United States House Republicans’ “big, beautiful bill”, a wide-ranging tax and spending legislation, is at a crucial moment.
The nearly 400-page legislation proposes sweeping changes which include extending the 2017 tax cuts, slashing taxes for businesses and individuals, and enacting deep cuts to social programmes like Medicaid and SNAP.
While Republicans tout the bill as a boon for economic growth and middle-class relief, nonpartisan analysts warn it could add trillions to the national debt and strip millions of Americans of medical and food assistance.
The bill will be voted on by the House Budget Committee today and, if passed, will be voted on the floor next week.
The most substantive part of the bill is an extension of the 2017 tax cuts. The tax bill would add at least an additional $2.5 trillion to the national deficit over the next 10 years and decrease federal tax revenue by roughly $4 trillion by 2034.
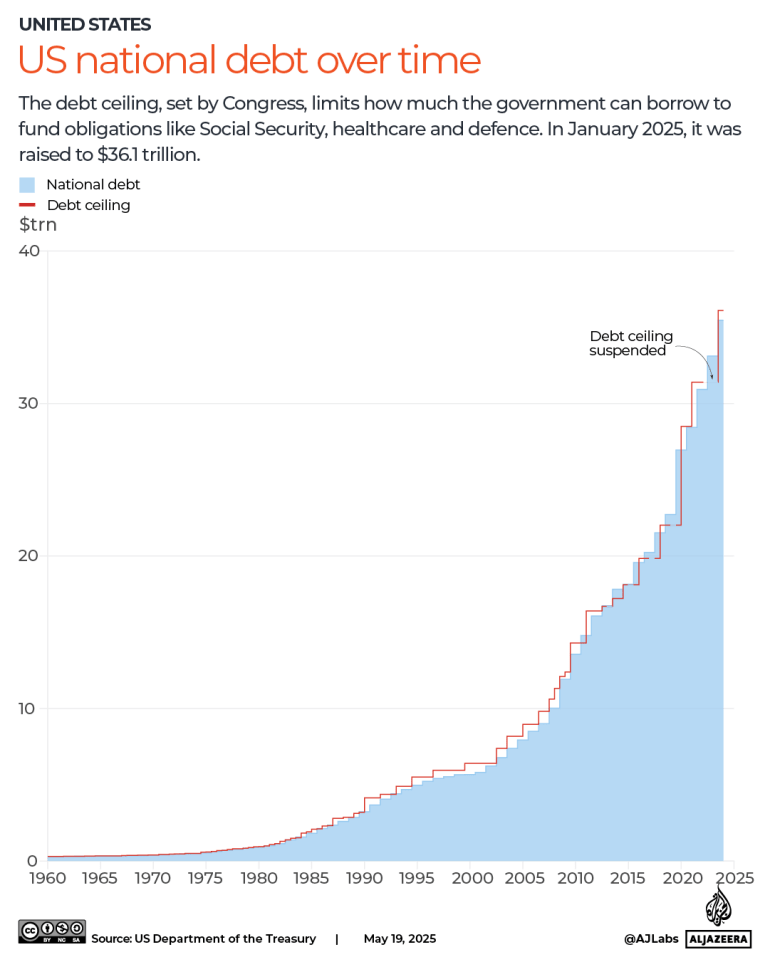
Passing the legislation will also raise the debt ceiling, which sets the amount of money the government can borrow to pay for existing expenditures, by $4 trillion, a sticking point for hardline Republicans who want deeper cuts.
Here are some of the key measures in the proposed bill in its current form.
Changes for households
The bill increases standard deductions for all Americans. Individual deductions will increase by $1,000, $1,500 for heads of households, and $2,000 for married couples.
The bill extends the child tax credit of $2,000, which would otherwise have ended with the expiration of the 2017 tax cuts at year’s end.
It bumps up the child tax credit by $500 per child for this tax year and runs through the end of 2028. It also includes a $1,000 savings account for children born between December 31, 2024 and January 1, 2029. The legislation would also allow families to annually contribute $5,000 tax-free.
There is a new tax deduction for Americans 65 and older. The new bill would give a $4,000 annual deduction starting this year for people making a gross income of $75,000 for a single person and $150,000 for a married couple. If passed, the rule would take effect for the current tax year and run until the end of 2028.
“It will just make tax paying more complicated and more uncertain when a lot of these things ultimately expire,” Adam Michel, director of tax policy studies at the right-leaning Cato Institute, told Al Jazeera.
Another provision in the bill modifies state and local tax (SALT) deductions. It allows filers to be able to write off some of what they paid in local and state taxes from their federal filings.
Under the 2017 tax act, that was capped at $10,000, but the new legislation would raise that to $30,000. Some Republicans, particularly those in states with higher taxes like New York and California, have been pushing to raise the cap or abolish it altogether. However, they have faced fiscal hawks and those who see the increases as relief for those already wealthy.
The bill includes an increased benefit for small businesses that allows them to deduct 23 percent of their qualified business income from their taxes, up from the current 20 percent.
There is also a call for no taxes on overtime pay for select individuals. It would not apply to people who are non-citizens, those who are considered “highly compensated employees,” and those who earn a tipped wage.
The bill, however, also eliminates taxes on tips, a critical campaign promise by both Donald Trump and his Democratic rival Kamala Harris. The bill would allow people who work in sectors like food service, as well as hair care, nail care, aesthetics, and body and spa treatments, to specifically deduct the amount of tipped income they receive.
At the federal level, employers will still not be required to pay tipped workers more than the subminimum wage of $2.13 hourly. The intention is that workers will be able to make up the difference in tipping the receipt from customers.
Cuts to the social safety net
The legislation calls to make $880bn in cuts to key government programmes with a focus mostly on Medicaid and food stamps.
The CBO found that more than 10 million people could lose Medicaid access and 7.6 million could lose access to health insurance completely by 2034 under the current plan.
Even far-right Republicans have called out the Medicaid cuts. In an op-ed in The New York Times this week, Republican Senator Josh Hawley of Missouri said the cuts are “morally wrong and politically suicidal”.
According to a new report from One Fair Wage shared with Al Jazeera, tipped workers could be hit especially hard, as 1.2 million restaurant and tipped workers could lose access to Medicaid.
“A no tax on tips proposal, which is like a minuscule percentage of their income and doesn’t affect two-thirds of tips workers because they don’t earn enough to pay federal income tax, is just nowhere near enough to compensate for the fact that we’re going to have millions of these workers lose the ability to take care of themselves, in some cases go into medical debt, in many cases just not take care of themselves,” Saru Jayaraman, president of One Fair Wage, an advocacy group for restaurant workers, told Al Jazeera.
The bill also introduces work requirements to receive benefits, saying that recipients must prove they work, volunteer or are enrolled in school for at least 80 hours each month.
At the same time, the bill also shortens the open enrolment period by a month for the Affordable Care Act (ACA), otherwise known as Obamacare. This means people who have employer-funded healthcare and lose their job might lose eligibility to buy a private plan on the healthcare exchange.
“It’s taking folks like 11 to 12 weeks to find a new job. The worse the labour market gets, that number will tick up. If you’re unemployed for three months, you get kicked off Medicaid,” Liz Pancotti, managing director of policy and advocacy at the Groundwork Collective, told Al Jazeera.
“Then, if you try to go buy a plan on the ACA marketplace, you are no longer eligible for subsidies … which I think is really cruel.”
Other major proposed cuts will hit programmes like Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Programme or SNAP, which helps 42 million low-income individuals afford groceries and comes at a time when food costs are still 2 percent higher than a year ago. The CBO found that 3 million people could lose SNAP access under the new plan.
The bill would also force states to take up more responsibility in funding the programmes. States would be required to cover 75 percent of the administrative costs, and all states would have to pay at least 5 percent of the benefits — 28 states would need to pay 25 percent.
“States are now going to be on the hook for billions of dollars in funding for these two vital programmes. They have a tough choice. One is, do they cut funding from others like K-12 education, roads, veteran services, etc, to cover this gap, or do they raise taxes so that they can raise more revenue to cover this gap,” Pancotti added.
Under the current law, the federal government is solely responsible for shouldering the cost of benefits. The proposed cuts would save $300bn for the federal government but hit state budgets hard.
Bill fuels Trump administration priorities
The bill would also cut the $7,500 tax credit for new electric vehicle purchases and $4,000 for a used EV, a move which could hurt several major US automakers that are already reeling from the administration’s tariffs on automobiles.
General Motors pumped billions into domestic EV production in the last year, which has included a $900m investment to retrofit an existing plant to build electric vehicles in Michigan and alongside Samsung, the carmaker invested $3.5bn in EV battery manufacturing in the US.
In February, Ford CEO Jim Farley said that revoking the EV tax credit could put factory jobs on the chopping block. The carmaker invested in three EV battery plants in Michigan, Kentucky and Tennessee. The federal government under the administration of former President Joe Biden paid out more than $2bn in EV tax credits in 2024.
The proposed legislation would also give the Trump administration authority to revoke the tax exempt status of nonprofit organisations that it deems as a “terrorist supporting organisation”. It would give the secretary of the treasury the ability to accuse any nonprofit of supporting “terrorism”, revoke their tax exempt status without allowing them due process to prove otherwise, which has raised serious concerns amongst critics.
“This measure’s real intent lurks behind its hyperbolic and unsubstantiated anti-terrorist rhetoric: It would allow the Treasury Department to explicitly target, harass and investigate thousands of U.S. organizations that make up civil society, including nonprofit newsrooms,” Jenna Ruddock, advocacy director of Free Press Action, said in a statement.
“The bill’s language lacks any meaningful safeguards against abuse. Instead it puts the burden of proof on organizations rather than on the government. It’s not hard to imagine how the Trump administration would use it to exact revenge on groups that have raised questions about or simply angered the president and other officials in his orbit.”
The bill would introduce new taxes on colleges, including a varying tax rate based on the size of a university’s endowment per student with the highest at 14 percent for universities with a per student endowment of more than $1.25m but less than $2m and 21 percent for those of $2m or more.
This comes amid the Trump administration’s increased tensions with higher education. In the last week, the Trump administration pulled $450m in grants to Harvard on top of the $2.2bn it pulled in April — a move which will hinder research into cancer and heart disease, among other areas. Harvard has an endowment of $53.2bn, making it one of the richest schools in the country.
The legislation would also increase funding for a border wall between the US and Mexico, which the administration has argued will help curb undocumented immigration. However, there is no evidence that such a wall has deterred border crossings.
A 2018 analysis from Stanford University found that a border wall would only curb migration by 0.6 percent, yet the bill would give more than $50bn to finish the border wall and maritime crossings. The bill would also provide $45bn for building and maintaining detention facilities and another $14bn for transport.