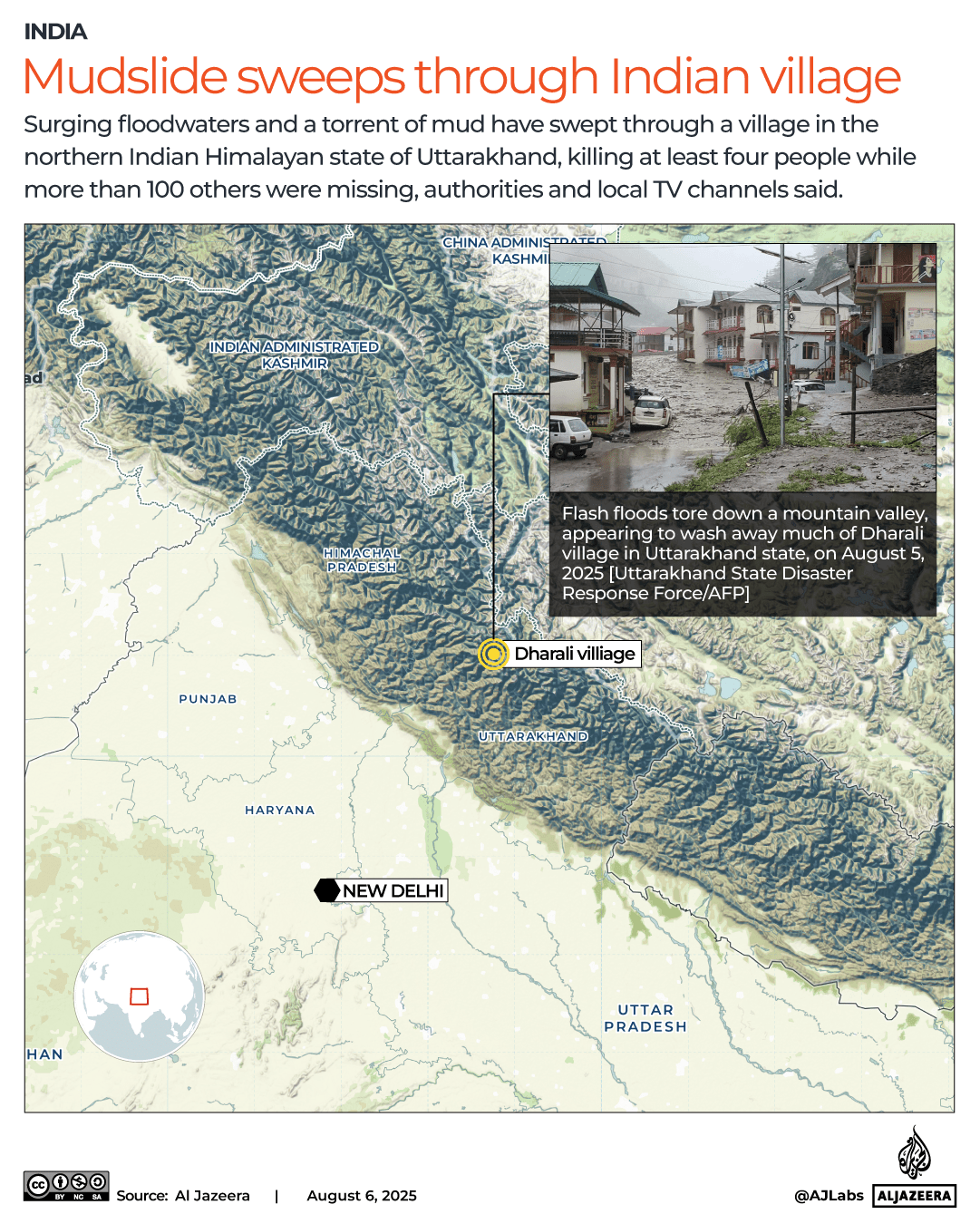
The pound has strengthened against most currencies in the last year, giving families more spending power if they’re heading overseas. Make sure you’re heading to one that offers good deals
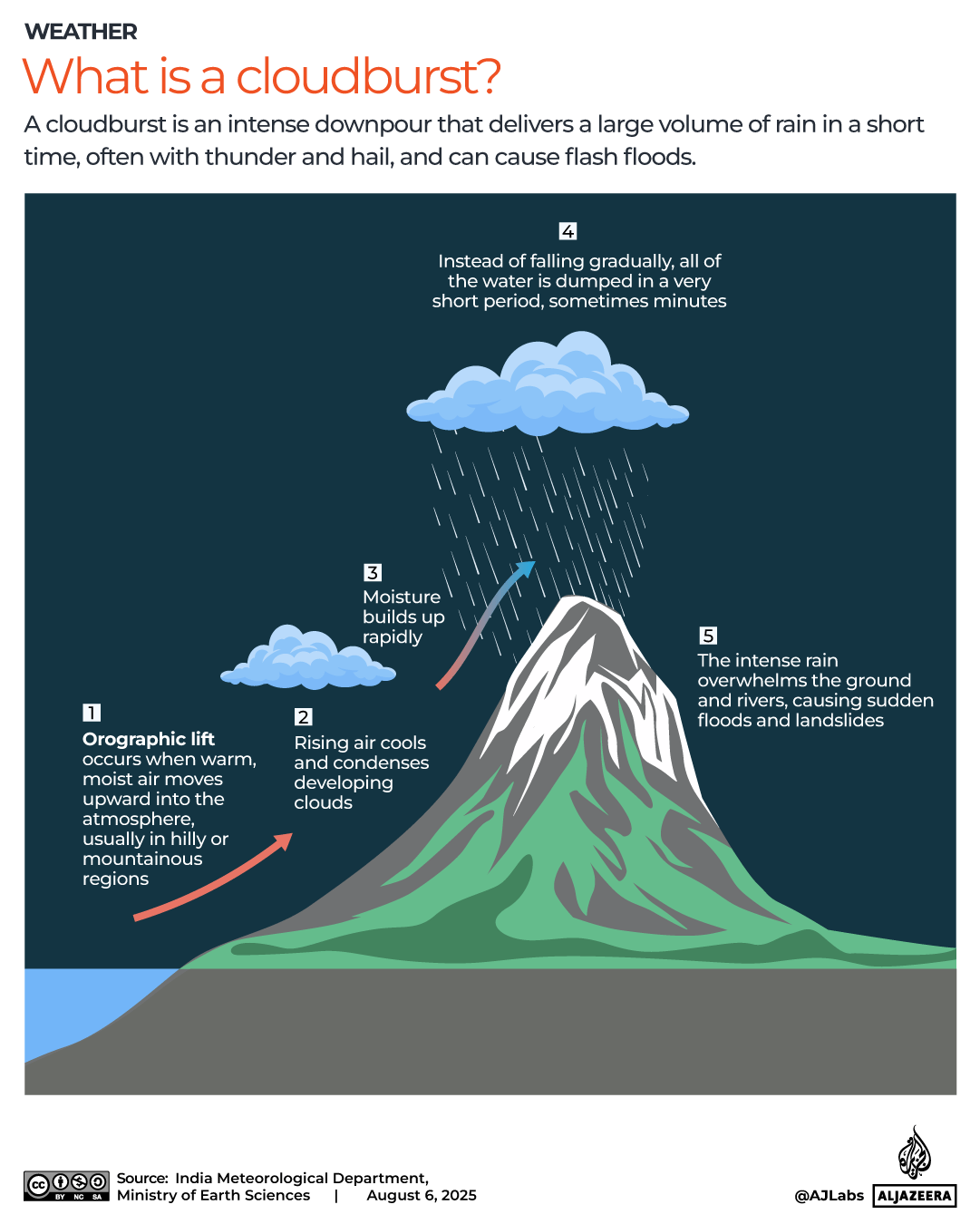
The world’s biggest rip-off destinations and those bucketlist spots perfect for a bargain break have been revealed.
When it comes to holidays, nothing sours the poolside mojito quicker than the feeling that your cash is disappearing too quickly.
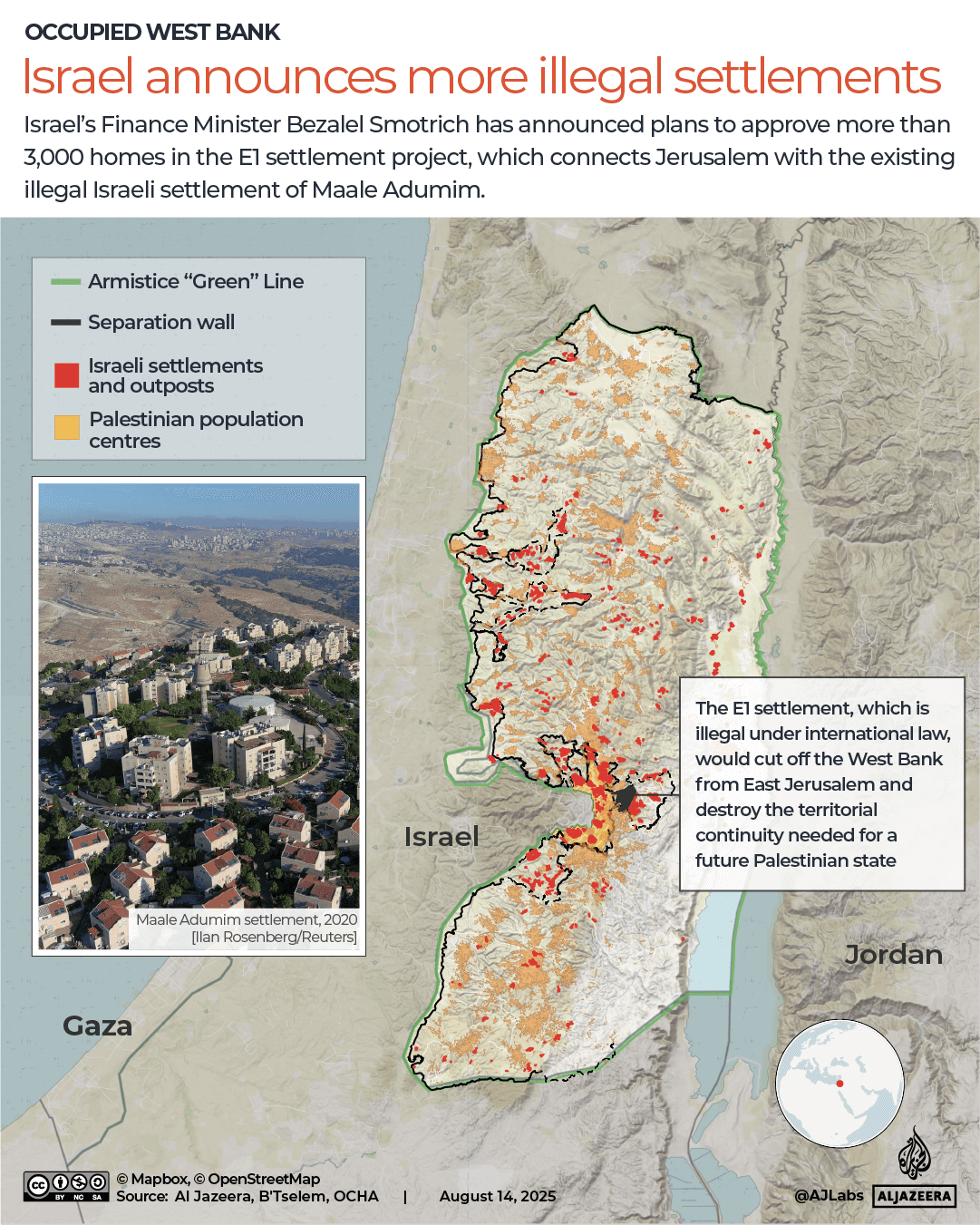
Thankfully, the Post Office has looked into where in the world the British pound delivers the most value for money this year. We’ve put the biggest bargain cities and outrageous rip-offs resorts on an interactive map, so you can book armed with all of the facts.
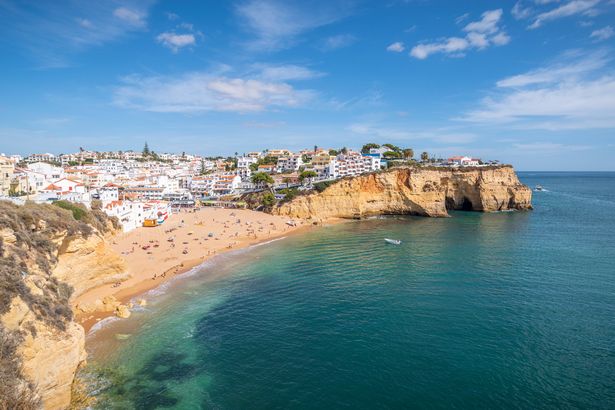
If you’re looking for the most bang for your buck, then head to the Algarve.
The Portugese coastal resort is a huge favourite with Brits, who take advantage of cheap, regular flights from across the UK to flock to the southern region en-masse each summer.
It’s basket of holiday goodies cost £58.95, 1.6 per cent less than in 2024. This is due to the rock-bottom cost of meals and drinks. The average cost of a three-course meal for two with wine in Albufeira weighed in at £40.33 – the lowest recorded across the 47 destinations surveyed (figure 9) and one third the cost in New York (£128.27).
The Algarve is one of 19 resorts or cities that got cheaper this year than last, according to Post Office research. Others to do so include Delhi, India; Phuket, Thailand; Spain’s Costa del Sol and Prague in the Czech Republic.
If you’re keen to stay in Europe, then Prague is a good bet. Far more than just stag-dos and strip clubs, the former Soviet city is enriched by a huge amount of history, art, and music.
The Czech capital’s basket of holiday goods cost £75.92 this year, a significant price fall of over 20 per cent compared to 2024.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, the biggest deals can be found a little further away from the UK, although bargain-hungry holidaymakers will have to factor in the cost of getting to these destinations when choosing where to go.
Cape Town in South Africa is the second cheapest destination looked at this year, with a basket of essentials costing £59.84. This is a great destination for Southern Hemisphere wine buffs as a glass of grape costs just £2.07; a fifth of the price it’ll set you back in New York.
Japan’s capital city, Tokyo, has been massively popular with Brits over the past year, thanks to the very favourable exchange rate.
A glass of wine and a bottle of beer can be purchased there for the equivalent of just over a fiver.
One destination to keep an eye on is Delhi. At £69.52, prices in the Indian city have dropped 10.7 per cent. Although alcohol prices there are a little on the steep side, soft drinks, water and food won’t lighten your wallet too much.
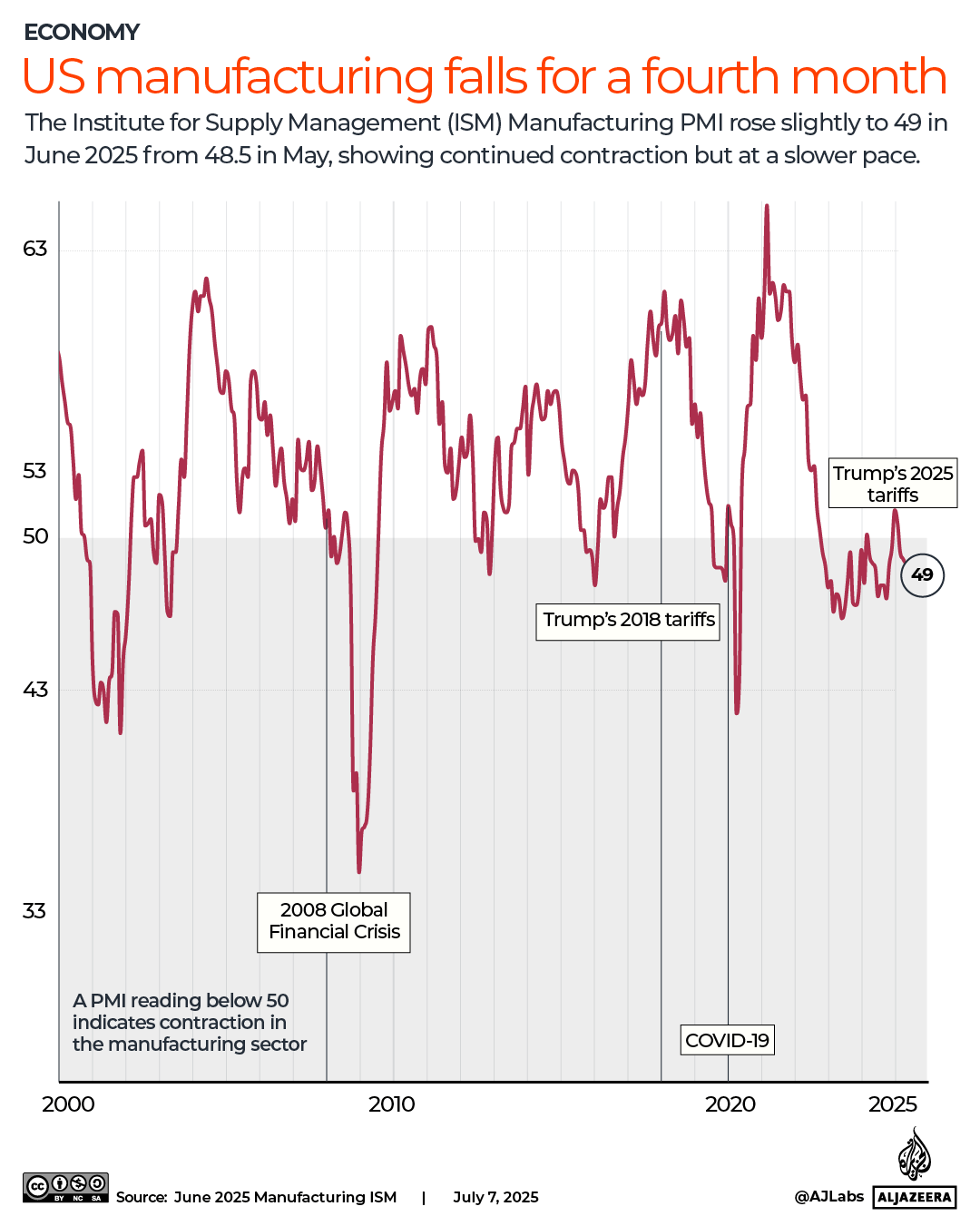
At the other end of the scale, New York is the most expensive of 47 destinations surveyed, with a barometer total of £167.85 – a rise of 15.6 per cent year-on-year. Not only will you have to spend upwards of £7 for a beer in the Big Apple, you’ll be expected to tip generously on top of that.
The eye-watering continues in Hawaii, the second most expensive destination on the list and the home of £9.18 insect repellent, and in Nice, France. Head to the French city, and you’ll find yourself being stingy with the suncream, as a bottle costs close to £17.
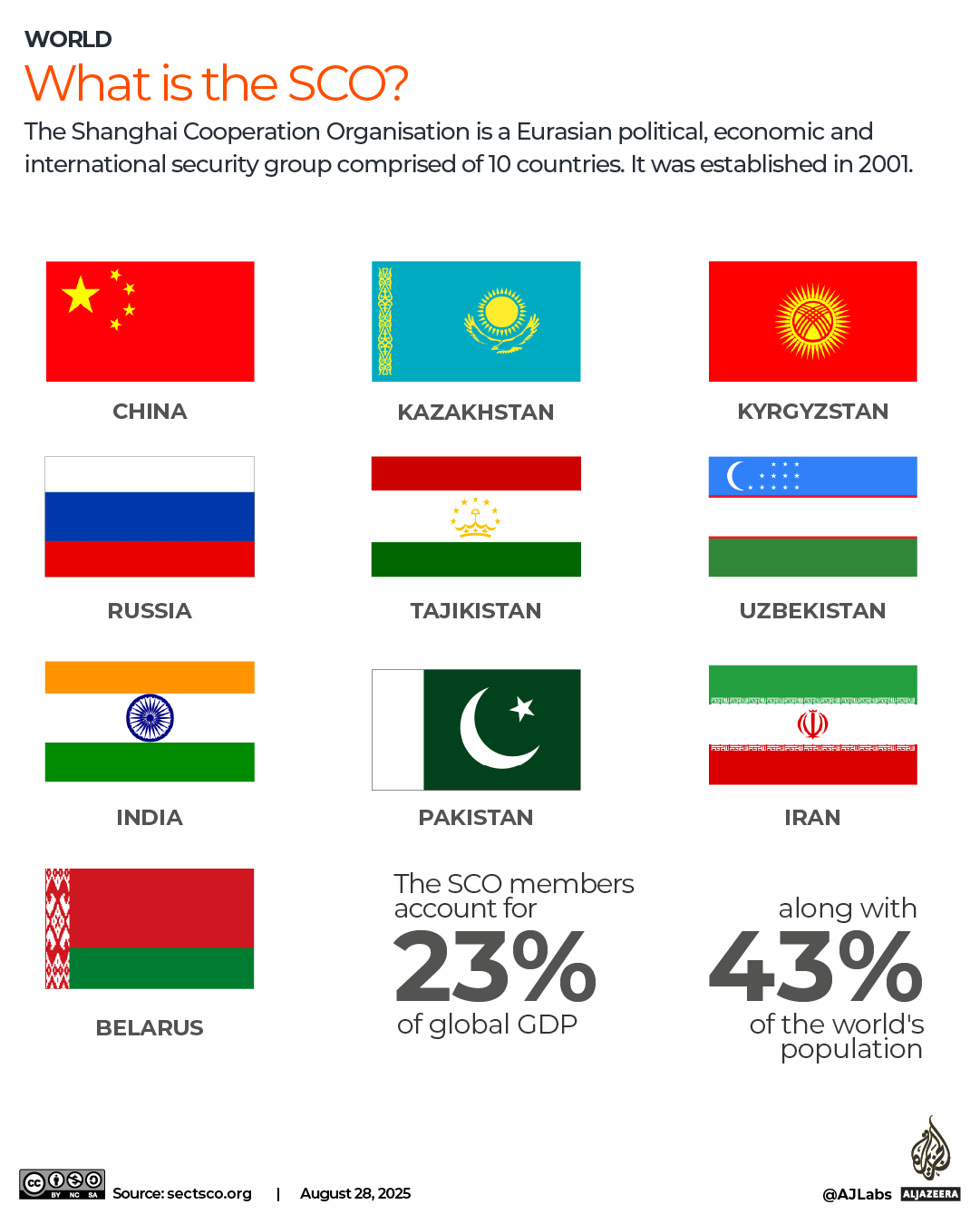
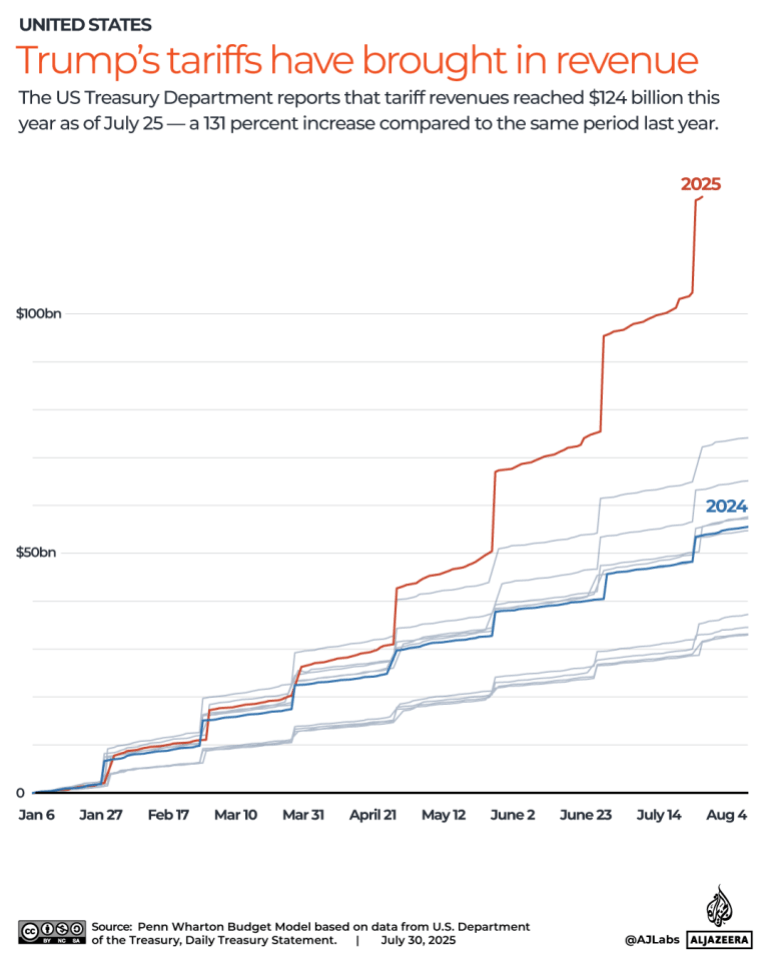
While the world has been in turmoil since Donald Trump returned to the White House (and perhaps was before), sterling remains strong against many other currencies.
Over three-quarters of Post Office’s top 30 currencies – including the euro and most other European currencies – have
weakened since last March. This could provide holidaymakers with a big incentive to choose destinations where sterling will provide more ‘bang for their buck.
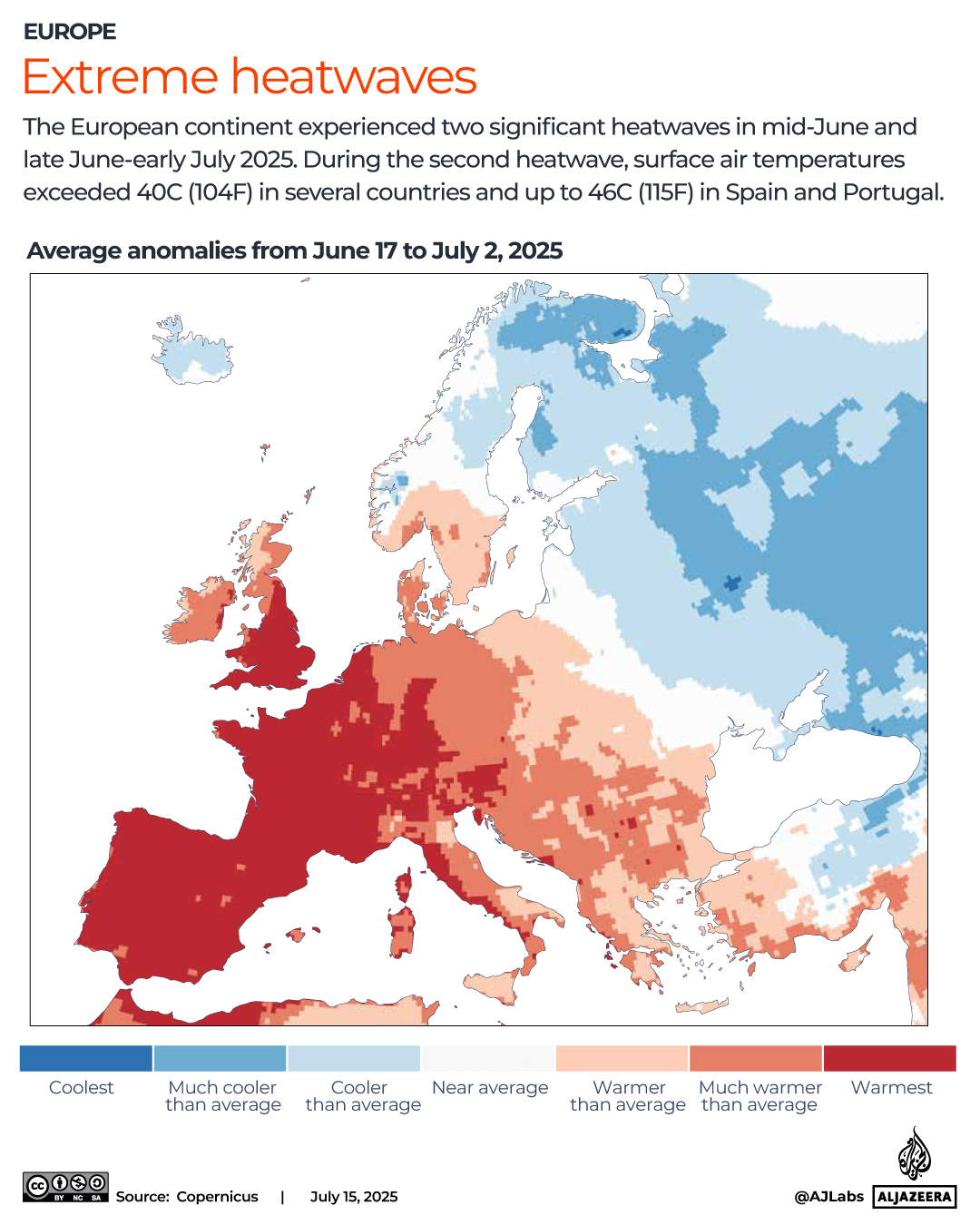
Appetite for traveling remains high and is growing. Three-in-five (60 per cent) of Brits surveyed about their holiday plans for the coming year told Post Office Travel Money that they will be travelling abroad – up from 51 per cent who were asked the same question a year ago.
Almost three-quarters (73 per cent) of them will holiday in Europe and most (95 per cent) will be making a repeat journey to a European destination.
Although a big majority are planning to get away this year, most share a desire to keep things as cheap and cheerful as possible.
Travelling away from busy periods is regarded as the best way to make travelling abroad more affordable, with two-in-five holidaymakers prepared to swap peak season travel for cheaper times of the year.
More than a quarter of those questioned say they will book cheaper accommodation (27 per cent), take fewer holidays (27 per cent) or go to a destination that costs less (26 per cent).
Do you have a story to tell us? Email us at [email protected]