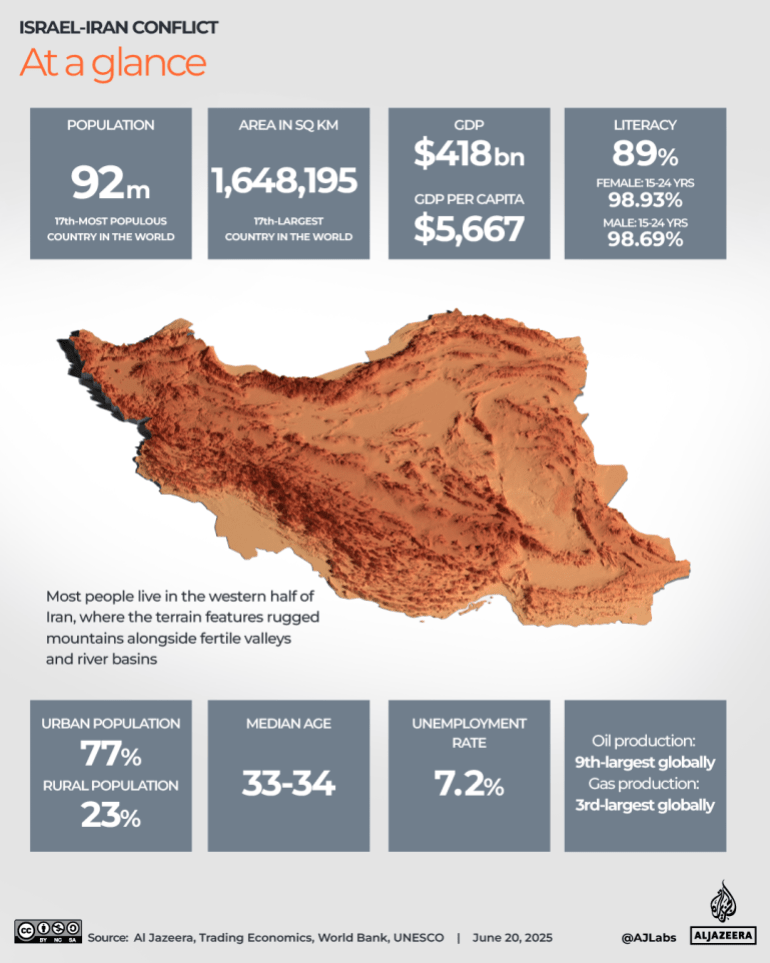
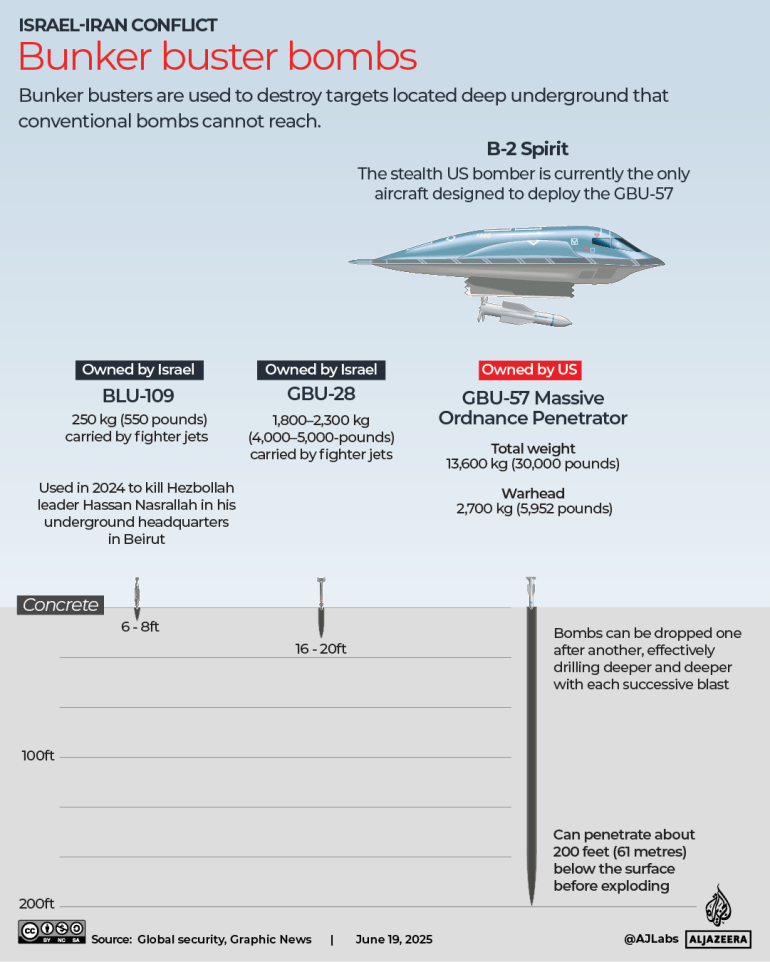
In the digital age, where power dynamics are increasingly defined by information flows and algorithmic influence, cyberspace has evolved from a mere technical domain into a fully fledged geopolitical arena. As Thomas Rid has argued, cyberwar is not a rupture but an extension of politics by other means, characterized by ambiguity, plausible deniability, and the absence of clear thresholds. In this new order, cybersecurity acts as an adaptive shield, protecting vital systems, while cyber defense becomes the digital sword, mobilizing state capabilities to detect, neutralize, and retaliate. This strategic pairing gives rise to an integrated doctrine, where every firewall becomes a sensor and every breach an opportunity for strategic hardening.
Thus, twenty-first-century conflicts no longer begin with declarations of war but with lines of malicious code. State-sponsored cyberattacks, technological espionage, and mass disinformation campaigns are the weapons of the future: silent yet potentially paralyzing. In this shadow war, financial systems, smart grids, healthcare infrastructures, and state institutions become critical pressure points, exposed to systemic shocks that can dislocate national continuity. In response, digital resilience is no longer a defensive posture but a vital imperative. It rests on the fusion of preventive cybersecurity and active cyber defense, forming an invisible architecture that balances anticipation with response. Partnerships like the one between Microsoft and U.S. Cyber Command, where Azure Sentinel’s AI bolsters offensive operations against Chinese APTs, illustrate the hybridization of technological shield and geopolitical weapon. Yet attribution remains a strategic Achilles’ heel; opacity and decentralization of attacks hamper deterrence logic.
For these reasons and inspired by nuclear doctrines, some states are now developing cyber deterrence strategies based on denial (making the attack ineffective) and targeted retaliation (imposing dissuasive costs). The U.S. Cyber Command’s “persistent engagement” model exemplifies this approach, where anticipation, calibrated response, and cognitive dominance form a triptych of integrated deterrence. On the other hand, the rise of artificial intelligence is disrupting this balance at dizzying speed. China’s DeepSeek R1, for instance, demonstrates that AI is no longer merely a tool for data processing but an autonomous force capable of identifying threats, executing countermeasures, and even making tactical decisions. This signals the emergence of a new form of algorithmic sovereignty, where strategic initiative shifts from human to calculated agency.
This paradigm shift is reshaping the military domain as well. Autonomous drones, automated intelligence platforms, and smart weapons systems are redefining doctrines of technological supremacy. Ukraine’s “Spider Web” operation marked a doctrinal rupture, deploying swarms of AI-coordinated micro-drones capable of dynamic, adaptive targeting in cluttered environments. It heralds the advent of fluid, decentralized warfare and prefigures future algorithmic conflicts.
Big Tech: Geopolitical Hydras
When Big Tech dictates the rules of cyberspace, states become variables in someone else’s equation. It is no longer armies but platforms that shape power balances. This paradigm shift cements the rise of an extraterritorial technological power not based on monopoly of legitimate violence but on mastery of data flows and digital architectures. Then, GAFAM (Google, Apple, Facebook, Amazon, Microsoft) now operates as systemic entities, wielding influence that eclipses traditional state sovereignty. Their power, driven by an unprecedented concentration of computational, financial, and informational capital, grants them a structuring role in international relations, rivaling even the core prerogatives of the state.
This rise isn’t merely economic or technological; it redefines global governance. These corporations act as the architects of the “matrix politica,” enforcing opaque algorithmic regulation of public discourse, social behaviors, and collective perception. By replacing legitimate legal norms with proprietary logic, they institute an unelected algorithmic order, generating “invisible prisons” where individuals become exploitable variables and national sovereignty becomes a residual fiction.
In this context, any viable cyber defense or deterrence strategy must confront this structural asymmetry. Strengthening state defenses against conventional cyber threats is no longer sufficient. The relationship between public authority and private technological hegemony must be recalibrated. Effective digital resilience demands a democratic reconquest of communication infrastructures and political oversight of the normative power wielded by platforms. Absent such rebalancing, cyberspace will continue to slide into a deterritorialized algorithmic sovereignty that deeply reconfigures the exercise of power in the 21st century.
This silent capture of normative power presents a strategic challenge to cyber deterrence doctrines. After all, what is the purpose of state deterrence if critical infrastructures, codebases, and mass cognitive systems are controlled by transnational private entities? Digital sovereignty must encompass offensive capabilities against state-backed cyber aggressors and against hegemonic drifts of platforms capable of reshaping cognitive battlegrounds, manipulating public perception, and influencing political decisions in real time.
This revolution comes at a cost. Deep learning algorithms can now launch sophisticated cyberattacks, detect invisible vulnerabilities, and strike without warning, pushing human intervention into the background. AI thus generates a strategic paradox: it enhances resilience while simultaneously magnifying vulnerabilities. Advances like DeepMind’s AlphaFold show how such technologies permeate critical domains, from biology to cybersecurity, blurring the lines between scientific progress and digital militarization. In this new era, AI is no longer a tool; it is a geopolitical actor.
In fact, major powers and actors are investing in this revolution in different ways. The United States, a pioneer in AI research, focuses on innovation and developing offensive and defensive cyber capabilities. China, aiming for technological supremacy by 2030, is coupling digital sovereignty with state surveillance to bolster its global position. The European Union adopts a more regulatory and ethical approach, seeking to govern AI use while preserving its technological autonomy.
Warfare in the Age of AI
The military domain, too, is being swept into the vortex of AI-led automation. Autonomous drones, smart weapon systems, and automated intelligence platforms are reshaping defense doctrines, ushering in a new form of technological supremacy. These tools offer asymmetric advantages to well-equipped powers but also pave the way for an unprecedented militarization of cyberspace.
Delegating lethal decisions to machines raises profound ethical dilemmas: who bears responsibility for algorithmic misfires? How do we regulate autonomous weapons in a world where legal norms lag behind innovation? Without clear answers, AI risks transforming the battlefield into a dehumanized theater of operations beyond political and moral control.
Subsequently, the proliferation of hybrid threats, cyberattacks, disinformation, and covert operations underscores the urgency of enhanced international cooperation. In fact, the Russo-Ukrainian conflict has highlighted cyberspace’s centrality in modern warfare, with the rise of cyber-volunteers, hacktivists, and destabilization campaigns. Ukraine’s IT Army exemplifies a new form of cyber mobility, where citizens and transnational collectives become key players in cyber conflict.
In this regard, Ukraine’s “Spider Web” operation against Russian targets demonstrates a new military application of AI in hybrid warfare. Here, AI no longer acts as a mere optimizer but as a digital war commander, orchestrating data collection, target identification, battlefield navigation, and dynamic strike execution. This machine-learning-powered architecture transforms each drone into both a sensor and a lethal vector, capable of real-time adaptation. More than a technological feat, Spider Web signals a metamorphosis of warfare, with AI assuming operational control and ushering in an era of autonomous algorithmic wars.
Fragmented Tech Ecosystems and Strategic Rivalries
Meanwhile, the militarization of cyberspace is accelerating. Leading powers are developing advanced cyber weapons, espionage tools, and surveillance systems to maintain digital supremacy. China’s “Made in China 2025” strategy channels massive investment into cybersecurity and tech sovereignty, while the U.S. doubles down on proactive defense to safeguard its hegemonic edge.
This trend drives increasing fragmentation of the global digital landscape, undermining the ideal of an open internet and encouraging the formation of rival digital blocs. The Sino-American tech rivalry extends beyond infrastructure development, despite enduring interdependencies in key sectors. While semiconductor and 5G decoupling advances, shared reliance persists in AI, cloud computing, and components. This duality complicates strategic choices. Each power must navigate between tech independence and global innovation access, accelerating cyber-nationalism and deepening digital polarization. Huawei’s Harmony OS and U.S. bans on Chinese semiconductors are clear signs of a growing digital decoupling that could redefine global tech ecosystems.
In this climate of intensifying threats and systemic interdependence, states are turning to cyber sovereignty strategies to secure critical infrastructure and reduce exposure to foreign interference. This forms part of a broader reconfiguration of global digital order, where control over data and information flows becomes a strategic lever.
International bodies such as NATO and the EU are gradually adapting. The EU’s Cyber Rapid Response Teams (CRRTs) and NATO’s adoption of offensive cyber doctrines signal a growing intent to pool resources and establish collective response mechanisms. Thus, China exemplifies the sovereigntist approach: its Great Firewall symbolizes a strategy combining national infrastructure protection, strict data regulation, and bolstered cyber-offensive capabilities.
From Code to Context: Redefining Cyberwarfare
Cyberwarfare is no longer about code but about context. Victory lies in merging civilian neural networks, predictive algorithms, and bio-neural systems, where every smartphone becomes a sensor and every hacktivist a cognitive disruptor. Tomorrow’s cyber defense rests on algorithmic sovereignty: an ecosystem where tactical metaverses, morphic AI drones, and quantum blockchains redefine resilience. In addition, Ukraine has shown that the future belongs to those who break hierarchies to build combat bio-networks—info-centric systems powered by quantum geolocation and operational proliferation of cyber volunteers. In this borderless arena, victory is won not by hacking machines but by hacking perceptions, hybridizing human agency, generative AI, and legal ambiguity.
Furthermore, cybersecurity is no longer a static defense line but a fractal weapon with evolutionary capabilities, where every intrusion becomes a counter-weapon and every psychokinetic attack an information battleground. That’s to say, this next-gen cyber architecture is based on adaptive algorithmic systems capable of dynamic reconfiguration in the face of ever-mutating threats. Its strength lies in an advanced synergy of AI, quantum cryptography, and autonomous protocols—modular, decentralized, and self-replicating systems that respond proportionately to the intensity and nature of cyberattacks. In a world shaped by asymmetry and uncertainty, this model grants states algorithmic superiority, shaping tomorrow’s deterrence and digital resilience.
Therefore, in the face of this accelerating tech revolution, global AI governance is no longer optional—it’s an existential necessity. Without robust legal frameworks and multilateral oversight, the world risks plunging into a digital arms race defined by opacity, irresponsibility, and strategic instability. It is no longer about regulating innovation; it is about preserving global balance in a world where the boundaries between war and peace, civil and military, and human and machine are increasingly blurred. Namely, an international architecture of trust and transparency is essential to prevent AI from becoming the unaccountable arbiter of tomorrow’s conflicts.
Disruption Scenario: Toward Unchecked Algorithmic Warfare
By 2032, the lack of international regulation on military AI triggers an uncontrolled rise of autonomous weapons and AI-powered cyber capabilities. Amid mounting tensions between the West and the Sino-Russian bloc, the race for AI military supremacy enters a tipping point. China, after scaling up AI militarization with Central Asian partners, unleashes targeted cyberattacks against European logistics and energy systems, paralyzing large parts of the continent. Simultaneously, autonomous drone swarms developed under a Sino-Russian program infiltrate NATO airspace disguised as meteorological probes.
Behind the scenes, Russia orchestrates a massive cognitive warfare operation using generative AI trained to manipulate Western public opinion. Deepfakes, forged documents, and fake military orders—Europe’s political systems are plunged into information chaos. In several capitals, key decisions are based on alerts fabricated by hostile AI. Thus, a devastating strike then hits a NATO logistics hub in the Baltic Sea, causing significant casualties. No state claims responsibility, but suspicion falls on Russia. Western attribution systems, despite being AI-enhanced, are circumvented by adversarial AI obfuscation networks. Indeed, caught in a spiral of disinformation and decision paralysis, a NATO member launches a massive cyber counterattack on Russian civilian infrastructure. Moscow retaliates with a hybrid strike combining autonomous weapons, electronic warfare, and satellite disruption. Within a week, a high-intensity hybrid conflict erupts regionally, with immediate nuclear escalation risk. Traditional command chains are disabled, decisions are made under AI pressure, and human agency vanishes. Strategic equilibrium, once upheld by nuclear deterrence and diplomacy, collapses under the weight of self-evolving, autonomous algorithms.
Moreover, conflicts no longer begin with declarations of war: they emerge, self-perpetuate, and unfold in an algorithmic fog where the line between peace and hostility vanishes. Humanity then realizes that, in failing to regulate, it has surrendered control to hostile, elusive, and autonomous intelligences.
Coding Sovereignty in the Algorithmic Fog
The future of cybersecurity lies in the ability of states to reconcile innovation, regulation, and strategic cooperation. The implementation of robust cyber doctrines, blending deterrence, algorithmic resilience, and control over critical infrastructure, will be key to preserving national sovereignty and global stability. That is to say, in the age of information supremacy, building cyber coalitions, massively investing in sovereign digital infrastructures, and establishing binding international norms are essential to secure peace and security. Cybersecurity is no longer a defensive tool; it is a core pillar of state power.
This indicates that cyberwar is no longer a future scenario; it is a strategic reality where supremacy depends on integrating offensive and defensive capabilities into a deterrent cyber ecosystem. The convergence of cyber intelligence, algorithmic resilience, and anticipatory response is reshaping defense doctrines, establishing a digital sovereignty rooted in system self-learning, cognitive warfare, and adversary vulnerability exploitation.
Finally, in this asymmetrical theatre, mastery over critical infrastructure and the ability to conduct hybrid operations will determine the balance of power in a cyberspace that has become the epicenter of global strategic rivalries. In the algorithmic fog of tomorrow’s wars, sovereignty is no longer declared, but it is coded, learned, and defended with every line of data.