The federal government needs to act fast to save one of the country’s most important social programs.
As of July, over 53 million Americans receive Social Security retirement benefits. A good number of these recipients rely on the Social Security program for most or, in some cases, all of their retirement income, so it’s hard to overstate just how important the program continues to be.
According to the Nationwide Retirement Institute 2025 Social Security Survey, over 60% of Social Security recipients feel as though they’d be financially vulnerable if there were cuts to Social Security benefits. That’s not too surprising, given how much people rely on the social program.
However, what may be surprising is just how soon cuts to Social Security benefits could happen at the current pace of deficit that the program is running on.
Image source: Getty Images.
How Social Security funding works
Before discussing the likelihood of Social Security benefit cuts, it’s essential to understand how the program is funded, which is through payroll taxes. The current rate is 12.4%, with employers and employees paying 6.2% each, and self-employed people paying the full 12.4%.
This tax revenue is put into the Social Security Trust Fund, which consists of the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance (OASI) Trust Fund and the Disability Insurance (DI) Trust Fund. The OASI program pays benefits to retirees, their families, and survivors of deceased recipients; the DI program pays benefits to disabled workers and their families.
The idea is that working-age people pay into the system to support current retirees, with the understanding that once they’re retired, they’ll be on the receiving end of this support.
What’s the likelihood of benefits being cut?
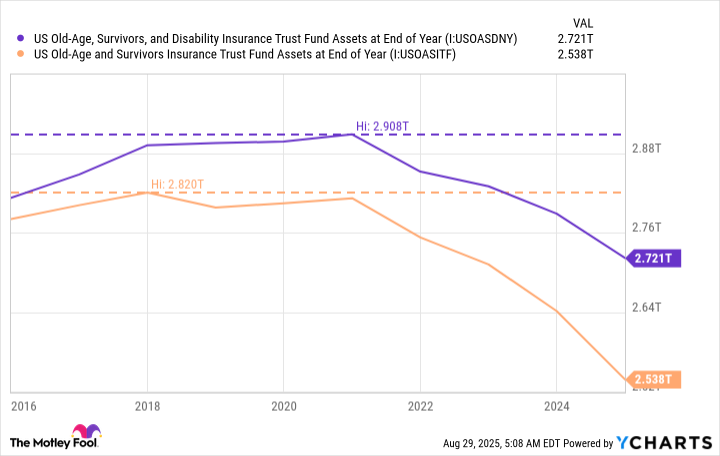
The Social Security Administration’s (SSA) 2025 Social Security Trustees Report highlighted that the Social Security program cost $1.485 trillion in 2024, while generating only $1.418 trillion in revenue, leaving a $67 billion deficit for the year. Both major Social Security trust funds have experienced a decline over the past decade.
US Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance Trust Fund Assets at End of Year data by YCharts
The same report noted that the OASI trust fund could be depleted by 2033, which would leave the SSA with the ability to pay only 77% of its expected benefits. Considering the number of recipients from the Nationwide report who said cuts would make them financially vulnerable, this is, to put it lightly, far from ideal.
If the current depletion rate continues, the Social Security Trust Fund could be underfunded by more than $25 trillion through 2099 (the DI Trust Fund reserves are not projected to become depleted during this period). If no changes are made, Social Security would need to cut benefits by about 23% beginning in 2034.
According to the Nationwide study, 83% of respondents are concerned about Social Security’s long-term viability, and 74% are worried that the program’s funding could run out in their lifetime. Unfortunately, at the current pace and lack of concrete solutions, these concerns are justified.
What’s causing the current Social Security deficit?
There isn’t a single reason for the current Social Security deficit, but there are four main causes contributing to the problem. The first is that baby boomers are retiring in large numbers, and there aren’t enough tax-paying workers paying into the Social Security program.
The second “problem” is that people are living longer, meaning they’re collecting benefits longer, increasing how much Social Security has to pay out each year. This is good for people, but bad for Social Security.
We’ve also seen an increase in high earners, which means less of their income is being taxed and paid into the program. In 2025, the most income that’s subject to the Social Security payroll tax is $176,100. Any money earned above that is free from the tax.
The last problem is that before the interest rate hike a couple of years ago, interest rates spent a long period at historically low rates. This is a problem for Social Security because the reserves are put into Treasury bonds to earn interest. Low interest rates mean less money earned on these reserves.
All hope isn’t lost
To end on a more positive note, it’s worth pointing out that this isn’t the first time that Social Security has faced funding issues, and in previous times, the federal government has been able to “fix” the issue.
The American political environment is a bit more unpredictable nowadays, so I can’t say for certain if the same will happen. However, given the program’s importance to the livelihoods of millions of Americans, one would assume that it would become a priority for politicians on both sides of the aisle.