Mark Volman, of Turtles ‘Happy Together’ fame, dies at 78
Mark Volman, the singer who co-founded the buoyant 1960s hitmakers the Turtles and was half of the humorous harmony duo Flo & Eddie, has died. He was 78.
Representatives for Volman confirmed the death to Rolling Stone, citing a “brief, unexpected illness.” In 2020, Volman was diagnosed with Lewy Body Dementia, but continued touring and only announced his diagnosis in 2023.
When promoting his memoir “Happy Forever: My Musical Adventures with the Turtles, Frank Zappa, T. Rex, Flo & Eddie, and More” in 2023, Volman went public with his 2020 diagnosis of Lewy body dementia, a disease that results in a decline in cognitive ability, affecting reasoning, memory and movement.
In a People magazine story, Volman accepted his fate: “I got hit by the knowledge that this was going to create a whole new part of my life. And I said, ‘OK, whatever’s going to happen will happen, but I’ll go as far as I can.’”
Volman’s partner in both the Turtles and Flo & Eddie was Howard Kaylan, a high-school friend who turned into a lifelong creative partner. Sharing a taste for sweet melodies, cultural fads and unrepentant silliness, Volman and Kaylan adeptly navigated the cultural changes of the 1960s, steering the Turtles from surf-rock survivors to psychedelic freaks over the course of a decade.
The group’s sweet spot arrived in the second half of the 1960s, when they polished their Southern Californian folk-rock with studio savvy, creating hits — “Happy Together,” “She’d Rather Be With Me,” “Elenore” and “You Showed Me” — that appealed to mainstream listeners — they were the favorite band of Richard Nixon’s daughter Tricia, even playing the White House in 1970 — while winking at hipper audiences.
As they drifted away from the middle of the road, the Turtles could occasionally give the sense that they were too smart for the room; one of their best albums, 1968’s “The Turtles Present the Battle of the Bands,” was constructed as a concept album where the group adopted a different guise and musical style for each track.

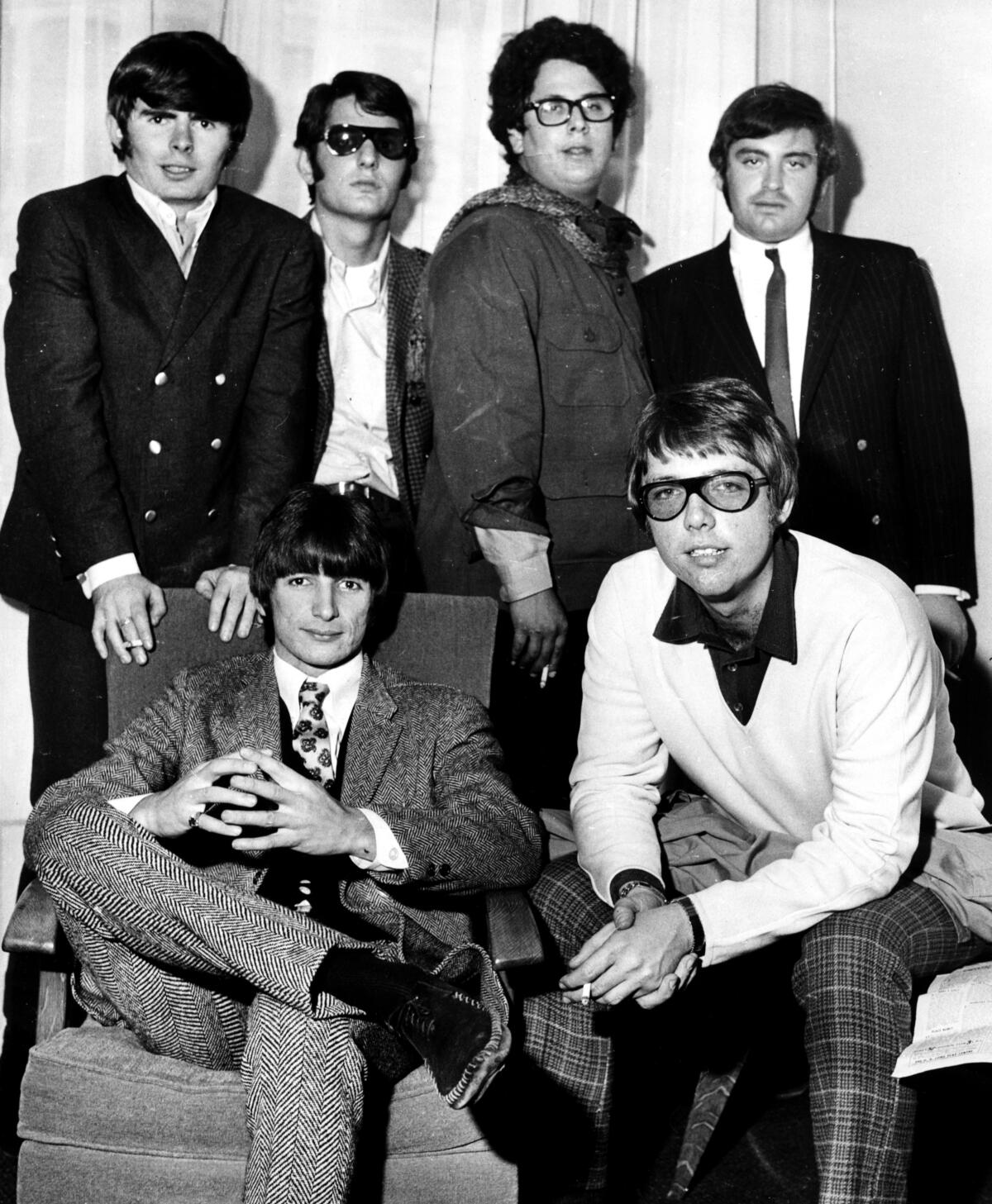
The Turtles in 1967, clockwise from top left: Al Nichol, Jim Tucker, Mark Volman, Howard Kaylan, Johnny Barbara and Jim Pon.
(Central Press / Hulton Archive / Getty Images)
Volman and Kaylan capitalized on this quirk when they rechristened themselves as Flo & Eddie, a moniker they devised after a bitter legal battle with their former record label left them without the right to perform either as the Turtles or using their own names. During this period, Frank Zappa invited Flo & Eddie to join his Mothers of Invention, giving the duo a boost that led to an enduring career.
Flo & Eddie specialized in providing harmonic support to high profile acts: they toured with Alice Cooper, sang on T. Rex’s landmark glam album “Electric Warrior” and were recruited to sing on Bruce Springsteen’s “Hungry Heart” when the Boss was looking for Beach Boys-like harmonies. On their own, Volman and Kaylan also honed their comedic shtick as recording artists, later taking their act to radio and, once they reacquired the rights to the Turtles moniker, on the road, playing the oldies circuit into the 2010s.
Unlike many other oldies acts, Volman and Kaylan possessed sharp business skills, acquired after their messy fallout with their record label, White Whale. Once they regained their master tapes, they licensed their catalog to reissue labels and kept a vigilant eye on how their recordings were disseminated in the marketplace.
On realizing that the Turtles’ “You Showed Me” provided a pivotal sample on De La Soul‘s 1989 debut album, “3 Feet High and Rising,” the duo sued the rap pioneers for $2.5 million in exemplary and punitive damages. The matter was settled out of court in favor of Volman and Kaylan; while the terms were not publicly disclosed, they reportedly were awarded $1.7 million in damages. The lawsuit and its fallout effectively ended the golden age of sampling in hip-hop.
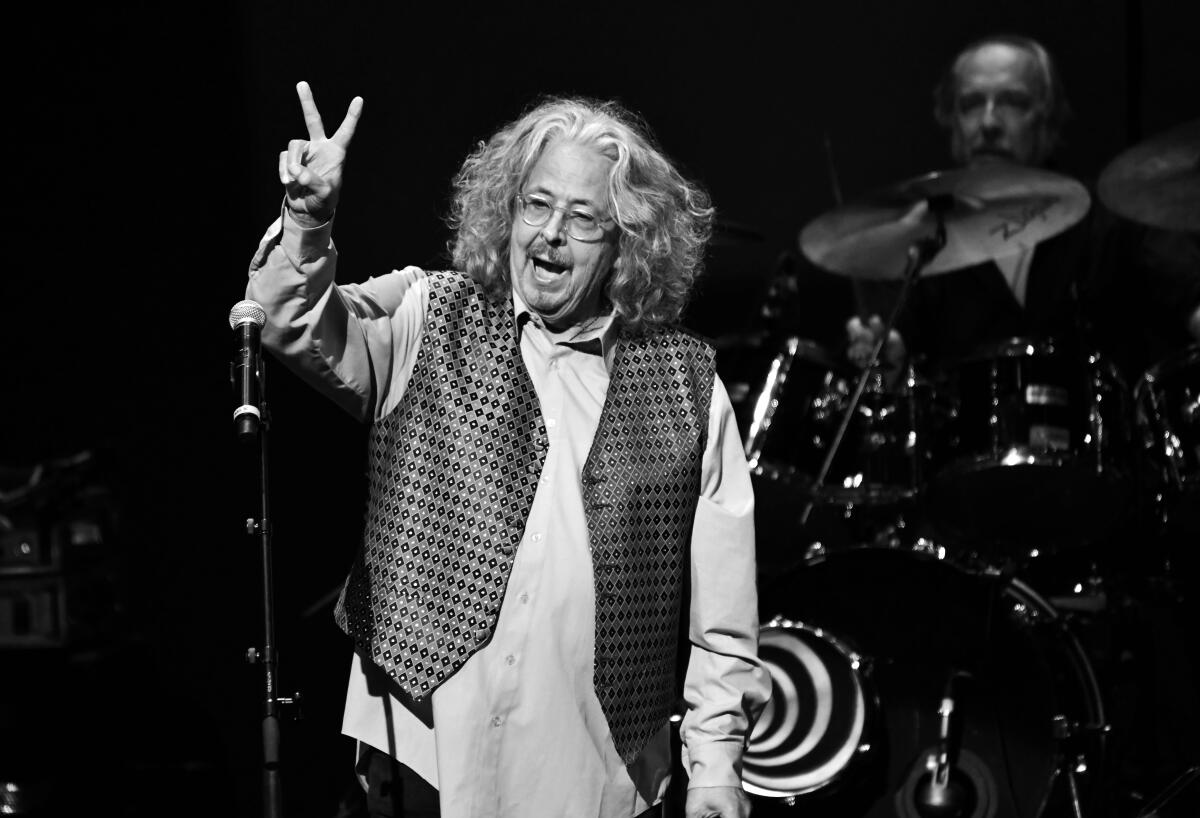

Mark Volman during the 10th anniversary of the Happy Together tour at Thousand Oaks Civic Arts Plaza in 2019.
(Scott Dudelson / Getty Images)
Born in Los Angeles on April 19, 1947, Volman grew up in a musical household in the neighborhood of Westchester. Even when he was young, relatives were struck by his exuberant personality. His aunt Ann Becker recalled in “Happy Forever”: “I can remember my mother shaking her head and saying, ‘That boy is so smart — he shouldn’t be so silly.’”
By the time he enrolled at Westchester High — his classmates included comedian Phil Hartman and Manson Family member Lynette “Squeaky” Fromme — Volman had gravitated toward irreverence.
Meeting New York transplant Kaylan in choir, Volman soon became part of the Crossfires, playing saxophone alongside his new friend in the surf-rock combo. The Crossfires had two singles to their name before they signed to the fledgling White Whale Records in 1965. Already in the process of abandoning surf for folk-rock — Volman and Kaylan swapped their saxes for lead vocals — the group’s members accepted their new label’s suggestion to rename themselves; they rejected the stylized spelling of the Tyrtles in favor of the Turtles.
Taking a cue from the Byrds’ hit version of Bob Dylan’s “Mr. Tambourine Man,” the Turtles released a revved-up cover of Dylan’s “It Ain’t Me Babe” that squarely hit the zeitgeist, climbing into the Billboard Top 10 in summer 1965. Volman later remembered, “I graduated from high school in February 1965 and was on tour in June with a Top 10 record and on the Dick Clark Show.”
A couple of spirited sequels, “Let Me Be” and “You Baby,” kept the band in the Top 40 into 1966 but the Turtles’ hot streak quickly cooled, as a series of singles — including “Outside Chance,” written by White Whale staffer Warren Zevon — barely scraped the charts. “Happy Together,” a song rejected by a number of pop groups, revived the group’s fortunes, thanks in part to a sterling arrangement masterminded by new bassist Chip Douglas.
“Happy Together” topped the charts and would become one of the standards of its era, appearing often in commercials and films. In 1967, it propelled the Turtles back to the upper reaches of the charts, a place they’d stay through 1969, as they accumulated such hits as “She’d Rather Be With Me” and “Elenore.”

By far the biggest act on the small-scale White Whale, the Turtles were subjected to pressure by the label to record more commercial material, yet Volman and Kaylan kept pushing the band to make hip music. When the label suggested firing the rest of the Turtles, the singers arranged for the remaining three members to share songwriting credits on “The Turtles Present the Battle of the Bands,” the first album they released after the success of “Happy Together.” On their final album, “Turtle Soup,” the Turtles hired Ray Davies as their producer; it was his first production outside his main band, the Kinks.
Tensions between the Turtles and White Whale escalated in 1970, leading the group to disband. In turn, the label exercised a clause in the band‘s recording contract that prevented the members from performing either “individually or collectively,” effectively barring Volman and Kaylan from continuing to work either as a group or as themselves. The pair decided to call themselves the Phlorescent Leech & Eddie, a name that would swiftly be shortened to Flo & Eddie; Volman was the former, Kaylan the latter.
Zappa brought the duo into his Mothers of Invention ensemble not long after the implosion of the Turtles. They stayed with him through an eventful year that included a concert in Montreux, Switzerland, that ended with the venue engulfed in fire; Deep Purple memorialized the event in “Smoke on the Water.”
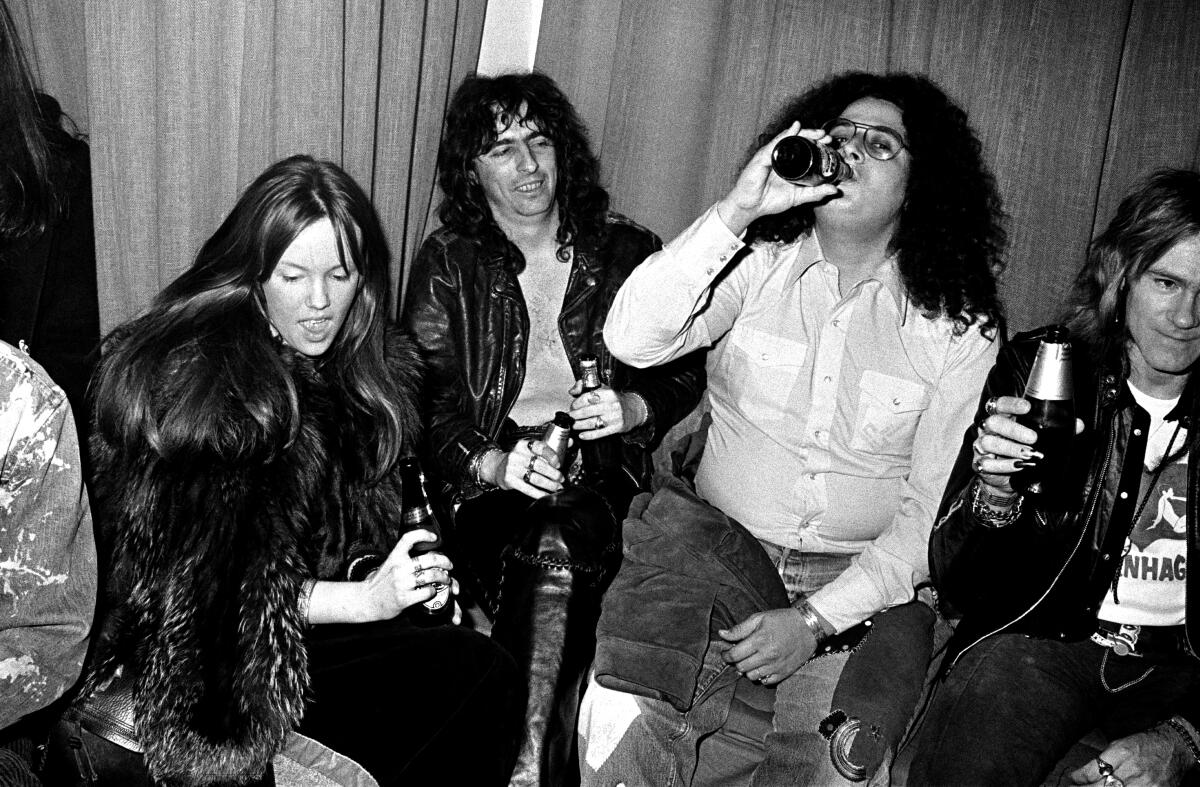

Alice Cooper, second from left, with Mark Volman (drinking beverage) and bandmates in Copenhagen, Denmark, 1972.
(Jorgen Angel / Redferns / Getty Images)
Beginning with 1972’s “The Phlorescent Leech & Eddie,” Flo & Eddie released a series of increasingly facetious albums throughout the 1970s, but they had greater success singing harmonies for T. Rex and Cooper. “Hungry Heart,” Springsteen’s first Top 10 hit, served as a curtain call for this period of Flo & Eddie’s career. Soon, the duo put their days as recording artists to rest. While they still would contribute original music to animated television shows, including specials focusing on “Strawberry Shortcake” and “The Care Bears” series, the duo stopped writing and recording new Flo & Eddie music.
The move coincided with the duo finally winning back the rights to their names. Volman and Kalyan began this process in 1974, when they acquired the Turtles’ master recordings when White Whale assets were up for auction.
A decade later, they were able to tour as The Turtles … featuring Flo & Eddie, a billing they’d retain into the 2010s, until Kaylan retired from the road in 2018. With Ron Dante filling in for Kaylan, Volman continued performing as the Turtles as part of their regular Happy Together package tours.
Although Flo & Eddie embraced their status on the oldies circuit, they hadn’t faded entirely from modern music. When De La Soul sampled “You Showed Me” for their track “Transmitting Live From Mars” in 1989, the trio failed to clear the rights prior to release, so Volman and Kaylan sued the group, winning a large settlement that established a precedent for sample clearance in hip-hop.
The duo launched another major lawsuit in 2013 when they filed suit against Sirius XM for failing to pay sound recording royalties in California, New York and Florida. A California judge ruled in the duo’s favor in 2014, while a Florida judge ruled for Sirius XM in 2015. Although a settlement was reached in 2016, Sirius XM would win subsequent legal appeals in Florida and California.
Volman went back to school in 1992, pursuing a bachelor’s degree at Loyola Marymount University in Los Angeles. After earning a master’s degree in screenwriting in 1999 at Loyola Marymount, Volman soon moved into teaching, eventually becoming an associate professor at the Mike Curb College of Entertainment & Music Business at Belmont University in Nashville, Tenn.
Volman is survived by his daughters, Sarina Marie and Hallie Rae, both from his marriage to Patricia Lee.