Trump hits Asian nations with tariffs, including allies Japan, South Korea | International Trade News
United States President Donald Trump is set to impose 25 percent tariffs on two key US allies, Japan and South Korea, beginning on August 1 as the administration’s self-imposed deadline for trade agreements of July 9 nears without a deal in place.
On Monday, the Trump administration said this in the first of 12 letters to key US trade partners regarding the new levies they face.
In near-identically worded letters to the Japanese and South Korean leaders, the US president said the trade relationship was “unfortunately, far from Reciprocal”.
Japan’s Prime Minister Shigeru Ishiba has said that he “won’t easily compromise” in trade talks with the Trump administration.
The US imports nearly twice as much from Japan as it exports to the country, according to US Census Bureau data.
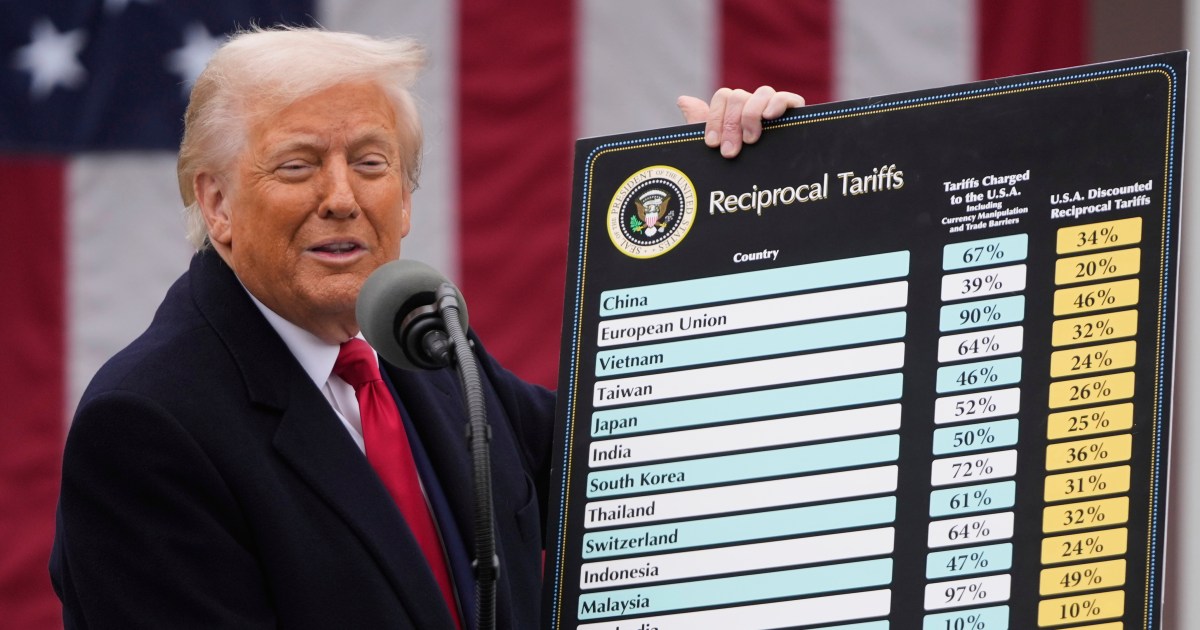
Currently, both Japan and South Korea have a 10 percent levy in place, the same as almost all US trading partners. But Trump said he was ready to lower the new levels if the two countries changed their trade policies.
“We will, perhaps, consider an adjustment to this letter,” he said in letters to the two Asian countries’ leaders that he posted on his Truth Social platform. “If for any reason you decide to raise your Tariffs, then, whatever the number you choose to raise them by, will be added onto the 25% that we charge.”
Trump also announced the US will impose 25 percent tariffs each on Malaysia and Kazakhstan, 30 percent on South Africa and 40 percent each on Laos and Myanmar.
US Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent said earlier on Monday that he expected several trade announcements to be made in the next 48 hours, adding that his inbox was full of last-ditch offers from countries to clinch a tariff deal by the deadline. Bessent did not say which countries could get deals and what they might contain.
In April, the White House said it would have 90 trade and tariff deals established within 90 days. That did not happen, and since that time, the administration has solidified two agreements — one with Vietnam, and the other with the United Kingdom.
“There will be additional letters in the coming days,” White House Press Secretary Karoline Leavitt said, adding that “we are close” on some deals. She said Trump would sign an executive order on Monday formally delaying the July 9 deadline to August 1.
BRICS tensions
Trump also put members of the developing nations’ BRICS group in his sights as its leaders met in Brazil, threatening an additional 10 percent tariff on any BRICS countries aligning themselves with “anti-American” policies.
The new 10 percent tariff will be imposed on individual countries if they take anti-American policy actions, a source familiar with the matter told Reuters news agency.
The BRICS group comprises Brazil, Russia, India and China and South Africa along with recent joiners Egypt, Ethiopia, Indonesia, Iran and the United Arab Emirates. Trump’s comments hit the South African rand, affecting its value in Monday trading.
Russia said BRICS was “a group of countries that share common approaches and a common world view on how to cooperate, based on their own interests”.
“And this cooperation within BRICS has never been and will never be directed against any third countries,” said Kremlin spokesman Dmitry Peskov.
European Union at the table
The European Union will not be receiving a letter setting out higher tariffs, EU sources familiar with the matter told Reuters on Monday.
The EU still aims to reach a trade deal by July 9 after European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and Trump had a “good exchange”, a commission spokesperson said.
It was not clear, however, whether there had been a meaningful breakthrough in talks to stave off tariff hikes on the largest trading partner of the US.
Adding to the pressure, Trump threatened to impose a 17 percent tariff on EU food and agriculture exports, it emerged last week.
The EU has been torn over whether to push for a quick and light trade deal or back its own economic clout in trying to negotiate a better outcome. It had already dropped hopes for a comprehensive trade agreement before the July deadline.
“We want to reach a deal with the US. We want to avoid tariffs,” the spokesperson said at a daily briefing.
Without a preliminary agreement, broad US tariffs on most imports would rise from their current 10 percent to the rates set out by Trump on April 2. In the EU’s case, that would be 20 percent.
Von der Leyen also held talks with the leaders of Germany, France and Italy at the weekend, Germany said. German Chancellor Friedrich Merz has repeatedly stressed the need for a quick deal to protect industries vulnerable to tariffs ranging from cars to pharmaceuticals.
Germany said the parties should allow themselves “another 24 or 48 hours to come to a decision”. And the country’s auto company Mercedes-Benz said on Monday its second-quarter unit sales of cars and vans had fallen 9 percent, blaming tariffs.
Markets respond
US markets have tumbled on Trump’s tariff announcements.
As of 3:30pm in New York (19:30 GMT), the S&P 500 fell by 1 percent, marking the biggest drop in three weeks. The tech-heavy Nasdaq Composite Index was down by a little more than 1 percent, while the Dow Jones Industrial Average also fell by more than a full percentage point.
US-listed shares of Japanese automotive companies fell, with Toyota Motor Corp down 4.1 percent in mid-afternoon trading and Honda Motor off by 3.8 percent. Meanwhile, the US dollar surged against both the Japanese yen and the South Korean won.