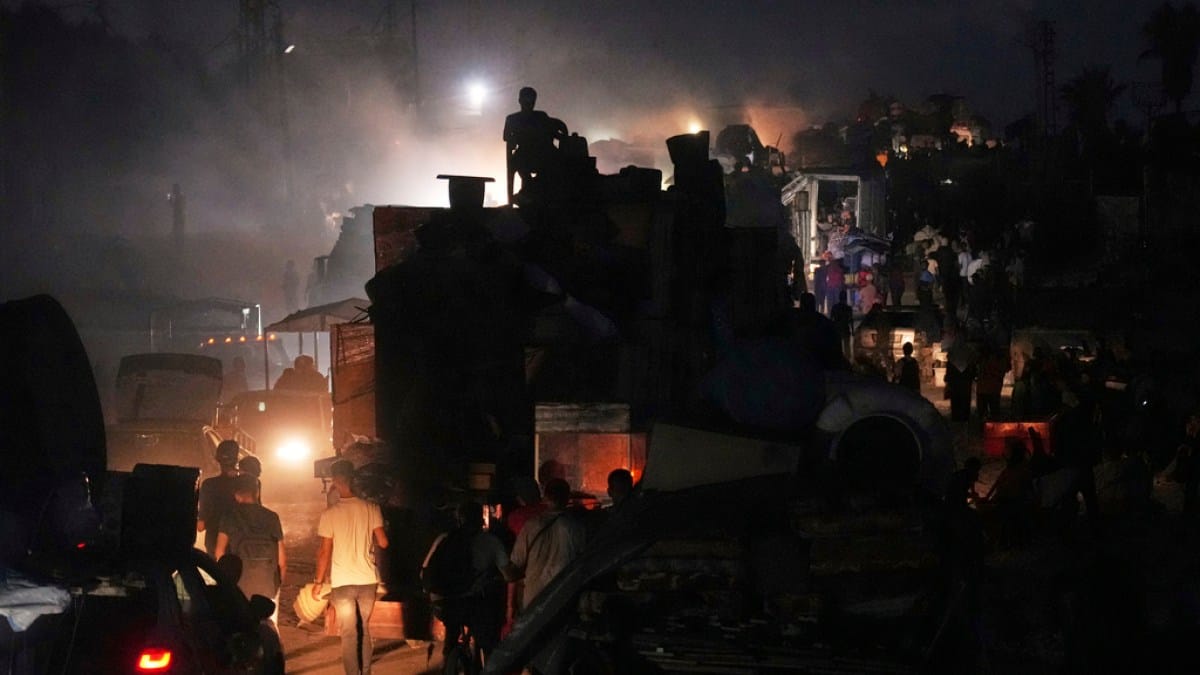
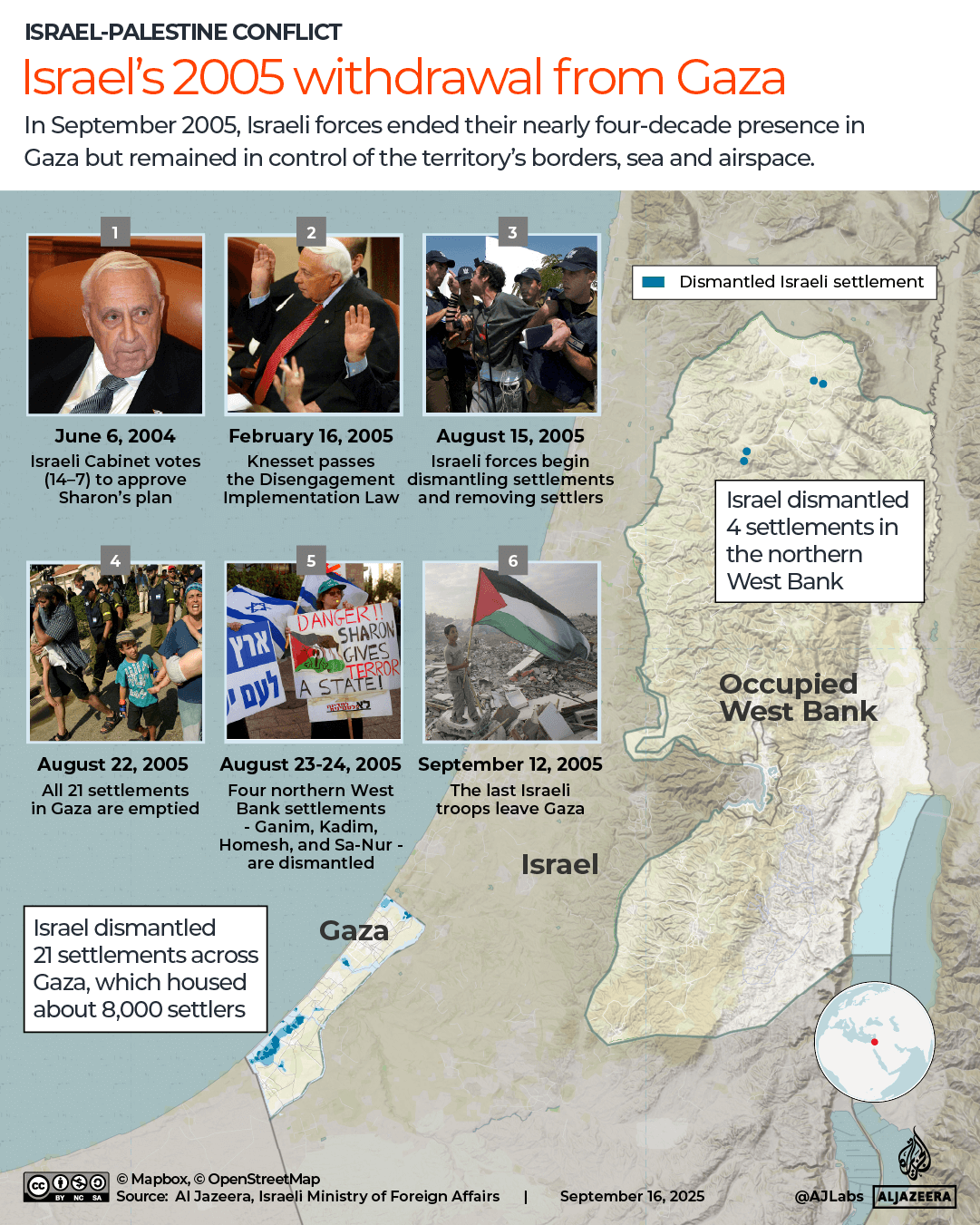
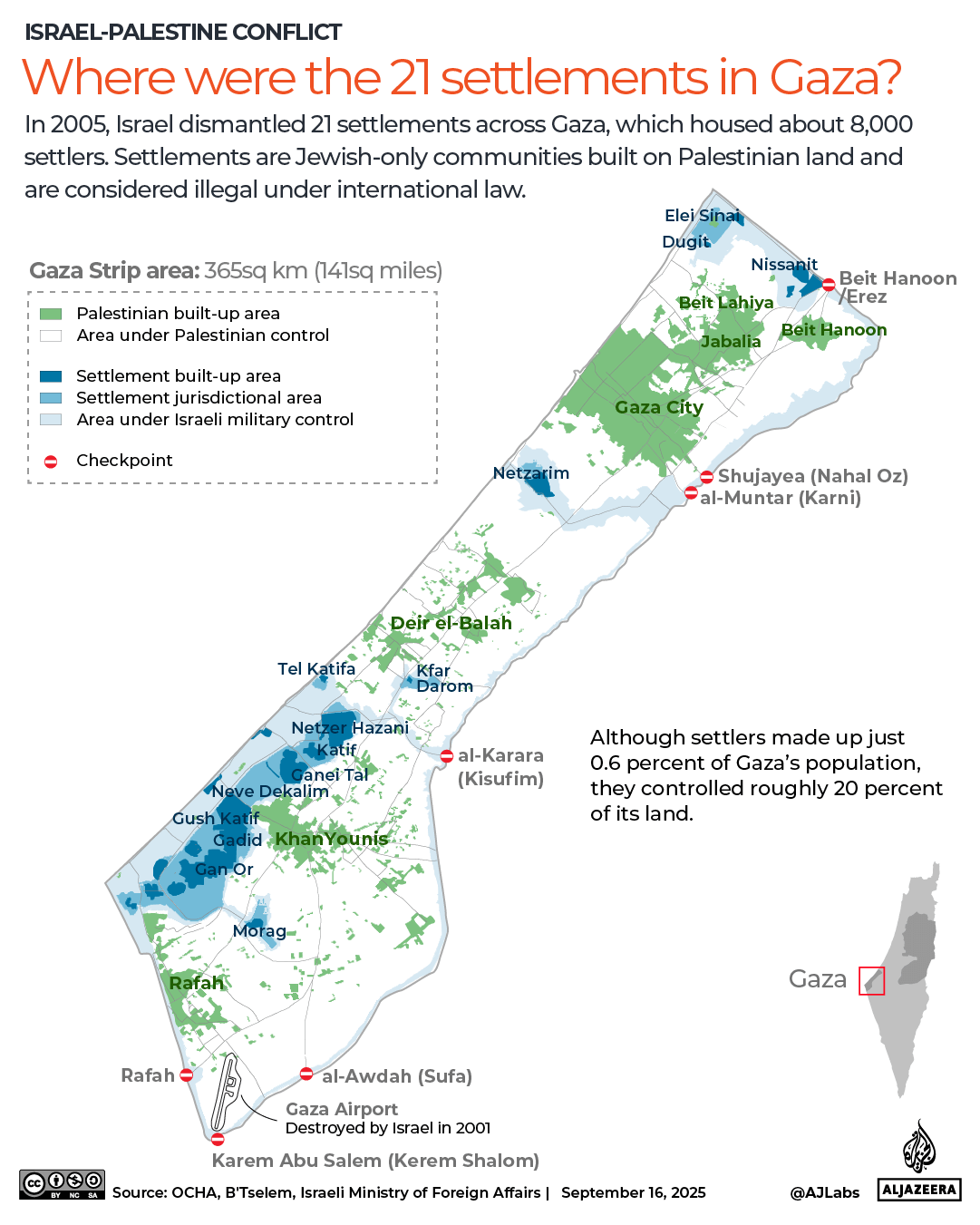
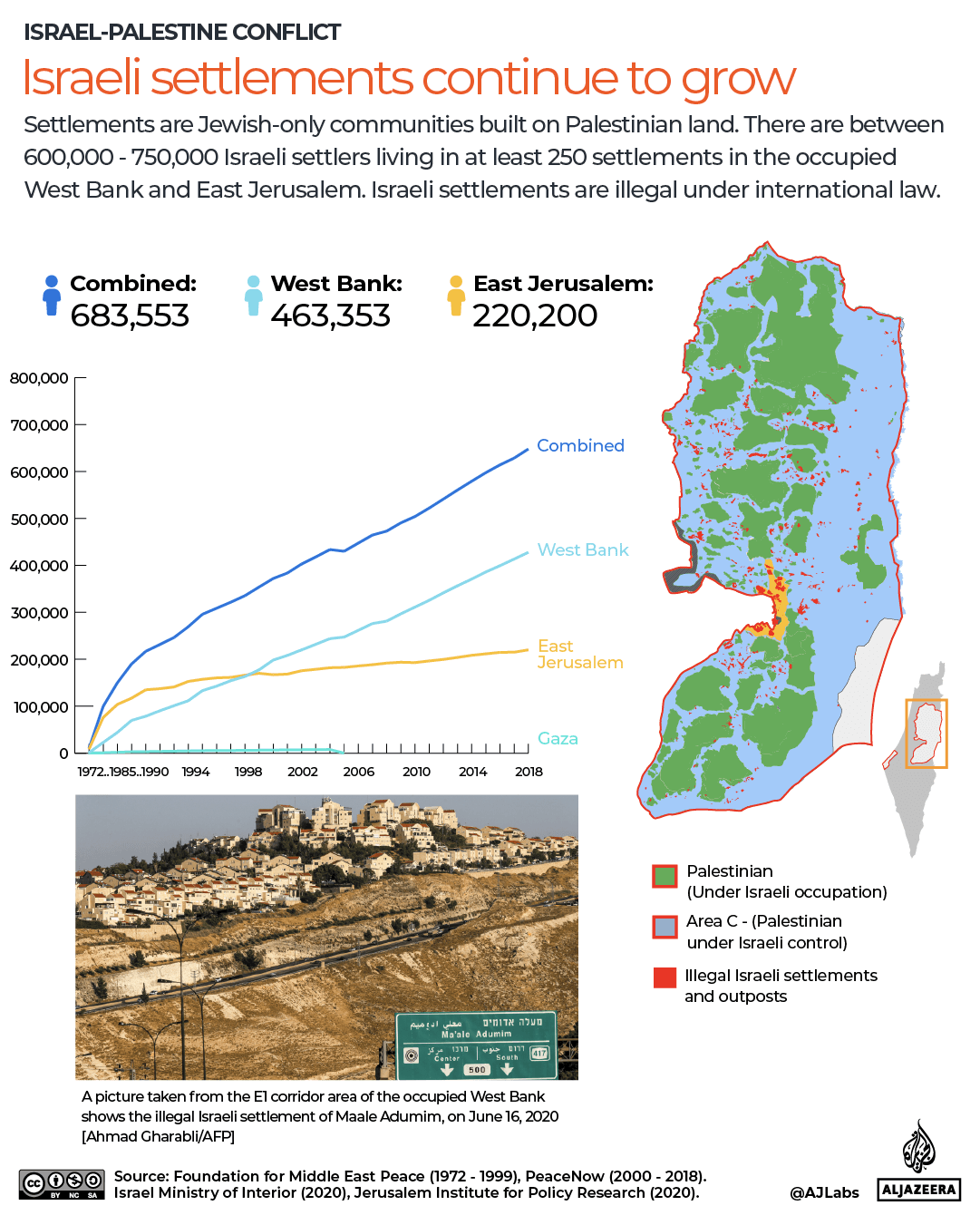
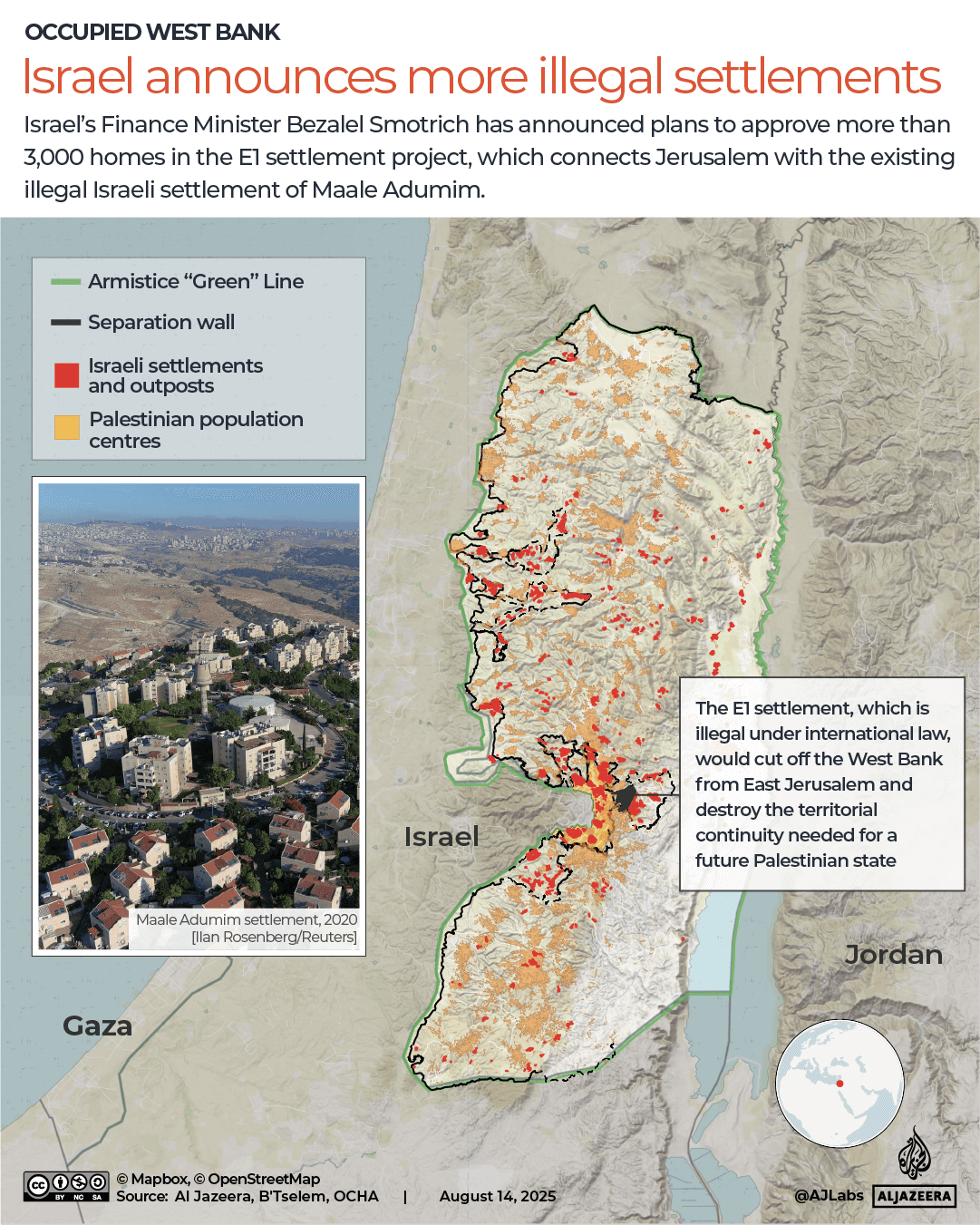
In April last year, I wrote that, given the genocide it is committing in Gaza, its violent occupation of the West Bank, numerous attacks on its neighbours, and apparent disregard for international and human rights law, it was time for the international community to declare Israel a rogue state. As if we hadn’t received enough confirmation of its rogue status since then, on September 9, Israel went ahead and carried out a strike on Qatar, a key mediator in negotiations between Hamas and Israel. This, while Gaza’s devastation deepens by the day.
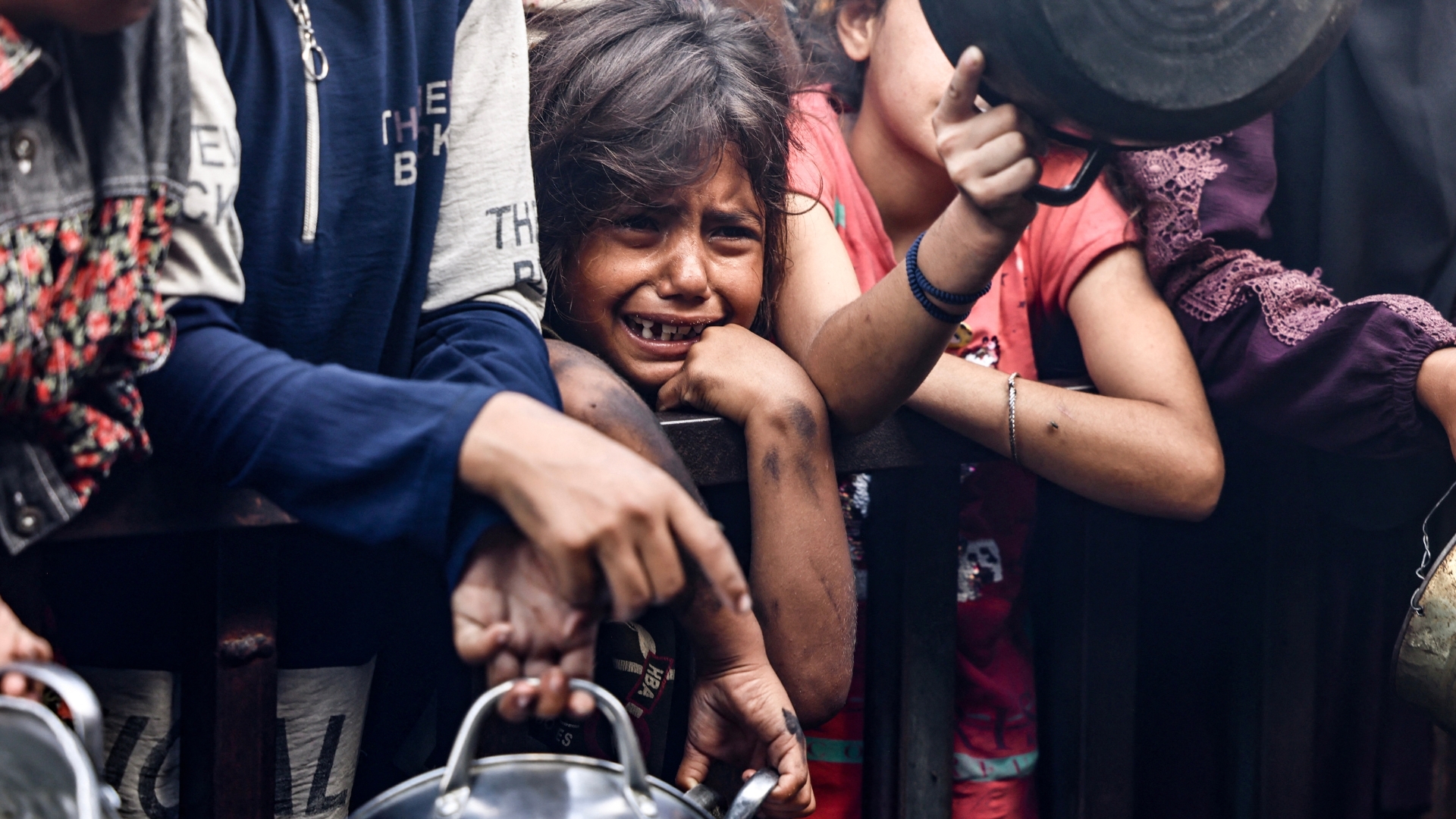
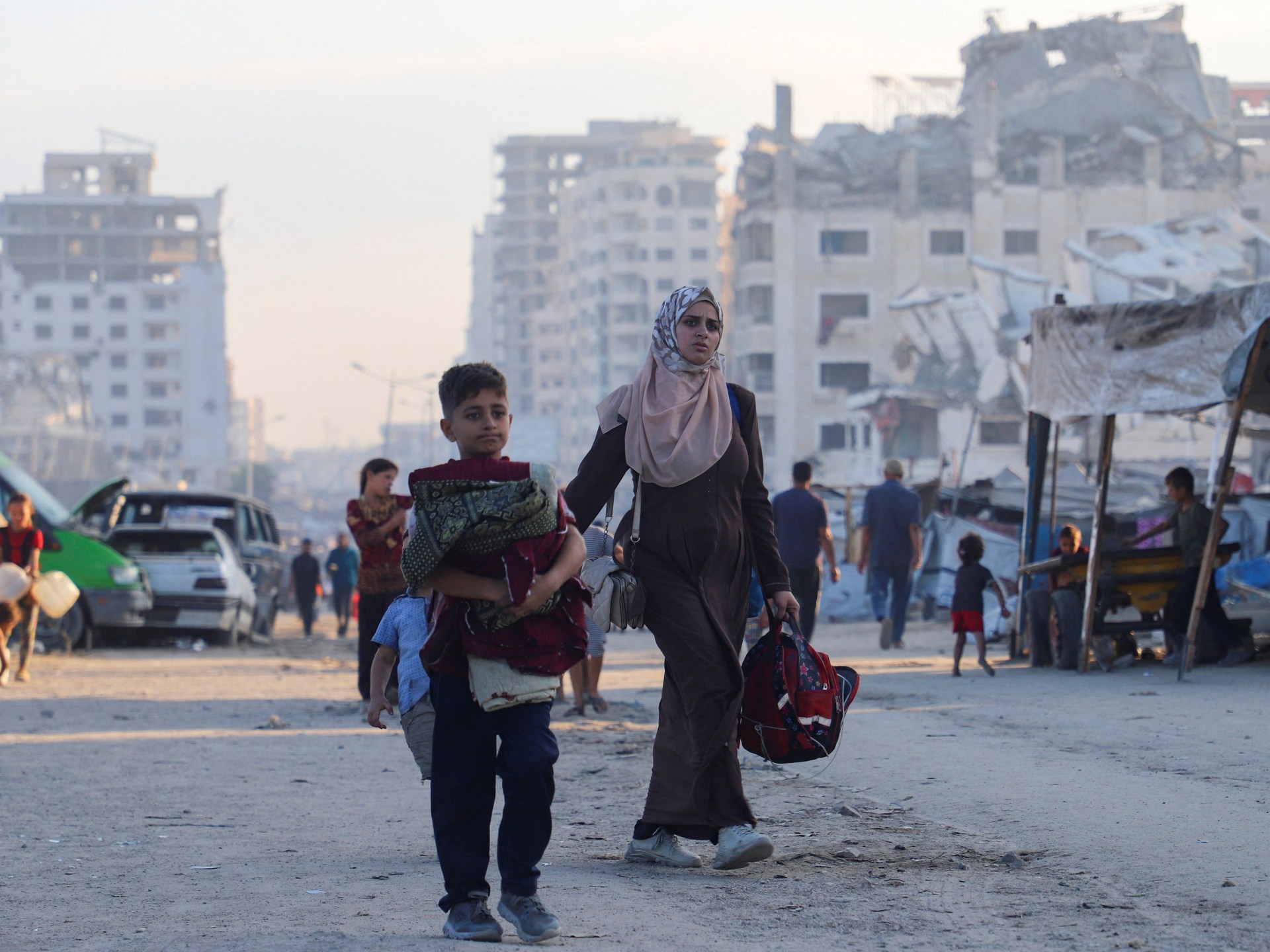
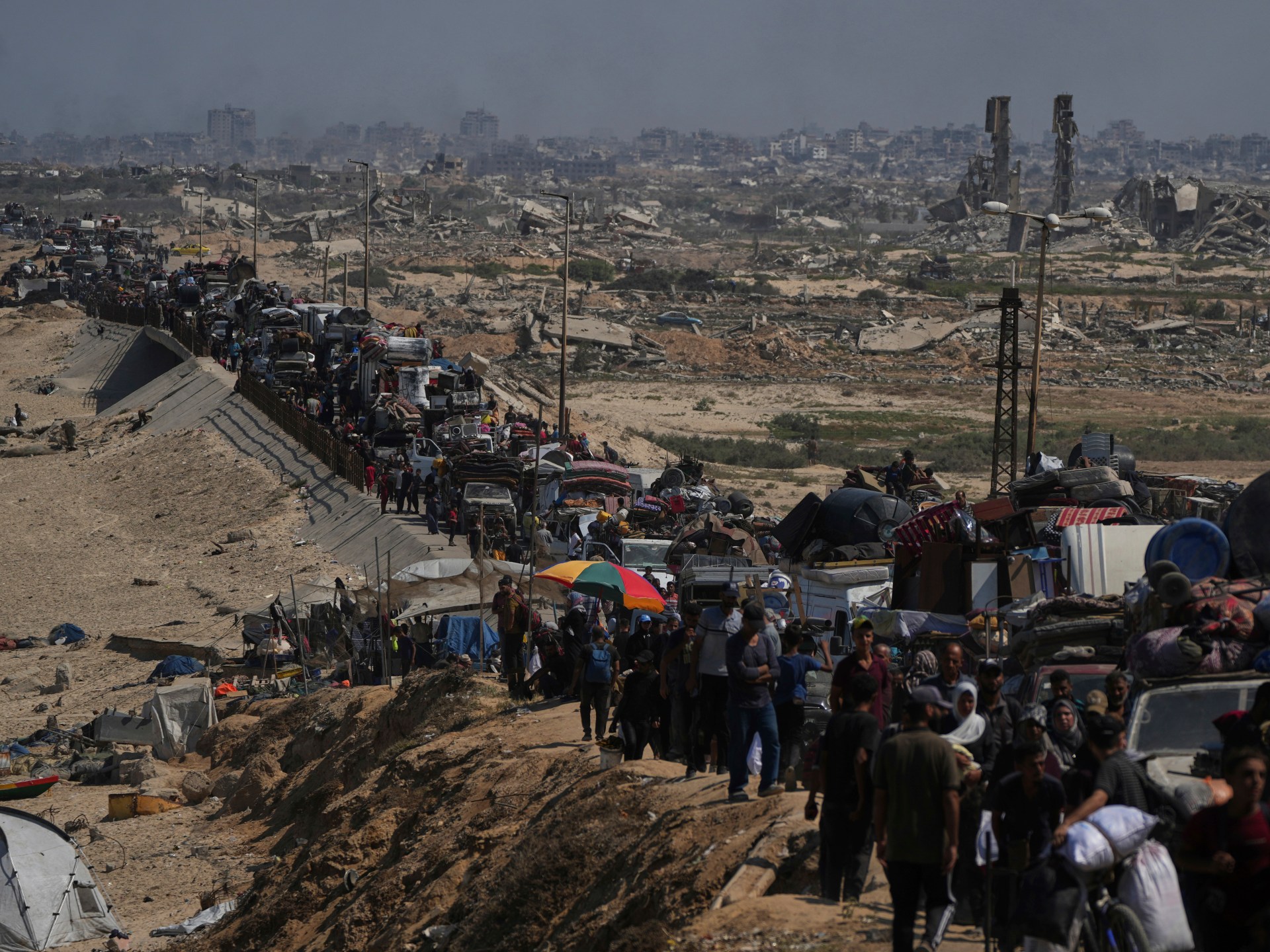
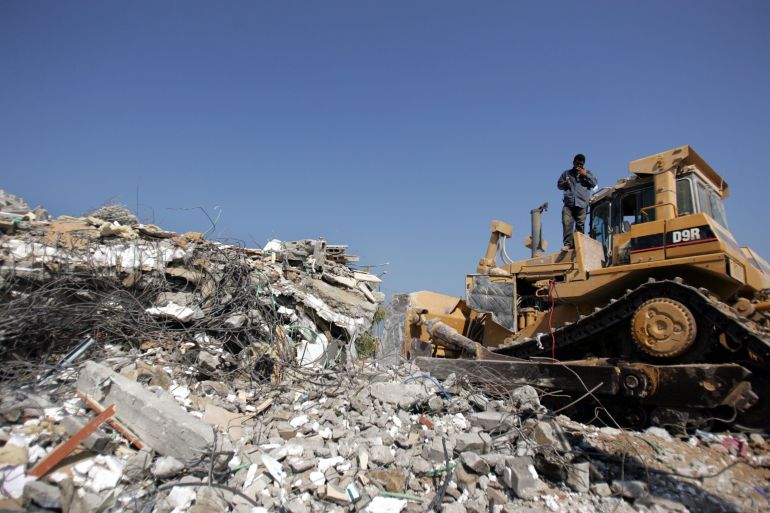
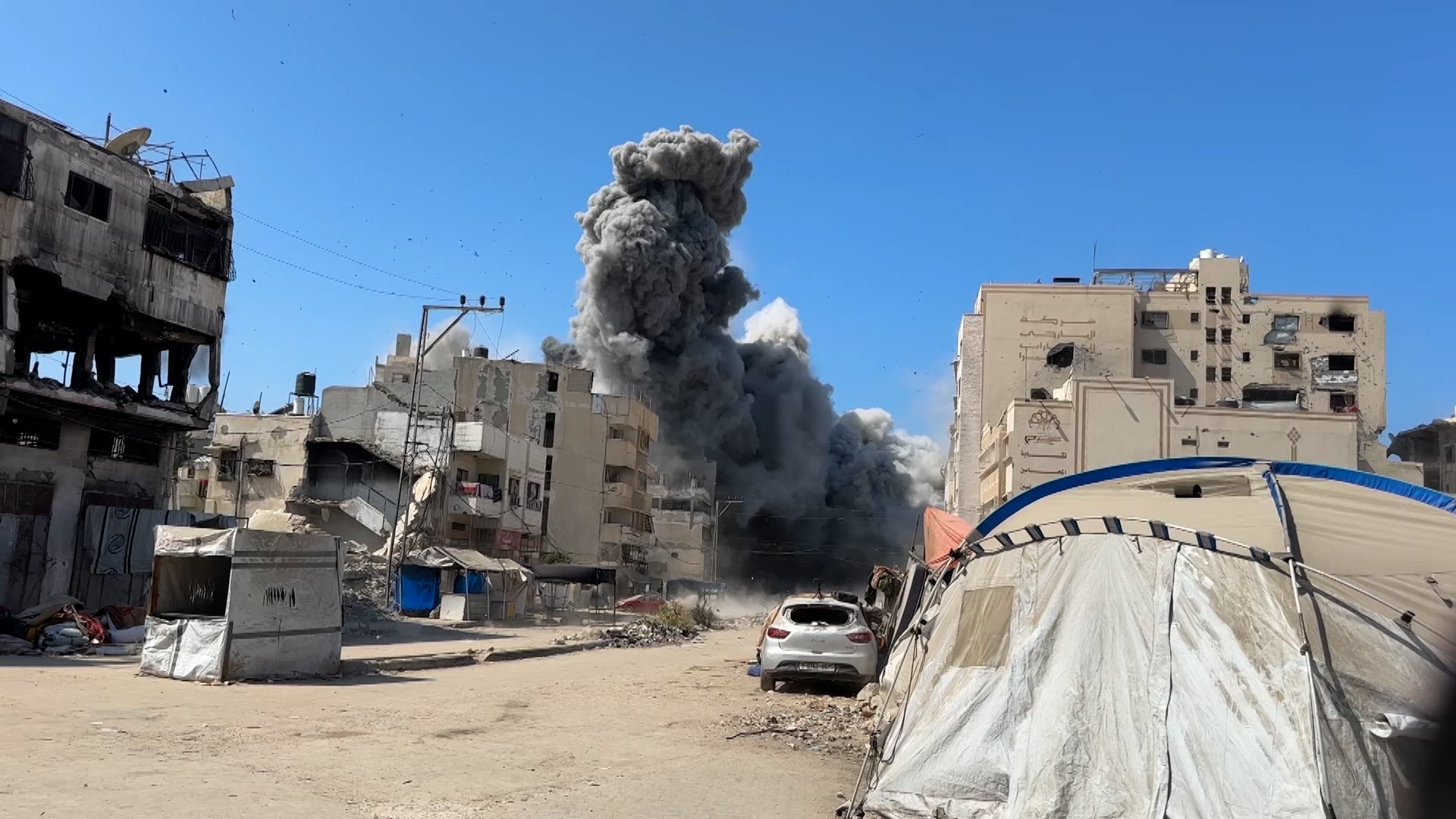
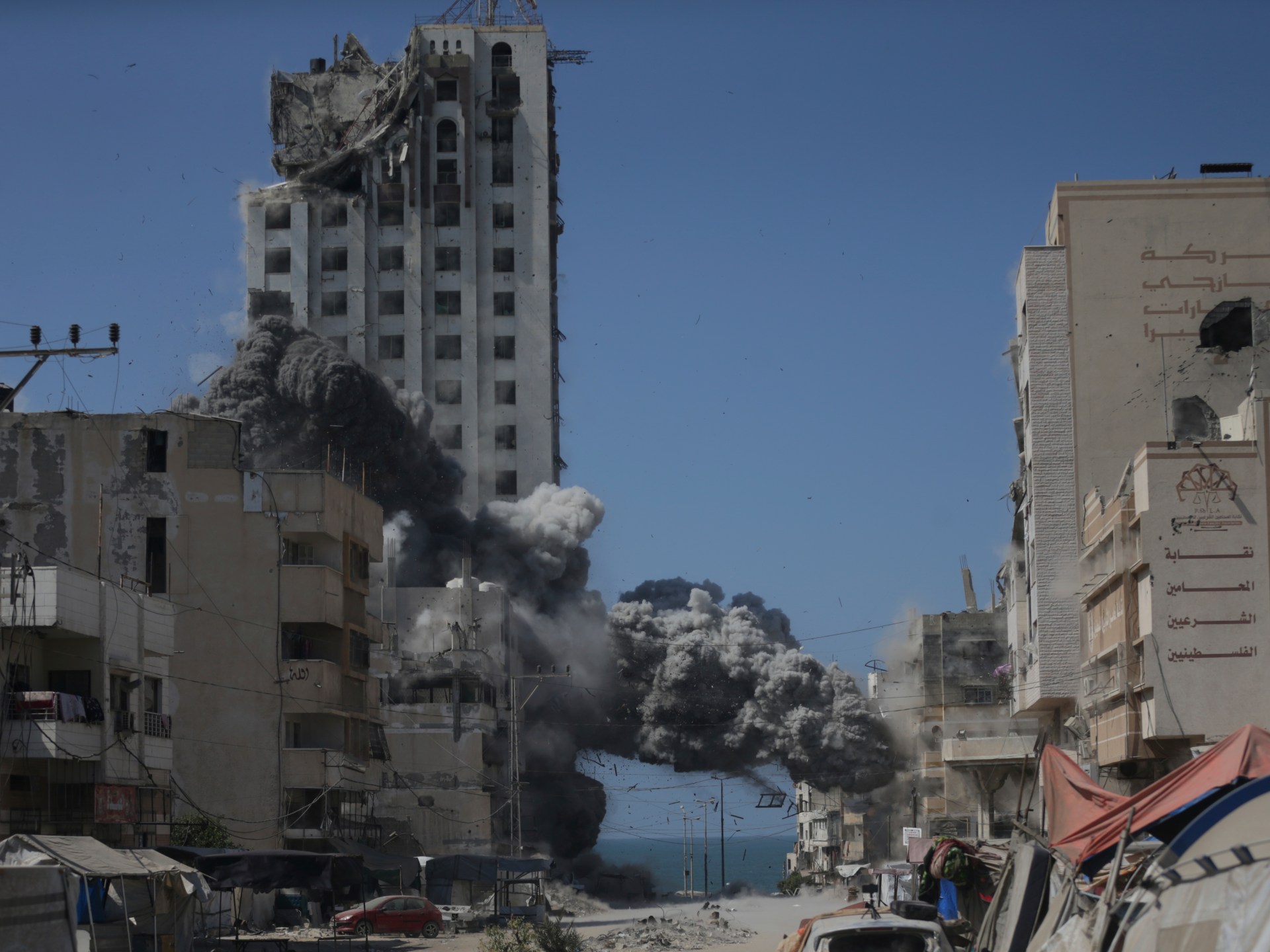
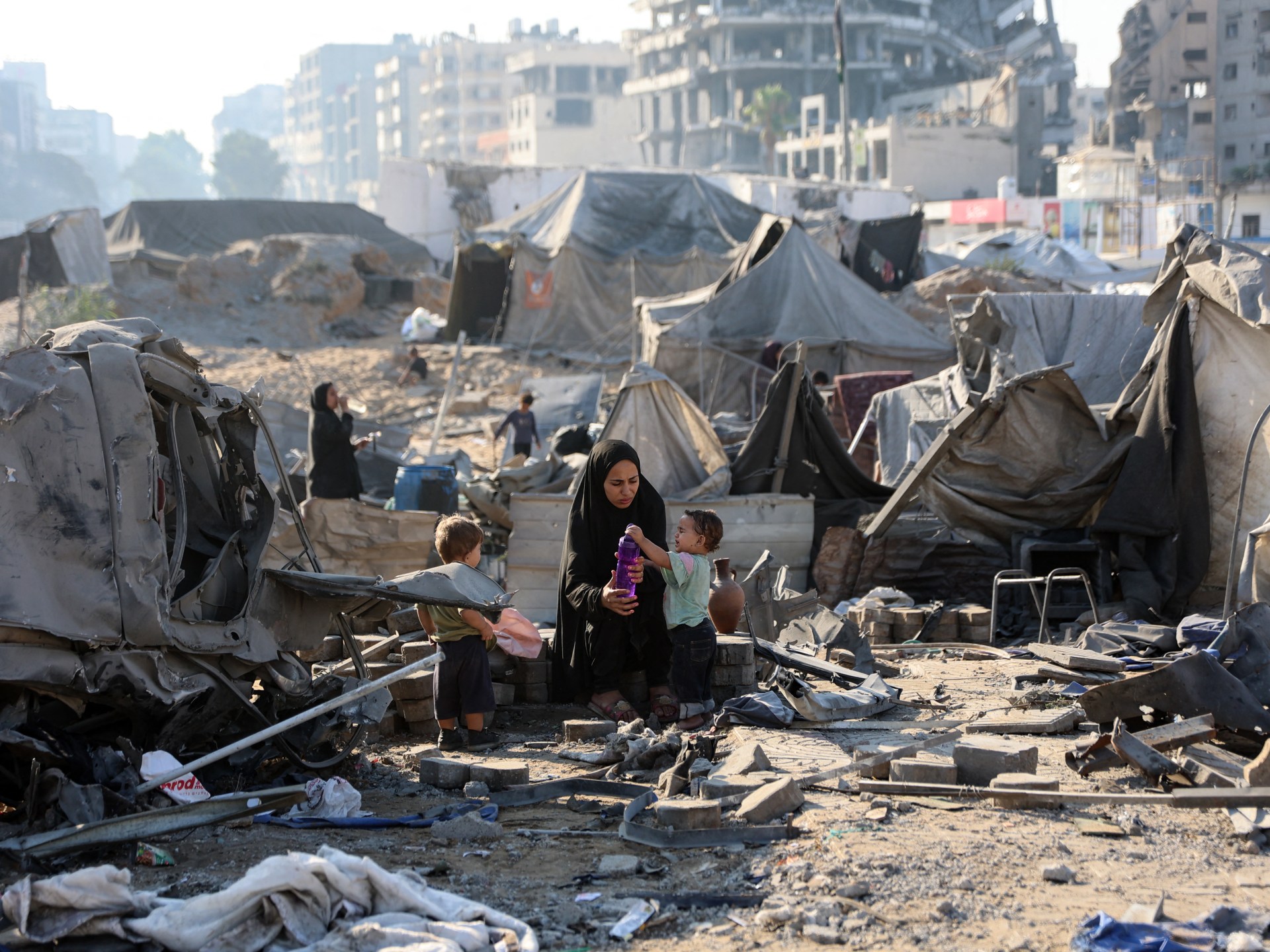
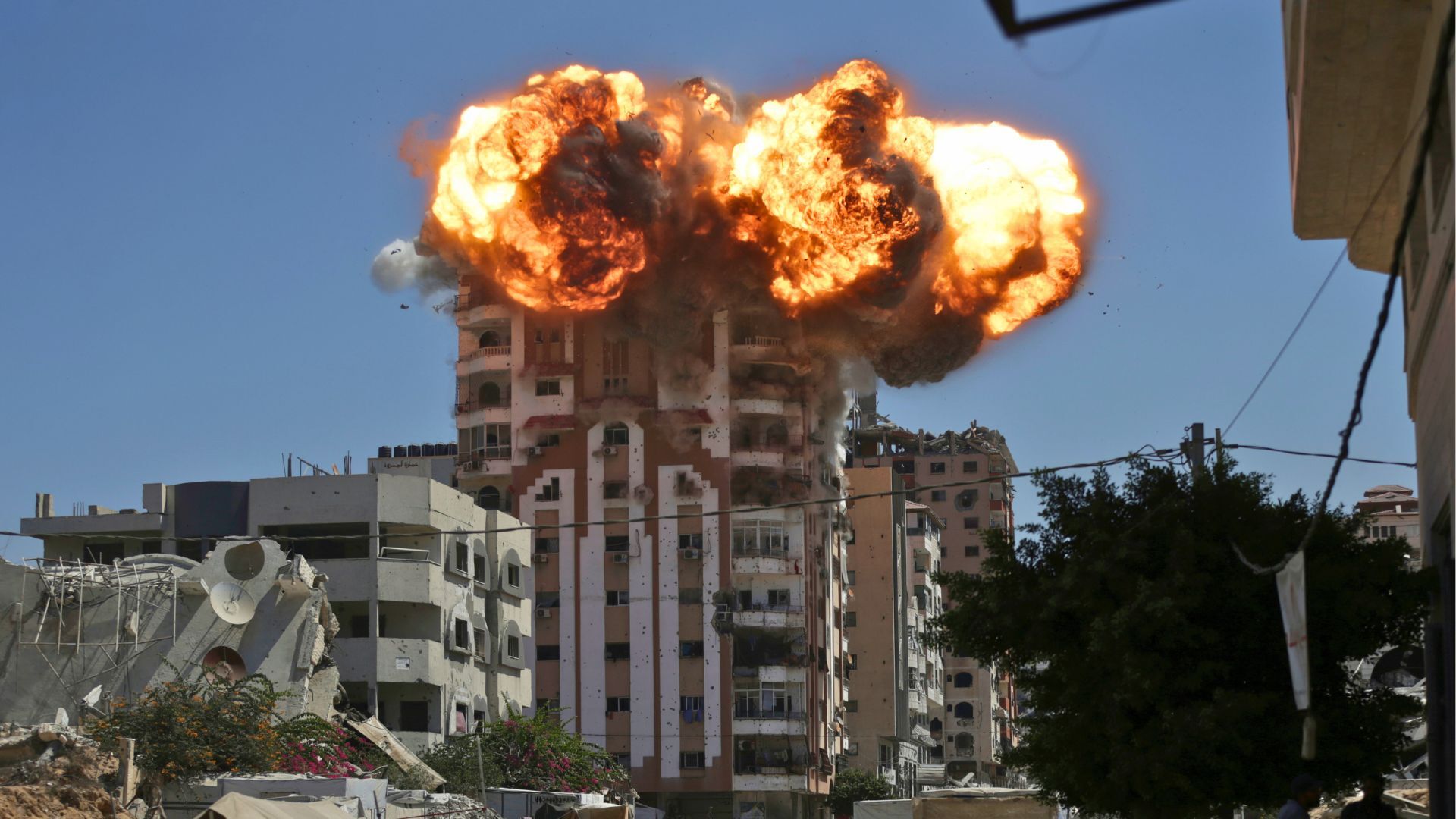
The last remaining high rises in Gaza City are now being flattened, and hundreds of thousands of people who had already been displaced multiple times are being pushed towards the south of the enclave. Israel claims the south is a “humanitarian zone”, but we know well that there is nowhere in Gaza where Palestinians are safe.
So, in the midst of all this, it feels futile to celebrate the United Nations General Assembly vote where 142 member states backed “tangible, timebound, and irreversible steps” towards a two-state solution to the Israel-Palestine conflict. The same resolution, rejected by just 12 states including Israel and the United States, also called on Hamas to free all hostages, end its rule in Gaza, and hand over its weapons to the Palestinian Authority, in line with the objective of establishing a sovereign and independent Palestinian state.
Gaza is still smouldering, and Palestinian communities are being systematically erased in the occupied West Bank. So how does it make sense to talk about a Palestinian state? Who, or what, would such a state serve?
Before this vote, the vast majority of countries in the world had already recognised the State of Palestine. Those missing from this map of recognition were primarily states in the Global North.
Through the UN General Assembly vote, France, Portugal, the United Kingdom, Malta, Belgium, Canada, and Australia have now signalled their support for Palestinian statehood, aligning themselves with the global majority. But let us be clear: these countries have no claim to the moral high ground.
We should remember that they waited through two years of Israeli genocide, which has killed at least 65,000 Palestinians, before voting in favour of a Palestinian state. They were similarly oblivious to the Palestinian right to self-determination during the years of Israeli and Egyptian-imposed military siege in Gaza before October 7, 2023. They did nothing to quell the ever-expanding illegal settlement movement in the occupied West Bank or the sharp increase in settler violence. In fact, they have done nothing to support the Palestinian right to self-determination since 1948.
So, why should this time be any different?
In fact, it is not different at all. As a scholar of international law, Noura Erakat recently told Al Jazeera, “It is way too little, far too late.” And these declarations are only meant to distract from the fact that many of these countries have financially and militarily enabled Israel to carry out its genocide.
The proof is in the pudding: the Palestinian state that is on offer. And what is clear is that Palestinian rights are not a priority.
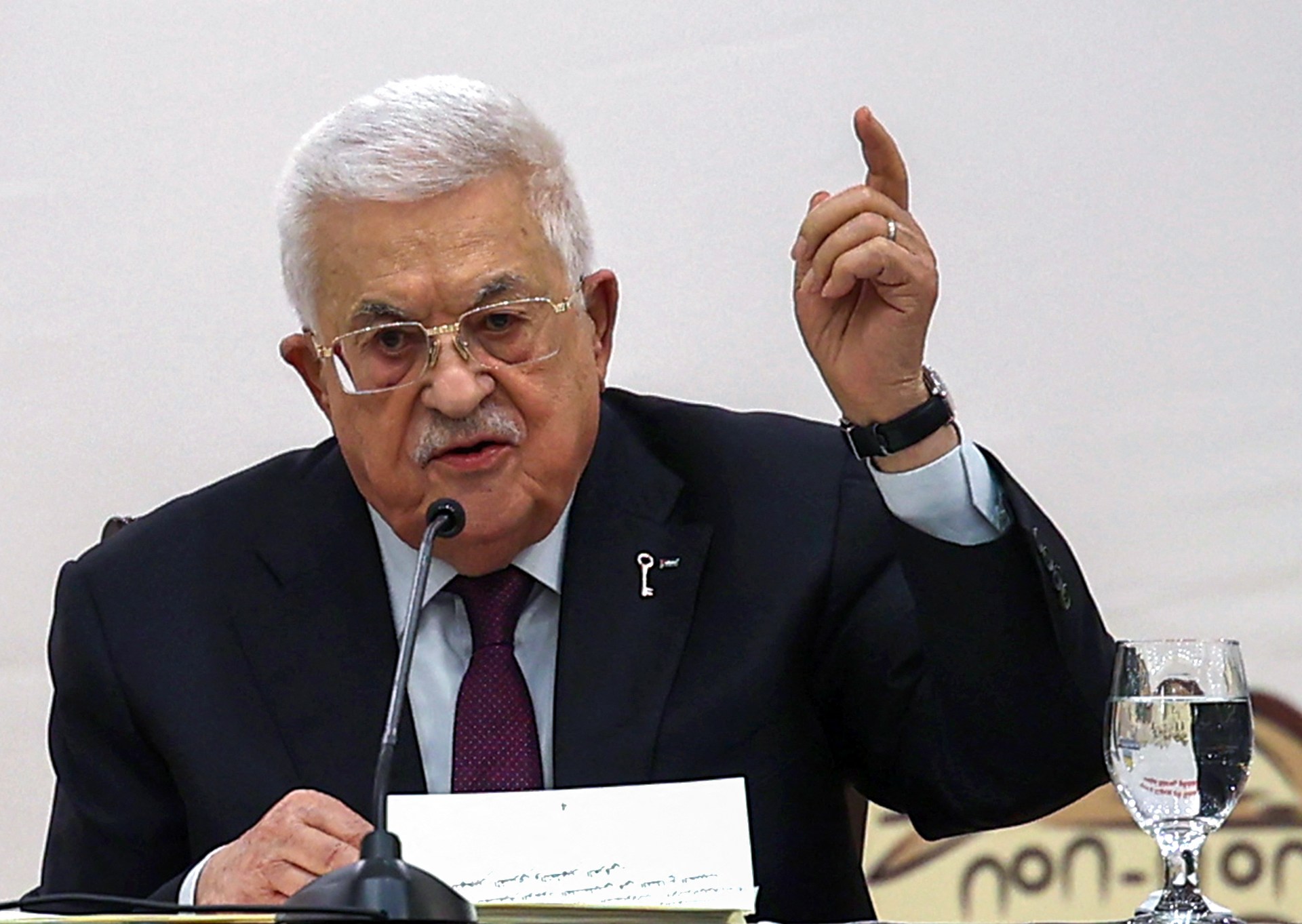
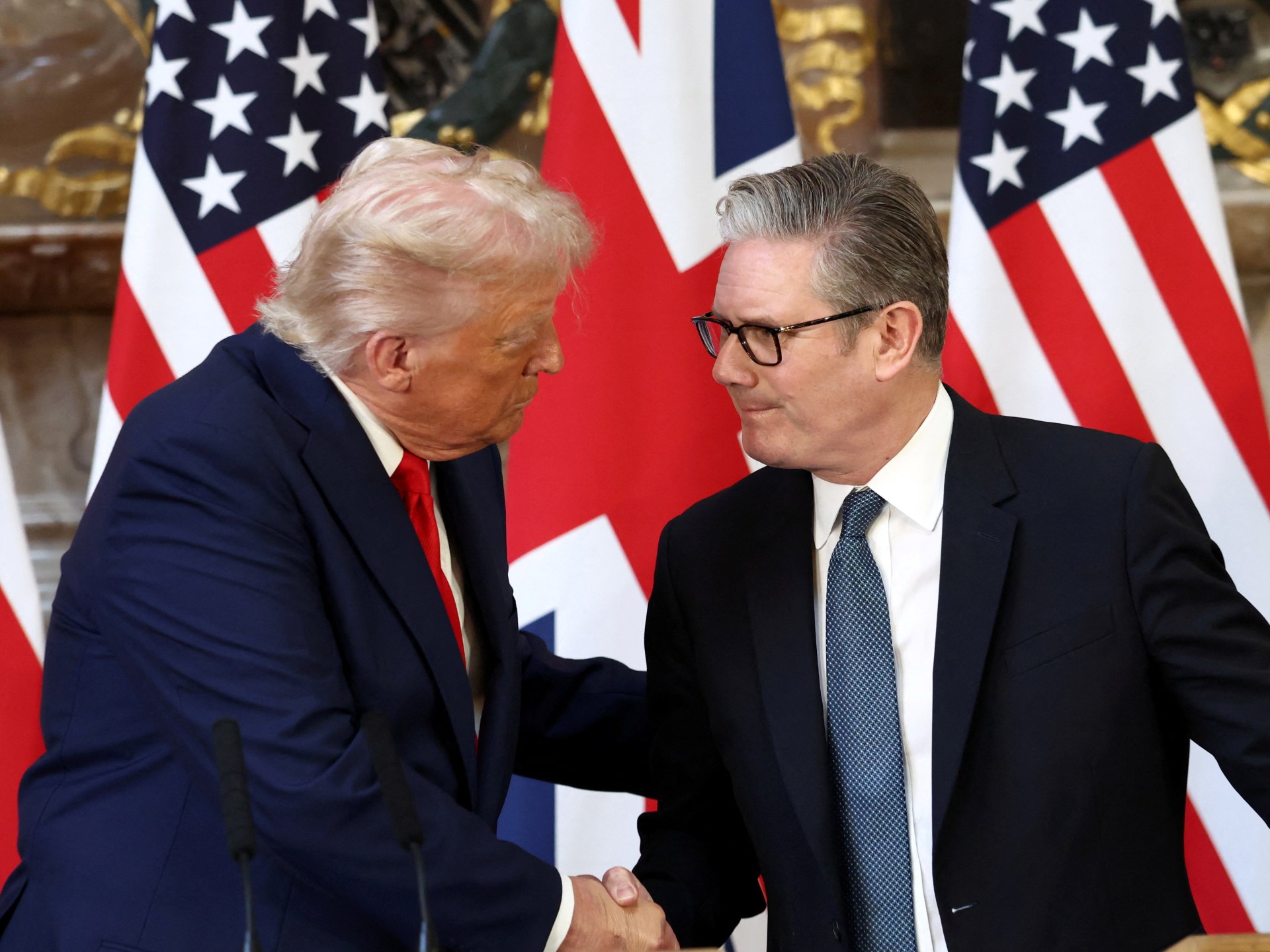
A few weeks before, British Prime Minister Keir Starmer said that the United Kingdom would recognise a Palestinian state at the UN General Assembly in September 2025 unless Israel took “substantive steps to end the appalling situation in Gaza, agree to a ceasefire and commit to a long-term sustainable peace, reviving the prospect of a two-state solution.” There was no mention of Palestinians’ inalienable right to self-determination or of the legitimacy of the Palestinian national struggle. Rather, it was framed as a punishment for Israel. Does this mean that if Israel had stopped the genocide and paid lip service to the (already dead) two-state solution, Britain would have voted differently?
Canada’s promise of recognition came with a long list of caveats. Notably, on the Government of Canada’s website, in the items that make up its “policy on key issues in the Israeli-Palestinian conflict”, the first commitment is “support for Israel and its security”.
It adds that Israel has the “right under international law to take the necessary measures, in accordance with human rights and international humanitarian law, to protect the security of its citizens from attacks by terrorist groups.” But what if Israel is already in violation of international law – as it is right now? Will Canada still stand by Israel and its security?
After reaffirming its support for Israel, Canada then declares support for the Palestinians’ “right to self-determination” and “a sovereign, independent, viable, democratic, and territorially contiguous Palestinian state”. But this comes with strings attached, including demands for governance reforms in the Palestinian Authority, the demilitarisation of the Palestinian state, and elections in 2026, “in which Hamas can play no part”.
Australia’s promise of recognition was similarly predicated on the Palestinian Authority pursuing certain reforms, including the termination of prisoner payments, schooling reform, and demilitarisation. It also demanded that Hamas “end its rule in Gaza and hand over its weapons”.
The joint statement by Foreign Minister Penny Wong and Prime Minister Anthony Albanese added: “There is much more work to do in building the Palestinian state. We will work with partners on a credible peace plan that establishes governance and security arrangements for Palestine and ensures the security of Israel.” But what of the security of Palestinians? Will Australia take any measures to protect them from Israel’s mass extermination? Or are Palestinians simply meant to work on building a state that Western powers can tolerate, while hoping that the Israeli government will eventually grow tired of its genocidal campaign?
The unbearable tragedy of it all is that we have already seen what happens when a peace process prioritises Israel’s right to security over Palestinians’ right to self-determination. It was called the Oslo Accords, where a genuine guarantee of a Palestinian state was never on the table.
In his essay The Morning After, Edward Said wrote of the vulgarity of the ceremonial way the Accords were signed at the White House and the diminutive manner in which Yasser Arafat offered thanks. Said rued that the Oslo Accords were not a path to statehood. Rather, they symbolised the “astonishing proportions of the Palestinian capitulation”.
It resulted in a Palestinian Authority — yes, the same Palestinian Authority that Western leaders have hedged their bets on — that had all the bells and whistles of a state. But the real state never arrived. With complete impunity, Israel continued its efforts to erase Palestinians. And the Palestinian Authority became an extension of the settler-colonial project, collaborating with Israeli forces to actively undermine the Palestinian national movement, all in the name of Israel’s security.
So, if Western leaders are sincere about “solving” the crisis, the only good solution is the one that places Palestinian rights on centre stage and involves some mechanism of political leverage and censure that is able to curb Israel’s rogue-like conduct. Without it, any recognition of Palestinian statehood is an empty performance, and the Israeli campaign of genocide and erasure is bound to continue with complete impunity.
The views expressed in this article are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect Al Jazeera’s editorial stance.